There are 60 students in a class. The following is the frequency distribution of the marks obtained by the students in a test:
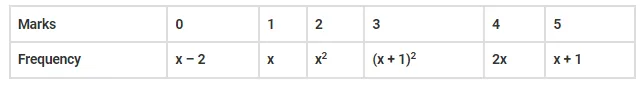
Where x is a positive integer. Determine the mean and standard deviation of the marks.
Given there are 60 students in a class. The frequency distribution of the marks obtained by the students in a test is also given.
Now we have to find the mean and standard deviation of the marks.
It is given there are 60 students in the class, so
∑fi=60
⇒ (x – 2) + x + x2 + (x + 1)2 + 2x + x + 1 = 60
⇒ 5x – 1 + x2 + x2 + 2x + 1 = 60
⇒ 2x2 +7x = 60
⇒ 2x2 +7x – 60 = 0
Splitting the middle term, we get
⇒ 2x2 + 15x – 8x – 60 = 0
⇒ x (2x + 15) – 4(2x + 15) = 0
⇒ (2x + 15) (x – 4) = 0
⇒ 2x + 15 = 0 or x – 4 = 0
⇒ 2x = -15 or x = 4
Given x is a positive number, so x can take 4 as the only value.
And let assumed mean, a=3.
Now put x = 4 and a = 3 in the frequency distribution table and add other columns after calculations, we get
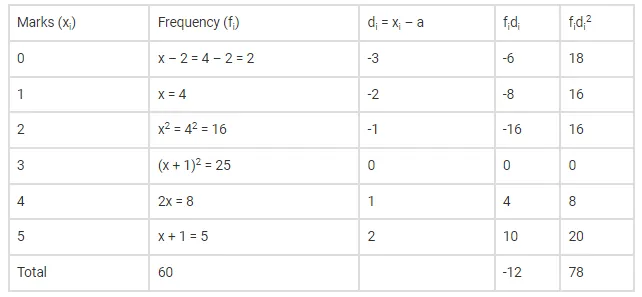
And we know standard deviation is
$\sigma=\sqrt{\frac{\sum f_{i} d_{i}^{2}}{n}-\left(\frac{\sum f_{i} d_{i}}{n}\right)^{2}}$
Substituting values from above table, we get
$\sigma=\sqrt{\frac{78}{60}-\left(\frac{-12}{60}\right)^{2}}$
Substituting values from above table, we get
$\sigma=\sqrt{\frac{78}{60}-\left(\frac{-12}{60}\right)^{2}}$
$\sigma=\sqrt{1.3-(0.2)^{2}}$
$\sigma=\sqrt{1.3-0.04}$
$\Rightarrow \sigma=1.12$
Hence the standard deviation is $1.12$
Now mean is
$\overline{\mathrm{x}}=\mathrm{A}+\frac{\sum \mathrm{f}_{\mathrm{i}} \mathrm{d}_{\mathrm{i}}}{\mathrm{N}}$
$=3+\left(-\frac{12}{60}\right)$
$=3-\frac{1}{5}=\frac{14}{5}$
$=2.8$
Hence the mean and standard deviation of the marks are $2.8$ and $1.12$ respectively.
