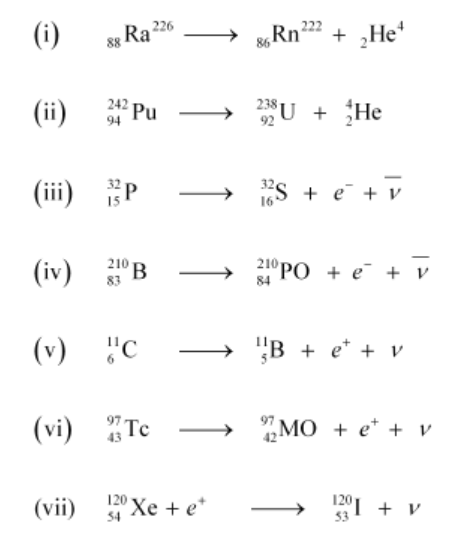
(i) $\alpha$-decay of ${ }_{88}^{226} \mathrm{Ra}$
(ii) $\alpha$-decay of ${ }_{94}^{242} \mathrm{Pu}$
(iii) $\beta^{-}$-decay of ${ }_{15}^{32} \mathrm{P}$
(iv) $\beta^{-}$-decay of ${ }_{83}^{210} \mathrm{Bi}$
(v) $\beta^{+}$-decay of ${ }_{6}^{11} \mathrm{C}$
(vi) $\beta^{+}$-decay of ${ }_{43}^{97} \mathrm{Tc}$
(vii) Electron capture of ${ }_{54}^{120} \mathrm{Xe}$
$\alpha$ is a nucleus of helium $\left({ }_{2} \mathrm{He}^{4}\right)$ and $\beta$ is an electron $\left(e^{-}\right.$for $\beta^{-}$and $e^{+}$for $\left.\beta^{+}\right)$. In every $\alpha$-decay, there is a loss of 2 protons and 4 neutrons. In every $\beta^{+}$-decay, there is a loss of 1 proton and a neutrino is emitted from the nucleus. In every $\beta^{-}$-decay, there is a gain of 1 proton and an antineutrino is emitted from the nucleus.
For the given cases, the various nuclear reactions can be written as: