XY is drawn parallel to the base BC of a ∆ABC cutting AB at X and AC at Y. If AB = 4 BX and YC = 2 cm, then AY =
XY is drawn parallel to the base BC of a ∆ABC cutting AB at X and AC at Y. If AB = 4 BX and YC = 2 cm, then AY =
(a) 2 cm
(b) 4 cm
(c) 6 cm
(d) 8 cm
Given: XY is drawn parallel to the base BC of a ΔABC cutting AB at X and AC at Y. AB = 4BX and YC = 2 cm.
To find: AY
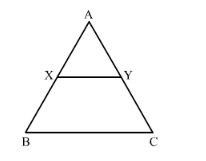
In ΔAXY and ΔABC,
∠AXY=∠B Corresponding angles∠A=∠A Common∴∆AXY~∆ABC AA similarity
We know that if two triangles are similar, then their sides are proportional.
It is given that AB = 4BX.
Let AB = 4x and BX = x.
Then, AX = 3x
$\frac{\mathrm{AX}}{\mathrm{BX}}=\frac{\mathrm{AY}}{\mathrm{YC}}$
$\frac{3 x}{1 x}=\frac{\mathrm{AY}}{2}$
$\mathrm{AY}=\frac{3 x \times 2}{1 x}$
$\mathrm{AY}=6 \mathrm{~cm}$
Hence the correct answer is C
Click here to get exam-ready with eSaral
For making your preparation journey smoother of JEE, NEET and Class 8 to 10, grab our app now.
