Hey, Do you want to learn about the Types of Equilibrium? If so. Then you are at the right place.
What is Equilibrium?
A body is said to be in translatory equilibrium if the net force acting on the body is zero, $\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}_{\text {net }}=0$
If the force are conservative then $\mathrm{F}=-\frac{\mathrm{dU}}{\mathrm{dr}}$
For equilibrium F = 0.
So, $-\frac{d U}{d r}=0$
Or
$\frac{\mathrm{dU}}{\mathrm{dr}}=0$
At equilibrium position slope of U-r graph is zero or the potential energy is optimum (maximum or minimum or constant).
Types of Equilibrium.
- Stable Equilibrium
- Unstable Equilibrium
- Neutral Equilibrium
Stable Equilibrium:
When a particle is slightly displaced from equilibrium and it tends to come back towards equilibrium then it is said to be in stable equilibrium
Unstable Equilibrium:
When a particle is displaced from equilibrium and it tends to move away from equilibrium position then it is said to be in unstable equilibrium
Neutral Equilibrium:
When a particle is displaced from equilibrium and no force acts on it then the equilibrium is said to be neutral equilibrium
The situation where F = 0 and $\frac{\mathrm{d} \mathrm{U}}{\mathrm{dr}}=0$ can be obtained under three conditions.
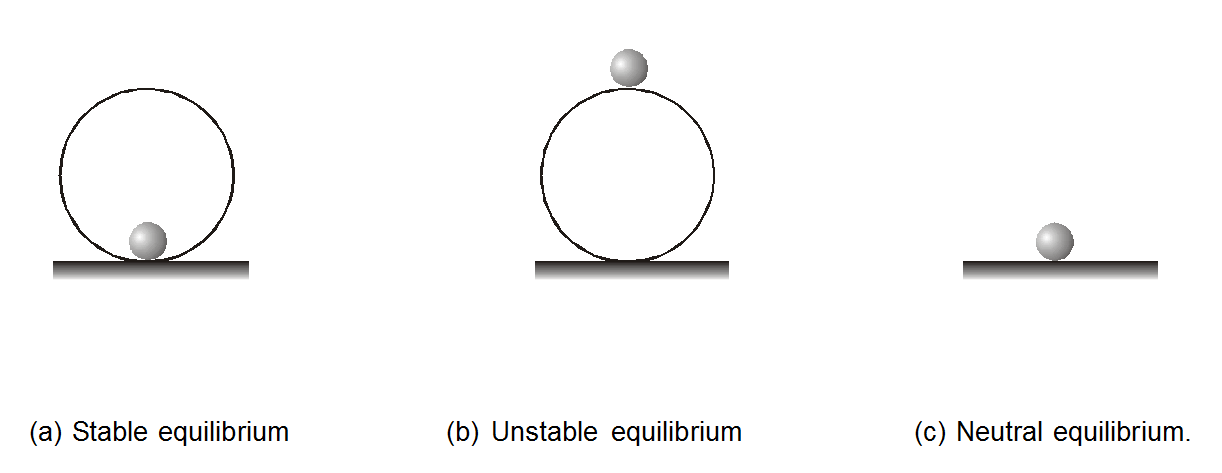
Three identical balls are placed in equilibrium in positions as shown in fig. (a), (b), and (c) respectively.
- The ball is placed inside a smooth spherical shell. This ball is in a stable equilibrium position.
- The ball is placed over a smooth sphere. This is in the Unstable equilibrium position.
- The ball is placed on smooth horizontal ground. This ball is in the Neutral equilibrium position.
Difference Between Stable, Unstable, and Neutral Equilibrium
| S.no | Stable equilibrium | Unstable equilibrium | Neutral equilibrium |
| 1 | Net force is zero | Net force is zero | Net force is zero |
| 2 | $\frac{d U}{d r}=0$ or slope of $U-r$ graph is zero | $\frac{\mathrm{dU}}{\mathrm{dr}}=0$ or slope of U-r graph is zero. | $\frac{\mathrm{dU}}{\mathrm{dr}}=0$ or slope of U-r graph is zero. |
| 3 | When displaced slightly, from its equilibrium position a net restoring force starts acting on the body which has a tendency to bring the body back to its equilibrium position. | When displaced slightly from its equilibrium position, a net force starts acting on the body which moves the body in the direction of displacement or away from the equilibrium position. | When displaced slightly from its equilibrium position the body has neither the tendency to come back to original position nor to move away from the original position. |
| 4 | Potential energy in equilibrium position is minimum as compared to its neighboring points or $\frac{\mathrm{d}^{2} U}{\mathrm{dr}^{2}}=$ positive |
Potential energy in equilibrium position is maximum as compared to its neighboring points or $\frac{d^{2} U}{d r^{2}}=$ negative |
Potential energy remains constant even if the body is displaced from its equilibrium position. or $\frac{d^{2} U}{d r^{2}}=0$ |
| 5 | When displaced from equilirbium position the centre of gravity of the body goes up. |
When displaced from equilibrium position the centre of gravity of the body comes down. | When displaced from equilibrium position the centre of gravity of the body remains at the same level. |
So, that's all from this article. If you found this Explanation of Types of Equilibrium helpful then please share it with your friends.
For a better understanding of this chapter, please check the detailed notes of the Work Energy and Power. To watch Free Learning Videos on physics by Saransh Gupta sir Install the eSaral App.
