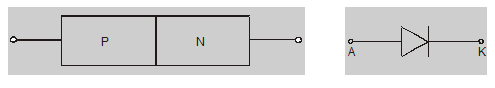
A diode is a PN junction device. If you want to know what is diode in electronics. Then keep reading.
Important terms related to diode:
So, that's it from this blog. I hope you get the idea about what is a diode in electronics. If you found this Explanation helpful then share it with your friends and followers.
Also read
Types of Semiconductor
To watch Free Learning Videos on physics by Saransh Gupta sir Install the eSaral App.
Diode
A diode is a PN junction device
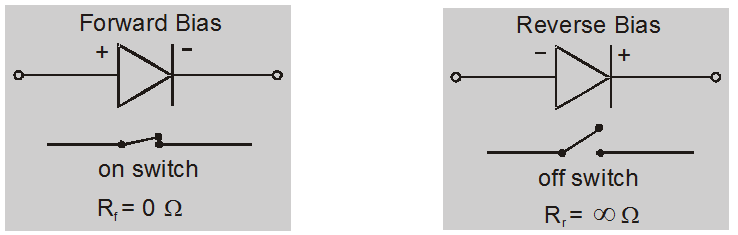
Ideal diode
- Conducts with zero resistance when forward biased.
- Offer an infinite resistance when reverse biased.
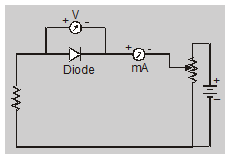
Practical Circuit For diode

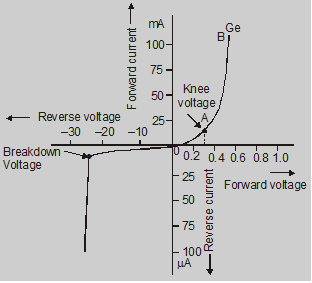
The practical characteristic curve for a diode:

Important terms related to diode:
- Knee VoltageKnee voltage is defined as the forward voltage at which the current through the junction starts increasing rapidly.For silicon = 0.7 volt for germanium = 0.3 volt
- Forward resistance or ac resistance:It is defined as the reciprocal of the slope of the forward characteristic curve.forward resistance
$r_{f}=\frac{1}{\text { slope of forwardcharacteristic }}$
$=\frac{1}{\Delta \mathrm{I}_{\mathrm{f}} / \Delta \mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{f}}}$
$=\frac{\Delta \mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{f}}}{\Delta \mathrm{l}_{\mathrm{f}}}$ - Junction breakdown :When the reverse voltage is increased a point is reached when the junction breaks down with sudden rise in reverse current. This value of the voltage is known as the breakdown voltage. Two types of breakdown occur:a. Zener breakdown:
a. Zener breakdown:
Takes place in junction which are heavily doped so having narrow depletion layers. A very strong electric field appears across the narrow depletion layer which breaks the bond.
b. Avalanche breakdown :
Occur in junctions which are lightly doped. (having wide depletion layer) so at a high electric field, the minority charge carriers, while crossing the junction acquire very high velocities. A chain reaction is established, giving rise to the high current. - Diffusion Current :Some electrons and holes have more kinetic energy $\left[\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{mv}^{2}>\mathrm{eV}\right]$ So $\mathrm{e}^{-}$ diffuse from n to p side and hole diffuse from p to n side due to diffusion of the charge carriers a current will flow known as diffusion current.
a. Because of the concentration difference diffusion occurs.
b. Diffusion results in an electric current from p side to the n side
c. When P-N. Jn is in no Bias = diffusion current = drift current
Net charge flow = 0
Net current = 0 - Drift Current: Due to thermal collisions, the covalent bond is broken. If an electron-hole pair is created in the depletion region, there is a regular flow of electrons towards the n side and of holes towards the p side. Current flow n side to p side called drift current.Drift current and the diffusion current are in the opposite direction
So, that's it from this blog. I hope you get the idea about what is a diode in electronics. If you found this Explanation helpful then share it with your friends and followers.
Also read
Types of Semiconductor
To watch Free Learning Videos on physics by Saransh Gupta sir Install the eSaral App.
