Bridge Rectifier is also a full-wave rectifier. If you want to learn about the Bridge rectifier and Bridge rectifier circuit diagram then keep reading.
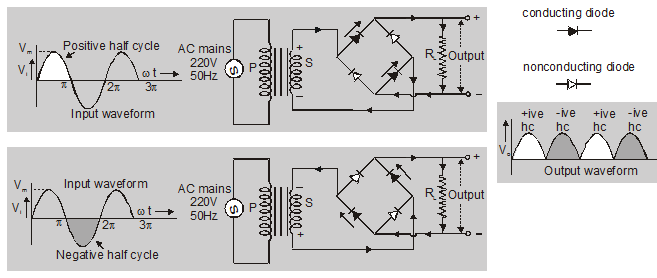
Use of bridge rectifier
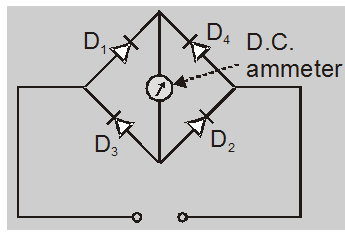
The bridge rectifier is used in the rectifier type voltmeter. The circuit arrangement is shown in fig. The rectifier elements are p-n junction diodes with a sensitive DC. ammeter as a load. This circuit can be used for the measurement of AC as well as DC voltage and currents. The DC ammeter reads the average value of currents. This may be calibrated to give r.m.s. values.
The bridge rectifier has the following advantages
$\eta=\frac{\text { dc power delivered to the load }}{\text { ac input power from transformer sec ondary }}$
$=\frac{P_{d c}}{P_{a c}}$
$=\frac{\mathrm{I}^{2} \mathrm{dc} \mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{L}}}{\mathrm{I}_{\mathrm{rms}}^{2}\left(\mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{F}}+\mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{L}}\right)}$
For bridge rectifier
$\eta=\frac{0.812 R_{L}}{2 R_{f}+R_{L}}$
for ideal diode
$R_{f}=0$
$\eta=81.2 \%$
So, that's all from this article. I hope you get the idea about the Bridge rectifier and Bridge rectifier circuit diagram. If you liked this article then please share it with your friends.
Also, read
Full Wave Rectifier circuit diagram
To watch Free Learning Videos on physics by Saransh Gupta sir Install the eSaral App.
Bridge Rectifier
It is also a full-wave rectifier.
Use of bridge rectifier
The bridge rectifier is used in the rectifier type voltmeter. The circuit arrangement is shown in fig. The rectifier elements are p-n junction diodes with a sensitive DC. ammeter as a load. This circuit can be used for the measurement of AC as well as DC voltage and currents. The DC ammeter reads the average value of currents. This may be calibrated to give r.m.s. values.

The bridge rectifier has the following advantages
- No center tap is required in the transformer secondary, hence both half cycles are similar.
- PIV across each diode is $\mathrm{E}_{0}$ (which is 2 $\mathrm{E}_{0}$ in a full wave rectifier).
- For a given power, output power transformer of small size can be used as the current in both the primary and secondary of the plate supply transformer flows for the entire cycle.
- The circuit requires two extra diodes
- It has poor voltage regulation.
The efficiency of rectifier:
The efficiency rectifier is defined as the ratio of DC output power to the AC input power$\eta=\frac{\text { dc power delivered to the load }}{\text { ac input power from transformer sec ondary }}$
$=\frac{P_{d c}}{P_{a c}}$
$=\frac{\mathrm{I}^{2} \mathrm{dc} \mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{L}}}{\mathrm{I}_{\mathrm{rms}}^{2}\left(\mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{F}}+\mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{L}}\right)}$
For bridge rectifier
$\eta=\frac{0.812 R_{L}}{2 R_{f}+R_{L}}$
for ideal diode
$R_{f}=0$
$\eta=81.2 \%$
So, that's all from this article. I hope you get the idea about the Bridge rectifier and Bridge rectifier circuit diagram. If you liked this article then please share it with your friends.
Also, read
Full Wave Rectifier circuit diagram
To watch Free Learning Videos on physics by Saransh Gupta sir Install the eSaral App.
