Hey, do you want to learn about the Charging and discharging of capacitors? If yes. Then you are at the right place.
The eqn. of emf at any time t is
$R I+\frac{q}{C}=E$
$\frac{R d q}{d t}+\frac{q}{C}=E$
$\int_{0}^{Q} \frac{d q}{(C E-q)}$
$=-\int_{0}^{t} \frac{d t}{R C}$
This on solving gives $Q=Q_{0}\left(1-e^{-t / R C}\right)$
where $Q_{0}=C E$
$\mathrm{RI}+\frac{\mathrm{q}}{\mathrm{C}}=0$
Or
$R \frac{d q}{d t}+\frac{q}{C}=0$
Or
$\int_{Q_{0}}^{Q} \frac{d q}{q}=-\int_{0}^{t} \frac{d t}{R C}$
Or
$Q=Q_{0} e^{-t / R C}$
For a better understanding of this chapter, please check the detailed notes of Electrostatics. To watch Free Learning Videos on physics by Saransh Gupta sir Install the eSaral App.
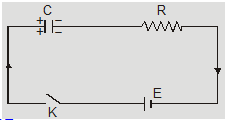
Charging and discharging of capacitors
Charging
When a capacitor C is connected to a battery through R then charging of capacitor takes place.
The eqn. of emf at any time t is
$R I+\frac{q}{C}=E$
$\frac{R d q}{d t}+\frac{q}{C}=E$
$\int_{0}^{Q} \frac{d q}{(C E-q)}$
$=-\int_{0}^{t} \frac{d t}{R C}$
This on solving gives $Q=Q_{0}\left(1-e^{-t / R C}\right)$
where $Q_{0}=C E$
Important Points
- The charge on a capacitor increases exponentially with time

- The current during charging process is$I=\frac{d Q}{d t}$$=-\frac{Q_{0}}{R C} e^{-t / R C}$$=-I_{0} e^{-t / R C}$
The current decreases exponentially with time.

- $\tau=R C$ is the capacitive time constant. It is the time in which the charge on the capacitor reaches 0.632 times of its maximum value during charging.
- The time constant is the time in which current reduces to $\frac{1}{\mathrm{e}}$ times or 0.368 times of its initial value
- At initial time $\mathrm{t}=0$ and $I=I_{\max }$ so circuit acts as short circuit or conducting wire.At $t=\infty \quad I=0$ so circuit acts as an open circuit or as a broken wire.
- The voltage increases exponentially with time as $V=V_{0}\left(1-e^{-t / R C}\right)$ during charging.
Discharging
If a completely charged capacitor C having charge $\mathrm{Q}_{0}$ is discharged through a resistance R then equation of emf at any time t is$\mathrm{RI}+\frac{\mathrm{q}}{\mathrm{C}}=0$
Or
$R \frac{d q}{d t}+\frac{q}{C}=0$
Or
$\int_{Q_{0}}^{Q} \frac{d q}{q}=-\int_{0}^{t} \frac{d t}{R C}$
Or
$Q=Q_{0} e^{-t / R C}$
Important Points
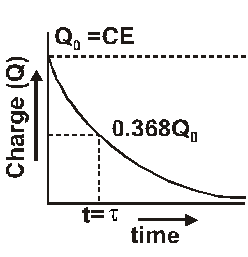
- During discharging charge on a capacitor decreases exponentially with time.
- The current during discharging process$I=\frac{d Q}{d t}=-\frac{Q_{0}}{R C} e^{-t / R C}$$=-I_{0} e^{-t / R C}$
 The current decreases exponentially with time.
The current decreases exponentially with time. - Time constant is the time in which charge on capacitor become $\frac{1}{\mathrm{e}}$ or 0.368 times of its initial value $\mathrm{Q}_{0}$
- Time constant is the time in which current reduces to $\frac{1}{\mathrm{e}}$ or 0.368 times of its initial value $\mathrm{I}_{0}$.The direction discharging current is opposite to that of charging.
- During discharging voltage decreases with time as $V=V_{0} e^{-t / R C}$
For a better understanding of this chapter, please check the detailed notes of Electrostatics. To watch Free Learning Videos on physics by Saransh Gupta sir Install the eSaral App.
