JEE Main Previous Year Papers Questions of Chemistry With Solutions are available at eSaral.
Simulator
Previous Years AIEEE/JEE Mains Questions
Q. A vessel at 1000 K contains $\mathrm{CO}_{2}$ with a pressure of 0.5 atm. Some of the $\mathrm{CO}_{2}$ is converted into CO on the addition of graphite. If the total pressure at equilibrium is 0.8 atm, the value of K is :-
(1) 0.3 atm (2) 0.18 atm (3) 1.8 atm (4) 3 atm
[AIEEE-2011]
Ans. (3)
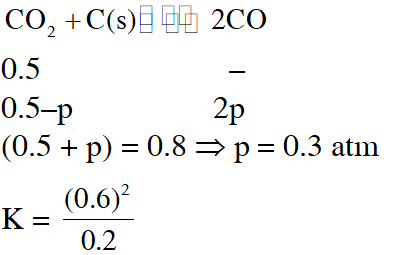
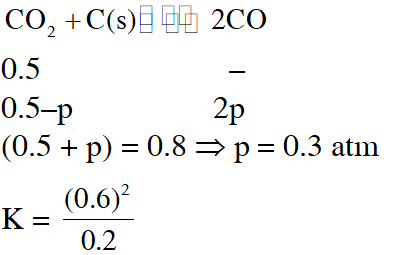
Q. The equilibrium constant $\left(\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{C}}\right)$ for the reaction $\mathrm{N}_{2}(\mathrm{g})+\mathrm{O}_{2}(\mathrm{g}) \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{NO}(\mathrm{g})$ at temperature T is $4 \times 10^{-4}$ The value of $\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{c}}$ for the reaction. $\mathrm{NO}(\mathrm{g}) \longrightarrow 1 / 2 \mathrm{N}_{2}(\mathrm{g})+1 / 2 \mathrm{O}_{2}(\mathrm{g})$ at the same temperature is :-
(1) 50.0
(2) 0.02
(3) $2.5 \times 10^{2}$
(4) $4 \times 10^{-4}$
[AIEEE-2012]
Ans. (1)
$\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{c}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{c}}}}$
Q. 8 mol of $\mathrm{AB}_{3}(\mathrm{g})$ are introduced into a 1.0 $\mathrm{d} \mathrm{m}^{3}$ vessel. If it dissociates as $2 \mathrm{AB}_{3}(\mathrm{g}) \square \quad \mathrm{A}_{2}(\mathrm{g})+3 \mathrm{B}_{2}(\mathrm{g})$
At equilibrium, 2mol of $\mathrm{A}_{2}$ are found to be present. The equilibrium constant of this reaction is :-
(1) 36 (2) 3 (3) 27 (4) 2
[JEE-MAINS(online)-2012]
Ans. (3)
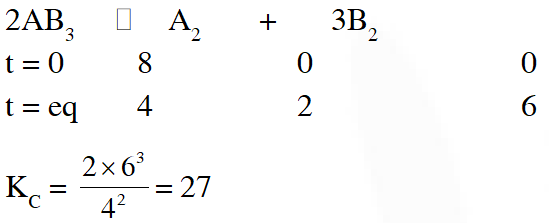
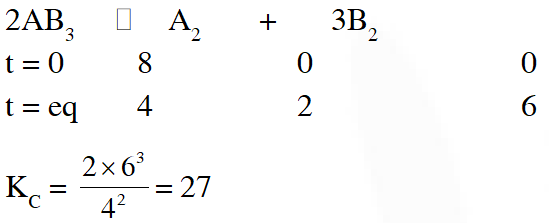
Q. The value of Kp for the equilibrium reaction $\mathrm{N}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{4}(\mathrm{g}) \square 2 \mathrm{NO}_{2}(\mathrm{g})$ is 2 The percentage dissociation of $\mathrm{N}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{4}(\mathrm{g})$ at a pressure of 0.5 atm is
(1) 71 (2) 50 (3) 88 (4) 25
[JEE-MAINS(online)-2012]
Ans. (1)
$\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{p}}=\frac{(2 \alpha)^{2}}{(1-\alpha)} \times \frac{0.5}{(1+\alpha)}$
Q. $\mathrm{K}_{1}, \mathrm{K}_{2}$ and $\mathrm{K}_{3}$ are the equilibrium constants of the following reactions (I), (II) and (III), respectively
(I) $\mathrm{N}_{2}+2 \mathrm{O}_{2} \square 2 \mathrm{NO}_{2}$
(II) $2 \mathrm{NO}_{2} \square \mathrm{N}_{2}+2 \mathrm{O}_{2}$
(III) $\mathrm{NO}_{2} \square \frac{1}{2} \mathrm{N}_{2}+\mathrm{O}_{2}$
The correct relation from the following is :
(1) $\mathrm{K}_{1}=\sqrt{\mathrm{K}_{2}}=\mathrm{K}_{3}$
(2) $\mathrm{K}_{1}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{K}_{2}}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{K}_{3}}$
$(3) \mathrm{K}_{1}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{K}_{2}}=\mathrm{K}_{3}$
(4)$\mathrm{K}_{1}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{K}_{2}}=\frac{1}{\left(\mathrm{K}_{3}\right)^{2}}$
[JEE-MAINS(online)-2012]
Ans. (4)
Fact
Q. One mole of $\mathrm{O}_{2}(\mathrm{g})$ and two moles of SO2(g) were heated in a closed vessel of one litre capacity at 1098 K. At equilibrium 1.6 moles of $\mathrm{SO}_{3}$ (g) were found. The equilibrium constant $\mathbf{K}_{C}$ of the reaction would be :-
(1) 60 (2) 80 (3) 30 (4) 40
[JEE-MAINS(online)-2012]
Ans. (2)
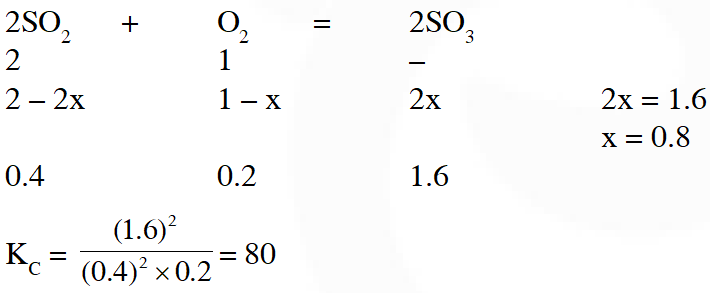
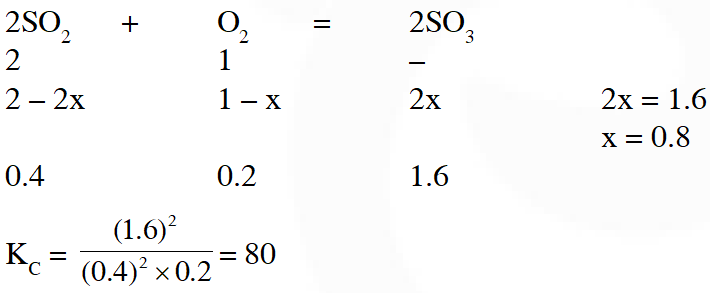
Q. $\mathrm{N}_{2}(\mathrm{g})+3 \mathrm{H}_{2}(\mathrm{g}) \square 2 \mathrm{NH}_{3}(\mathrm{g}), \mathrm{K}_{1}$
$\mathrm{N}_{2}(\mathrm{g})+\mathrm{O}_{2}(\mathrm{g}) \square 2 \mathrm{NO}(\mathrm{g}), \mathrm{K}_{2} \quad(\mathrm{B})$
$\mathrm{H}_{2}(\mathrm{g})+\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{O}_{2}(\mathrm{g}) \square \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{g}), \mathrm{K}_{3} \quad(\mathrm{C})$
The equation for the equilibrium constant of the reaction
$2 \mathrm{NH}_{3}(\mathrm{g})+\frac{5}{2} \mathrm{O}_{2}(\mathrm{g}) \square 2 \mathrm{NO}(\mathrm{g})+3 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{g}),\left(\mathrm{K}_{4}\right)$
in terms of $\mathrm{K}_{1}, \mathrm{K}_{2}$ and $\mathrm{K}_{3}$ is :
(1) $\frac{\mathrm{K}_{1} \mathrm{K}_{3}^{2}}{\mathrm{K}_{2}}$
(2) $\frac{\mathrm{K}_{2} \mathrm{K}_{3}^{3}}{\mathrm{K}_{1}}$
(3) $\frac{\mathrm{K}_{1} \mathrm{K}_{2}}{\mathrm{K}_{3}}$
(4) $\mathrm{K}_{1} \mathrm{K}_{2} \mathrm{K}_{3}$
[JEE-MAINS(online)-2013]
Ans. (2)
Fact
Q. In reaction $\mathrm{A}+2 \mathrm{B} \square 2 \mathrm{C}+\mathrm{D}$, initial concentration of B was 1.5 times of |A|, but at equilibrium the concentrations of A and B became equal. The equilibrium constant for the reaction is
(1)4 (2) 6 (3) 12 (4) 8
[JEE-MAINS(online)-2013]
Ans. (1)
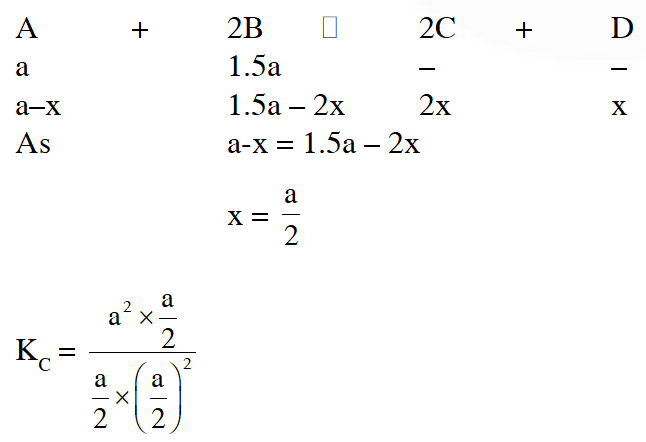 $\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{c}}=4$
$\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{c}}=4$
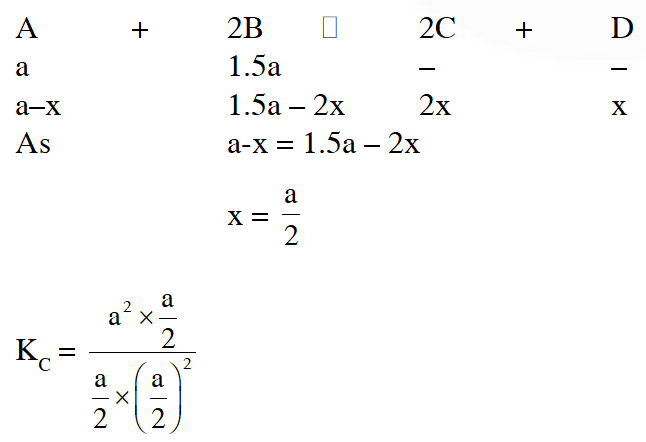 $\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{c}}=4$
$\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{c}}=4$
Q. For the decomposition of the compound, represented as
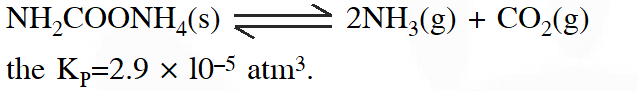 If the reaction is started with 1 mol of the compound, the total pressure at equilibrium would be
(1) $38.8 \times 10^{-2}$ atm
(2) $1.94 \times 10^{-2}$ atm
(3) $5.82 \times 10^{-2}$ atm
(4) $7.66 \times 10^{-2}$ atm
[JEE-MAINS(online)-2014]
If the reaction is started with 1 mol of the compound, the total pressure at equilibrium would be
(1) $38.8 \times 10^{-2}$ atm
(2) $1.94 \times 10^{-2}$ atm
(3) $5.82 \times 10^{-2}$ atm
(4) $7.66 \times 10^{-2}$ atm
[JEE-MAINS(online)-2014]
Ans. (3)
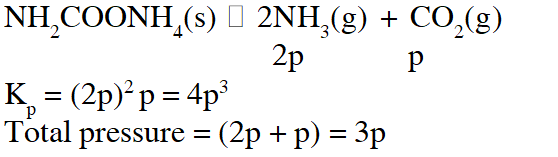
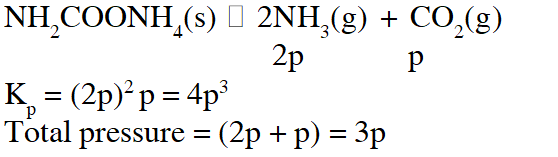
Q. For the reaction $\mathrm{SO}_{2(\mathrm{g})}+\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{O}_{2(\mathrm{g})} \square \mathrm{SO}_{3(\mathrm{g})},$ if $\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{p}}=\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{C}}(\mathrm{RT})^{\mathrm{x}}$ where the symbols have usual meaning then the value of x is : (assuming ideality)
( 1)$\frac{1}{2}$
( 2) 1
(3) –1
$(4)-\frac{1}{2}$
[JEE-MAINS 2014]
Ans. (4)
$\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{p}}=\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{C}}(\mathrm{RT})^{-\frac{1}{2}}$
Q. The equilibrium constants at 298 K for a reaction $\mathrm{A}+\mathrm{B} \rightleftharpoons \mathrm{C}+\mathrm{D}$ is 100 If the initial concentration of all the four species were 1 M each, then equilibrium concentration of D
(in mol $\mathrm{L}^{-1}$) will be :
(1) 1.182 (2) 0.182 (3) 0.818 (4) 1.818
[JEE-Mains 2016]
Ans. (4)
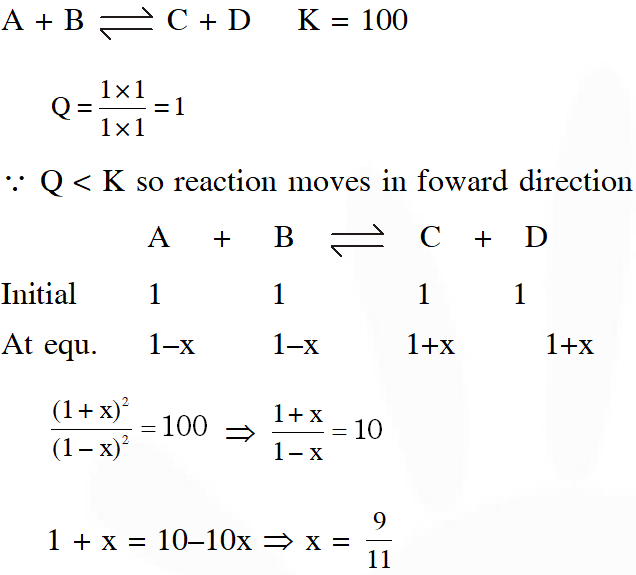
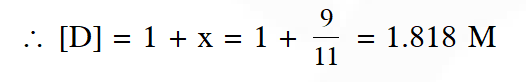
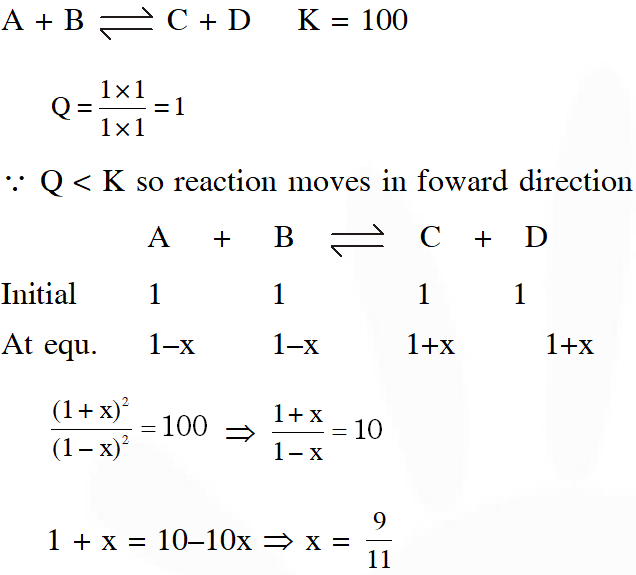
Comments
Lukas
Feb. 6, 2024, 12:35 p.m.
Thanks for some other informative blog. Where else may I get that
type of information written in such an ideal method?
I have a mission that I'm just now working on, and I have been on the look out for such
info. seraphina.top
sadiq
Nov. 10, 2020, 11:21 p.m.
thank you in other websites the questions are simple but here they are tricky and good solution releaving method is excellent thank you very
Click here to get exam-ready with eSaral
For making your preparation journey smoother of JEE, NEET and Class 8 to 10, grab our app now.
