Current loop as a Magnetic Dipole - Magnetism | Class 12th Physics Notes
JEE Mains & AdvancedCurrent loop as a Magnetic Dipole
Ampere found that the distribution of magnetic lines of force around a finite current-carrying solenoid is similar to that produced by a bar magnet. This is evident from the fact that a compass needle when moved around these two bodies shows similar deflections. After noting the close resemblance between these two, Ampere demonstrated that a simple current loop behaves like a bar magnet and put forward that all the magnetic phenomena are due to circulating electric current. This is Ampere’s hypothesis.
India's Best Exam Preparation for Class 12th - Download Now
We consider a circular coil carrying current I. When seen from above current flows in the anti-clockwise direction. 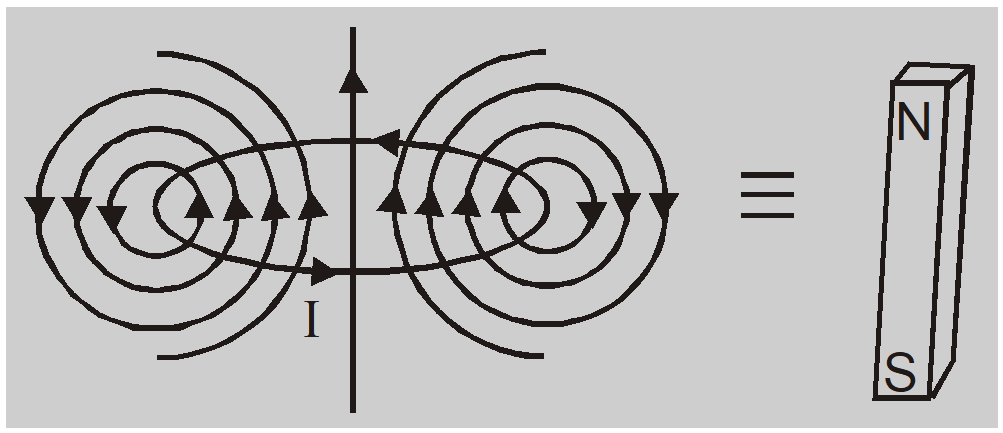
- The magnetic field lines due to each elementary portion of the circular coil are circular near the element and almost straight near the center of the circular coil.
- The magnetic lines of force seem to enter at the lower face of the coil and leave at the upper face.
- The lower face through which lines of force enter behaves as a south pole and the upper face through which field lines leave behaves as the north pole.
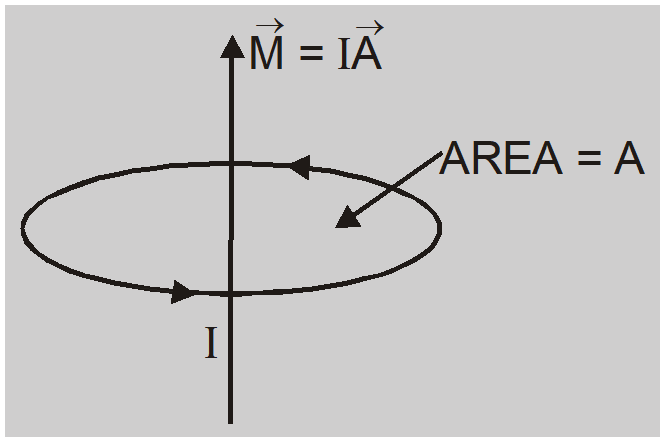
- A planar loop of any shape behaves as a magnetic dipole.
- The dipole moment of current loop $(\mathrm{M})=$ ampere turns (nI) $\times$ area of coil (A) or $\mathrm{M}=\mathrm{nIA}$.
- The unit of dipole moment is ampere meter $^{2}\left( A - m ^{2}\right)$
- The magnetic dipole moment is a vector with direction from S pole to N pole or along the direction of normal to the planar area.
India's Best Exam Preparation for Class 12th - Download Now
Atoms as a Magnetic Dipole
In an atom, electrons revolve around the nucleus. These moving electrons behave as small current loops. So atom possesses a magnetic dipole moment and hence behaves as a magnetic dipole.
The angular momentum of electron due to orbital motion $L = m _{ e } vr$
The equivalent current due to orbital motion $I =-\frac{ e }{ T }=-\frac{ ev }{2 \pi r }$ 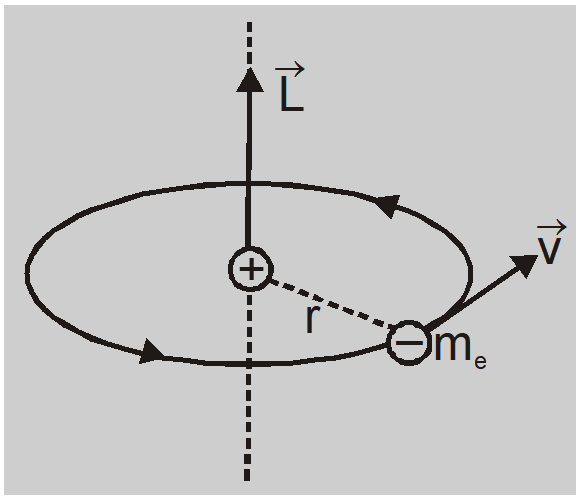
–ve sign shows direction of current is opposite to direction of motion of electron.
Magnetic dipole moment $M=I A=-\frac{e v}{2 \pi r} \cdot \pi r^{2}=-\frac{e v r}{2}$
Using $L=m_{e}$ vr we have $\quad M=-\frac{e}{2 m_{e}} L$
In vector form $\overrightarrow{ M }=-\frac{ e }{2 m _{ e }} \overrightarrow{ L }$
The direction of magnetic dipole moment vector is opposite to angular momentum vector.
According to Bohr's theory $L=\frac{n h}{2 \pi} \quad n=0, \quad 1, \quad 2 \ldots \ldots$
So $M=\left(\frac{e}{2 m_{e}}\right) \frac{n h}{2 \pi}=n\left(\frac{e h}{4 \pi m_{e}}\right)=n \mu_{B}$
Where $\mu_{\mathrm{B}}=\frac{\mathrm{eh}}{4 \pi \mathrm{m}_{e}}$
$=\frac{\left(1.6 \times 10^{-19} \mathrm{C}\right)\left(6.62 \times 10^{-34} \mathrm{Js}\right)}{4 \times 3.14 \times\left(9.1 \times 10^{-31} \mathrm{~kg}\right)}$
$=9.27 \times 10^{-24} \mathrm{Am}^{2}$
is called Bohr Magneton. This is natural unit of magnetic moment.
Also Read:
Biot Savart's Law
India's Best Exam Preparation for Class 12th - Download Now
Click here for the Video tutorials of Magnetic Effect of Current Class 12
About eSaral At eSaral we are offering a complete platform for IIT-JEE & NEET preparation. The main mission behind eSaral is to provide education to each and every student in India by eliminating the Geographic and Economic factors, as a nation’s progress and development depends on the availability of quality education to each and every one. With the blend of education & technology, eSaral team made the learning personalized & adaptive for everyone.
India's Best Exam Preparation for Class 12th - Download Now
For free video lectures and complete study material, Download eSaral APP.
