Force on a Current-Carrying Conductor in Magnetic field
A current-carrying conductor produces a magnetic field around it. i.e. Behaves like a magnet and exerts a force when a magnet is placed in its magnetic field. Similarly a magnet also exerts equal and opposite force on the current-carrying conductor. The direction of this force can be determined using Flemings left-hand rule.Current Element
Current element is defined as a vector having a magnitude equal to the product of current with a small part of the length of the conductor and the direction in which the currentis flowing in that part of the conductor.
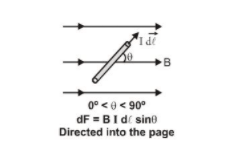 With the help of experiments Ampere established that when a current element 1 de is placed
With the help of experiments Ampere established that when a current element 1 de is placed
in a magnetic field $\overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}},$ it experiences a force
$\overrightarrow{\mathrm{dF}}=\mathrm{I} \overrightarrow{\mathrm{d}} \ell \times \overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}}$
The magnitude of force is $\quad \mathrm{dF}=\mathrm{B} \mathrm{I}$ d\ell $\sin \theta$
$[\theta \text { is the angle between the } \overrightarrow{\mathrm{d} \ell} \text { and } \overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}}]$
(i) When $\sin \theta=\min =0,$ i.e., $\theta=0^{\circ}$ or $180^{\circ}$
Then force on a current element $=0$ (minimum)
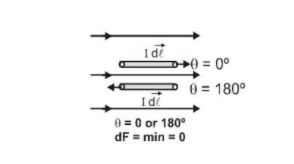 A current element in a magnetic field does not experience any force if the current in it is collinear with the field.
A current element in a magnetic field does not experience any force if the current in it is collinear with the field.
(ii) When $\sin \theta=\max =1,$ i.e., $\theta=90^{\circ}$
The force on the current will be maximum ( $=$ BI d\ell)
Force on a current element in a magnetic field is maximum $(=\text { BI } \mathrm{d} \ell)$
When it is perpendicular to the field.
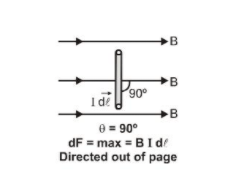 The direction of force is always perpendicular to the plane containing I $\overrightarrow{\mathrm{d} \ell}$ and $\overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}}$.
The direction of force is always perpendicular to the plane containing I $\overrightarrow{\mathrm{d} \ell}$ and $\overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}}$.
 The direction of the force on current element I $\mathrm{d} \vec{\ell}$ and $\overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}}$ are perpendicular to each other can also be determined by applying either of the following rules:
The direction of the force on current element I $\mathrm{d} \vec{\ell}$ and $\overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}}$ are perpendicular to each other can also be determined by applying either of the following rules:
- Fleming's Left-Hand Rule
- Right Hand Palm Rule
About eSaral At eSaral we are offering a complete platform for IIT-JEE & NEET preparation. The main mission behind eSaral is to provide education to each and every student in India by eliminating the Geographic and Economic factors, as a nation’s progress and development depend on the availability of quality education to each and every one. With the blend of education & technology, eSaral team made the learning personalized & adaptive for everyone.
For free video lectures and complete study material, Download eSaral APP.
Click here to get exam-ready with eSaral
For making your preparation journey smoother of JEE, NEET and Class 8 to 10, grab our app now.
