Manufacturing industries class 10th notes
Class 10
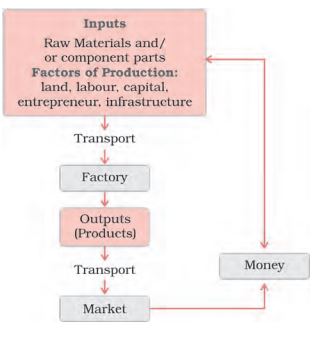
Manufacturing industries class 10th notes mark this industry as the most important industry of metallurgy. Manufacturing industries are those industries that involve the production of goods or products by using various raw materials, machinery, and labor. Manufacturing industries play a vital role in the economic development of any country. They are the backbone of the industrial sector and contribute significantly to the country's GDP
Importance of manufacturing industries in economic development
-
Employment Generation: Manufacturing industries provide employment to a large number of people, from skilled to unskilled labor. This helps in reducing unemployment and poverty in the country.
-
Economic Growth: Manufacturing industries contribute to the growth of the economy by producing goods that are needed for consumption, investment, and export. This leads to an increase in the country's GDP.
-
Development of Infrastructure: Manufacturing industries require a lot of infrastructure such as roads, ports, airports, and electricity. The development of these infrastructure facilities helps in the growth of other sectors as well.
-
Technological Advancements: Manufacturing industries drive technological advancements as they need to continuously improve their processes to remain competitive. This leads to the development of new technologies that can be used in other sectors.
-
Export Earnings: Manufacturing industries contribute significantly to the country's export earnings. They produce goods that are in demand globally, leading to foreign exchange earnings for the country.
Industries contribute significantly to the national economy of a country by providing goods and services that are essential for consumption, investment, and export.
Importance of Industry's Contribution to the National Economy:
-
Economic Growth: Industries are the primary drivers of economic growth and contribute significantly to a country's Gross Domestic Product (GDP). They produce goods and services that are needed for consumption, investment, and export, leading to an increase in the country's GDP.
-
Employment Generation: Industries provide employment to a large number of people, from skilled to unskilled labor. This helps in reducing unemployment and poverty in the country./: Industries require a lot of infrastructure such as roads, ports, airports, and electricity. The development of these infrastructure facilities helps in the growth of other sectors as well.
-
Technological Advancements: Industries drive technological advancements as they need to continuously improve their processes to remain competitive. This leads to the development of new technologies that can be used in other sectors.
-
Foreign Exchange Earnings: Industries contribute significantly to the country's foreign exchange earnings. They produce goods that are in demand globally, leading to an increase in the country's foreign exchange reserves.
-
Government Revenue: Industries generate revenue for the government in the form of taxes, duties, and tariffs. This revenue can be used for the development of other sectors and for the welfare of the citizens.
Industry Location - Manufacturing industries class 10th notes
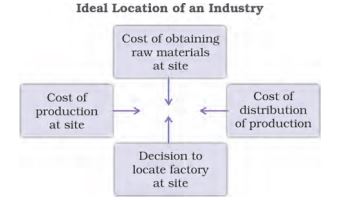
Industry location is the process of selecting a suitable site for setting up an industry based on various factors such as availability of raw materials, labor, market, capital, and power.
Importance of Industry Location:
-
Availability of Raw Materials: Industries require raw materials for their production process, and selecting a location close to the source of raw materials helps in reducing transportation costs and time.
-
Availability of Labor: The availability of skilled and unskilled labor is essential for the success of an industry. Industries need to select a location where there is an adequate supply of labor.
-
Market: Industries need to select a location where their products can be easily marketed and distributed. A location close to the market helps in reducing transportation costs and time.
-
Capital: Industries require a significant amount of capital to set up and operate. Selecting a location where capital is readily available or where financial institutions are present helps in the smooth functioning of the industry.
-
Power: Industries require a continuous supply of power for their production process. Selecting a location where there is a stable and reliable power supply helps in avoiding production delays and losses.
-
Government Policies: Government policies such as tax incentives, subsidies, and regulations play a significant role in industry location decisions. Industries need to select a location where they can take advantage of these policies.
In conclusion, industry location is a crucial factor in the success of an industry. Selecting a suitable location based on factors such as availability of raw materials, labor, market, capital, power, and government policies can help in the smooth functioning and growth of an industry.
Five basis on which industries are classified - Manufacturing industries class 10th notes
- On the basis of source of raw materials used — Agro-based and mineral-based.
- According to their main role — Basic and Consumer industries.
- On the basis of capital investment — Small-scale and large-scale industries.
- On the basis of ownership — Public Sector, Private Sector, Cooperative Sector, Joint Sector.
- Based on the bulk and weight of raw material and finished goods — Heavy industries, Light
If the investment is more than one crore rupees in any industry, it is considered as a large scale industry. For example, Iron and Steel industry, Cement industry.
If the investment is less than one crore rupees, it is considered as a small scale industry.
Agro-based industries:
They obtain their raw materials from agricultural products. Example: Textiles—cotton, jute, silk and woolen. Rubber, Sugar, Coffee, Tea and Edible Oil, etc.
Mineral-based industries:
They obtain their raw materials from minerals. Example: Iron and steel, cement, machine tools, petro-chemicals, etc.
Four types of industries based on ownership are
Public Sector industries are owned and operated by government agencies, such as BHEL and SAIL. Private Sector industries are owned and operated by individuals or groups, such as TTSCO, Bajaj Auto Ltd., and Dabur Industries. Joint Sector industries are jointly run by the Public and Private Sector, such as Oil India Ltd. Cooperative Sector industries are owned and operated by producers or suppliers of raw materials and workers, who pool in their resources and share profits or losses proportionately, such as the sugar industry in Maharashtra and coir industry in Kerala.
Importance of Different Sectors in Industries:
-
Public Sector: Public Sector industries are essential in promoting public welfare and strategic industries, such as defense, infrastructure, and energy. These industries help in generating employment, ensuring the availability of essential goods and services, and promoting balanced regional development.
-
Private Sector: Private Sector industries are vital in promoting entrepreneurship, innovation, and efficiency. These industries operate on market principles and contribute significantly to the country's GDP and employment generation.
-
Joint Sector: Joint Sector industries are important in promoting collaboration between the Public and Private Sector, leading to the sharing of expertise, resources, and risks. These industries help in the development of key sectors, such as agriculture, power, and telecommunications.
-
Cooperative Sector: Cooperative Sector industries are crucial in promoting community ownership and participation, leading to the development of sustainable and equitable industries. These industries help in the development of rural areas, promoting the welfare of farmers and workers, and ensuring the availability of essential goods and services.
In conclusion, different sectors in industries, including Public, Private, Joint, and Cooperative Sectors, play a crucial role in promoting public welfare, entrepreneurship, collaboration, and community ownership. These sectors contribute significantly to the country's economic growth, employment generation, and balanced regional development.
The Indian Textile industry holds a unique position in the economy due to its significant contributions to industrial production (14%), employment (35 million persons directly, second only to agriculture), foreign exchange earnings (about 24.6%), and GDP (4%). It stands out as the only industry in the country that is self-reliant and complete in the value chain.
Importance of the Indian Textile Industry:
-
Industrial Production: The Indian Textile industry's significant contribution to industrial production plays a crucial role in the country's economic growth and development.
-
Employment: The industry's vast employment generation, employing the largest number of people after agriculture, helps in promoting social welfare and reducing poverty.
-
Foreign Exchange Earnings: The industry's substantial share in foreign exchange earnings helps in improving the country's balance of payments and increasing the country's foreign reserves.
-
GDP Contribution: The industry's contribution to GDP helps in promoting economic growth and development.
-
Self-Reliance : The Indian Textile industry's self-reliance and complete value chain make it a significant contributor to the country's industrial and economic development.
In conclusion, the Indian Textile industry's unique position in the economy, including its contributions to industrial production, employment, foreign exchange earnings, GDP, and self-reliance, makes it a crucial sector in promoting the country's economic growth and development.
Factors for concentration/location of cotton textile industry in Maharashtra and-Gujarat:
The concentration/location of the cotton textile industry in Maharashtra and Gujarat can be attributed to several factors, including the abundant and cheap availability of raw cotton, the moist climate in these coastal states, well-developed transportation systems, accessible port facilities, and proximity to the market.
Importance of Factors:
-
Raw Cotton Availability: The abundant and cheap availability of raw cotton in Maharashtra and Gujarat has been a significant factor in the growth and development of the cotton textile industry in these states.
-
Moist Climate: The moist climate in these coastal states has also helped in the development of the cotton textile industry, as humid conditions are necessary for weaving the cloth, preventing the yarn from breaking.
-
Transportation System and Port Facilities: The well-developed transportation system and accessible port facilities in Maharashtra and Gujarat have made it easier to transport raw materials and finished goods, contributing to the growth of the industry in these states.
-
Proximity to Market: The cotton clothes are ideal to wear in the warm and humid climate of Maharashtra and Gujarat, making the proximity to the market an essential factor in the industry's growth and development.
Problems faced by the cotton textile industry:
Power supply is erratic in our country. Machinery needs to be upgraded, especially in weaving and processing sectors. Low output of labor. We still need to import cotton in spite of the fact that the production of cotton in the country has increased. Stiff competition from the synthetic fiber industry
Factors responsible for the concentration of jute industry on the banks of Hoogly:
The factors responsible for the concentration of the jute industry on the banks of the Hoogly include the proximity of the jute-producing areas to the Hoogly Basin, the provision of inexpensive water transport by the Hoogly River, the existence of a well-connected network of railways, waterways, and roadways, the availability of abundant water for processing raw jute, the presence of cheap labor from West Bengal, Bihar, Odisha, and Uttar Pradesh, and the provision of banking, insurance, and port facilities by Kolkata as a port and large urban center.
The reasons for locating sugar mills close to the fields
The reasons for locating sugar mills close to the fields include the bulky and perishable nature of the raw material, sugarcane, which cannot be transported long distances due to its sucrose content drying up quickly, requiring it to be processed within 24 hours of harvest. The sugar industry is shifting towards southern and western states due to the higher sucrose content of the cane produced, favorable climatic conditions resulting in a longer growing and crushing season, and the success of cooperatives in these states. The seasonal nature of the sugar industry also makes it ideal for the cooperative sector, while the yield per hectare is higher in southern states.
The iron and steel industry is considered a basic or key heavy industry.
Iron and steel industries is concentrated in and around Chhotanagpur Plateau Region because
The concentration of iron and steel industries in and around Chhotanagpur Plateau Region is due to the following reasons:
- This region has a low cost of iron-ore which is mined here.
- High grade raw materials are available in close proximity.
- There is availability of cheap labour.
- The home market has vast growth potential.
- There is an efficient transport network for their distribution.
- Availability of power because this region has many thermal and hydel power plants.
- Liberalisation and FDI have contributed to the growth of the iron and steel industry.
Aluminium
Aluminium is a light metal that is resistant to corrosion and a good conductor of heat. It is malleable and becomes strong when mixed with other metals. It is used for manufacturing aircraft, making utensils and packing material, making wires, and has gained popularity as a substitute for steel, copper, zinc, and lead in a number of industries.
Electronic industry:
The electronic industry produces a wide range of products from transistor sets to televisions and computers for the masses. It has helped us set up telephone exchanges, telephones, cellular telecom, radios, and many other equipment which have application in space technology, aviation, defense, meteorological departments, etc. This industry has generated employment for a large number of people and has been a major foreign exchange earner because of its fast-growing Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) Sector. India is one of the leading countries in software development, with 18 software technology parks that provide high data communication facility to software experts.
Types of industrial pollution:
- Air pollution is emitted by chemical and paper factories, brick kilns, refineries and smelting plants, and burning of fossil fuels in factories that ignore pollution norms. Air-borne particulate materials contain both solid and liquid particles like dust, sprays, mist, and smoke.
- Water pollution is caused by dyes, detergents, acids and salts, heavy metals like lead and mercury, pesticides and fertilizers, synthetic chemicals with carbon, plastics, and rubber, etc. discharged in the water bodies without treatment, which pollute these water bodies.
- Noise pollution is created by generators, compressors, machines, furnaces, looms, exhaust fans, etc. used by industries, which create a lot of noise. Noise can raise blood pressure and can have physiological effects as well.
- Land pollution is caused by dumping of industrial wastes especially glass, harmful chemicals, industrial effluents, packing, salts, and garbage into the soil.
- Thermal pollution is caused by wastes from nuclear power plants, nuclear and weapon production facilities, which cause cancer and birth defects.
Factories can fit smoke stacks with fabric filters, electrostatic precipitators, and other equipment to reduce particulate matter in the air. Industries can use equipment like electrostatic precipitators, scrubbers, and inertial separators to control aerosol emissions. Coal can be replaced with oil or gas in factories to reduce smoke emissions.
Water Pollution can be controlled by using following methods
Industries can control water pollution by:
Minimizing water usage for processing through recycling and reusing. Harvesting rainwater to fulfill water needs for industries and domestic purposes. Treating hot water and effluents before releasing them into rivers and ponds using the following methods: mechanically screening, grinding, flocculation, and sedimentation for primary treatment. Biological processes for secondary treatment. Biological, chemical, and physical processes for tertiary treatment, which involves recycling of wastewater.
Pro active approach adopted by National Thermal Power Corporation (NTPC) to preserve natural environment
National Thermal Power Corporation (NTPC) adopts a pro-active approach to preserve natural environment and resources by:
- Adopting latest techniques for optimum utilization and up-gradation of equipment.
- Maximizing ash utilization to minimize waste generation.
- Nurturing ecological balance by providing green belts.
- Managing ash pond, ash water recycling system and liquid waste management to reduce environmental pollution.
- Implementing ecological monitoring, reviews and online data base management for all its power stations.
- Reusing and recycling water in multiple stages to minimize water usage in processing. Harvesting rainwater for domestic and industrial water requirements.
- Treating hot water and effluents before releasing them in rivers and ponds through primary, secondary and tertiary treatment processes.
- Reducing particulate matter in air by fitting factories with electrostatic precipitators, fabric filters, scrubbers and inertial separators. Using oil or gas instead of coal to reduce smoke emissions.
- Fitting machinery and equipment with silencers to prevent noise pollution.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the study of Manufacturing Industries is a crucial part of the class 10th curriculum, and the Manufacturing Industries class 10th notes provide a comprehensive understanding of various aspects of the industry. These notes cover topics such as types of industries, raw materials, manufacturing processes, and the challenges faced by the industry. By studying Manufacturing Industries class 10th notes, students can gain a deeper insight into the workings of the industry and develop an appreciation for the role of manufacturing in our economy. Therefore, it is essential for students to pay attention to their Manufacturing Industries class 10th notes and make the most out of this valuable resource to excel in their academic and professional careers.
Download the eSaral App for complete Class 10 Video lectures, Study material, revision and much more.
Also read,