JEE Main Previous Year Question of Math with Solutions are available at eSaral. Practicing JEE Main Previous Year Papers Questions of mathematics will help the JEE aspirants in realizing the question pattern as well as help in analyzing weak & strong areas.
eSaral helps the students in clearing and understanding each topic in a better way. eSaral is providing complete chapter-wise notes of Class 11th and 12th both for all subjects.
Besides this, eSaral also offers NCERT Solutions, Previous year questions for JEE Main and Advance, Practice questions, Test Series for JEE Main, JEE Advanced and NEET, Important questions of Physics, Chemistry, Math, and Biology and many more.
Download eSaral app for free study material and video tutorials.
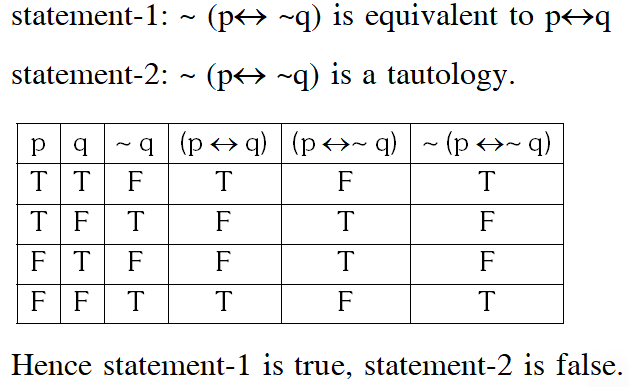
Q. Statement-1: $\sim(p \leftrightarrow \sim q)$ is equivalent to $p \leftrightarrow q$
Statement-2 $: \sim(p \leftrightarrow \sim q)$ is a tautology.
(1) Statement–1 is true, Statement–2 is false.
(2) Statement–1 is false, Statement–2 is true.
(3) Statement–1 is true, Statement–2 is true ;
Statement–2 is a correct explanation for Statement–1.
(4) Statement–1 is true, Statement–2 is true ;
Statement–2 is not a correct explanation for statement–1.
[AIEEE-2009]
Ans. (1)

Q. Let $S$ be a non-empty subset of $R$. Consider the following statement:
$p:$ There is a rational number $x \in S$ such that $x>0$
which of the following statements is the negation of the statement p?
(1) There is a rational number $x \in$ S such that $x \leq 0$
(2) There is no rational number $x \in S$ such that $x \leq 0$
(3) Every rational number $x \in S$ satisfies $x \leq 0$
(4) $x \in S$ and $x \leq 0 \Rightarrow x$ is not rational.
[AIEEE-2010]
Ans. (3)
Given $\mathrm{S} \subseteq \mathrm{R}$ and
$\mathrm{p}=$ There is a rational number $\mathrm{x} \in \mathrm{S}$ such that $\mathrm{x}>0$
then $\sim \mathrm{p}:$ Any rational number $\mathrm{x} \in \mathrm{S}$ such that $\mathrm{x}$ $\not>$ 0
i.e. $\sim \mathrm{p}:$ Every rational number $\mathrm{x} \in \mathrm{S}$ satisfy $\mathrm{x} \leq 0$
Q. Consider the following statements
p : Suman is brilliant
q : Suman is rich
r : Suman is honest
The negation of the statement "Suman is brilliant and dishonest if and only if Suman is rich" can be expressed as :-
( 1)$\sim \mathrm{q} \leftrightarrow \sim \mathrm{p} \wedge \mathrm{r}$
( 2)$\sim(\mathrm{p} \wedge \sim \mathrm{r}) \leftrightarrow \mathrm{q}$
( 3)$\sim \mathrm{p} \wedge(\mathrm{q} \leftrightarrow \sim \mathrm{r})$
( 4)$\sim(\mathrm{q} \leftrightarrow(\mathrm{p} \wedge \sim \mathrm{r}))$
[AIEEE-2011]
Ans. (2,4)
Given Statement :
$(\mathrm{p} \wedge \sim \mathrm{r}) \Leftrightarrow \mathrm{q}$
Negations of $\mathrm{p} \Leftrightarrow \mathrm{q}$ are
$\sim(\mathrm{p} \Leftrightarrow \mathrm{q}), \sim(\mathrm{q} \Leftrightarrow \mathrm{p})$
$\sim \mathrm{p} \Leftrightarrow \mathrm{q}$ and $\sim \mathrm{q} \Leftrightarrow \mathrm{p}$
Hence negations of given statement
are $\sim(\mathrm{q} \Leftrightarrow(\mathrm{p} \wedge \sim \mathrm{r}))$
and $\sim(\mathrm{p} \wedge \sim \mathrm{r}) \Leftrightarrow \mathrm{q}$
Q. The only statement among the followings that is a tautology is :
( 1) $\mathrm{q} \rightarrow[\mathrm{p} \wedge(\mathrm{p} \rightarrow \mathrm{q})]$
(2) $\mathrm{p} \wedge(\mathrm{p} \vee \mathrm{q})$
(3) $\mathrm{p} \vee(\mathrm{p} \wedge \mathrm{q})$
(4) $[\mathrm{p} \wedge(\mathrm{p} \rightarrow \mathrm{q})] \rightarrow \mathrm{q}$
[AIEEE-2011]
Ans. (4)
$[\mathrm{p} \wedge(\mathrm{p} \rightarrow \mathrm{q})] \rightarrow \mathrm{q}$
$[\mathrm{p} \wedge(\sim \mathrm{p} \vee \mathrm{q})] \rightarrow \mathrm{q}$
$[(\mathrm{p} \wedge \sim \mathrm{p}) \vee(\mathrm{p} \wedge \mathrm{q})] \rightarrow \mathrm{q}$
$[\mathrm{c} \vee(\mathrm{p} \wedge \mathrm{q})] \rightarrow \mathrm{q}$
$\left\{\begin{array}{c}{\mathrm{p} \wedge \sim \mathrm{p} \equiv \mathrm{c} \equiv \mathrm{contradiction}} \\ {\because \mathrm{c} \vee \mathrm{p} \equiv \mathrm{p}}\end{array}\right.$
$\Rightarrow(\mathrm{p} \wedge \mathrm{q}) \rightarrow \mathrm{q}$
$\Rightarrow \sim(\mathrm{p} \wedge \mathrm{q}) \vee \mathrm{q}$
$\Rightarrow(\sim \mathrm{p} \vee \sim \mathrm{q}) \vee \mathrm{q}$
$\Rightarrow \sim \mathrm{p} \vee(\mathrm{q} \vee \sim \mathrm{q})$
$\Rightarrow \sim \mathrm{p} \vee(\mathrm{t}) \equiv$ tautology
Q. The negation of the statement
"If I become a teacher, then I will open a school", is :
(1) I will not become a teacher or I will open a school.
(2) I will become a teacher and I will not open a school.
(3) Either I will not become a teacher or I will not open a school.
(4) Neither I will become a teacher nor I will open a school.
[AIEEE-2012]
Ans. (2)
Q. Consider :
Statement-I: $(\mathrm{p} \wedge \sim \mathrm{q}) \wedge(\sim \mathrm{p} \wedge \mathrm{q})$ is a fallacy.
Statement-II : $(\mathrm{p} \rightarrow \mathrm{q}) \leftrightarrow(\sim \mathrm{q} \rightarrow \sim \mathrm{p})$ is a tuatology
(1) Statement-I is true, Statement-II is true; statement-II is a correct explanation for Statement-I.
(2) Statement-I is true, Statement-II is true; statement-II is not a correct explanation for Statement-I.
(3) Statement-I is true, Statement-II is false.
(4) Statement-I is false, Statement-II is true.
[JEE-MAINS-2013]
Ans. (2)
Given statement is $\sim(\mathrm{p} \leftrightarrow \sim \mathrm{q})$
As we know $\sim(\mathrm{p} \leftrightarrow \mathrm{q}) \equiv \sim \mathrm{p} \leftrightarrow \mathrm{q}$ or $\mathrm{p} \leftrightarrow \sim \mathrm{q}$
$\therefore \sim(\mathrm{p} \leftrightarrow \sim \mathrm{q}) \equiv \mathrm{p} \leftrightarrow \mathrm{q}$
Q. The statement $\sim(p \leftrightarrow \sim q)$ is :
(1) equivalent to $p \leftrightarrow q$
(2) equivalent to $\sim p \leftrightarrow q$
(3) a tautology
(4) a fallacy
[JEE(Main)-2014]
Ans. (1)
Given statement is $\sim(\mathrm{p} \leftrightarrow \sim \mathrm{q})$
As we know $\sim(\mathrm{p} \leftrightarrow \mathrm{q}) \equiv \sim \mathrm{p} \leftrightarrow \mathrm{q}$ or $\mathrm{p} \leftrightarrow \sim \mathrm{q}$
$\therefore \sim(\mathrm{p} \leftrightarrow \sim \mathrm{q}) \equiv \mathrm{p} \leftrightarrow \mathrm{q}$
Q. The negation of $\sim \mathrm{s} \vee(\sim \mathrm{r} \wedge \mathrm{s})$ is equivalent to :
( 1) $\mathrm{s} \vee(\mathrm{r} \vee \sim \mathrm{s})$
(2) $\mathrm{s} \wedge \mathrm{r}$
(3) $\mathrm{s} \wedge \sim \mathrm{r}$
( 4) $\mathrm{s} \wedge(\mathrm{r} \wedge \sim \mathrm{s})$
[JEE(Main)-2015]
Ans. (2)
$\square \mathrm{s} \vee(\square \mathrm{r} \wedge \mathrm{s})$
$(\square \mathrm{s} \vee \sim \mathrm{r}) \wedge(\square \mathrm{s} \wedge \mathrm{s})$
$(\square \mathrm{s} \vee \sim \mathrm{r}) \wedge \mathrm{t}$
$(\square \mathrm{s} \vee \sim \mathrm{r})$
$\sim(\square \mathrm{s} \vee \sim \mathrm{r})$
$\mathrm{s} \wedge \mathrm{r}$
Q. The Boolean Expression (p\wedge\simq) Vq\vee(\simp\wedgeq) is equivalent to :-
(1) $\mathrm{pv} \sim \mathrm{q}$
(2) $\sim \mathrm{p} \wedge \mathrm{q}$
(3) $\mathrm{p} \wedge \mathrm{q}$
(4) $\mathrm{p} \vee \mathrm{q}$
[JEE(Main)-2016]
Ans. (4)
Given boolean expression is
$(\mathrm{p} \wedge \sim \mathrm{q}) \vee \mathrm{q} \vee(\sim \mathrm{p} \wedge \mathrm{q})$
$(\mathrm{p} \wedge \sim \mathrm{q}) \mathrm{Vq}=(\mathrm{p} \vee \mathrm{q}) \wedge(\sim \mathrm{q} \vee \mathrm{q})=(\mathrm{p} \vee \mathrm{q}) \wedge \mathrm{t}=(\mathrm{p} \vee \mathrm{q})$
Now,
$(\mathrm{pVq}) \vee(\sim \mathrm{p} \wedge \mathrm{q})=\mathrm{p} \vee \mathrm{q}$
Q. The following statement $(\mathrm{p} \rightarrow \mathrm{q}) \rightarrow[(\sim \mathrm{p} \rightarrow \mathrm{q}) \rightarrow \mathrm{q}]$ is :
(1) a fallacy
(2) a tautology
(3) equivalent to $\sim \mathrm{p} \rightarrow \mathrm{q}$
(4) equivalent to $\mathrm{p} \rightarrow \sim \mathrm{q}$
[JEE(Main)-2017]
Ans. (2)
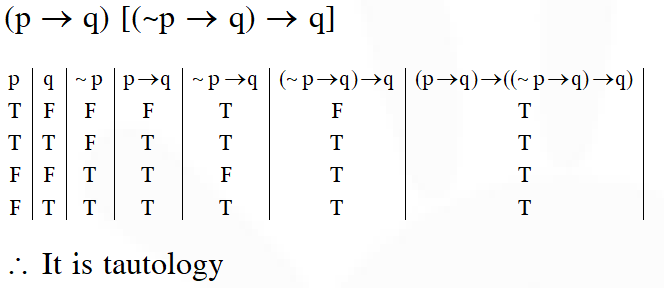
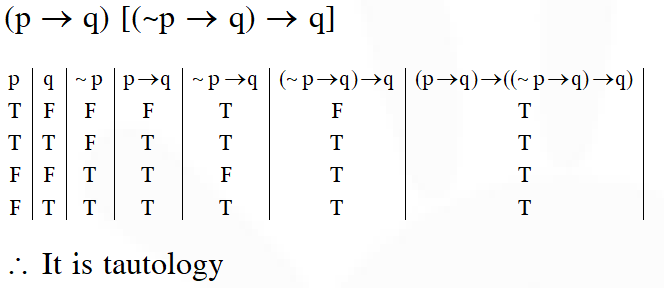
Q. The Boolean expression $\sim(p \vee q) \vee(\sim p \wedge q)$ is equivalent to :
(1) p (2) q (3) $\sim \mathrm{q}$ ( 4)$\sim \mathrm{p}$
[JEE(Main)-2018]
Ans. (4)
$\sim(p \vee q) \vee(\sim p \wedge q)$
$(\sim p \wedge \sim q) \vee(\sim p \wedge q)$
$\Rightarrow \sim p \wedge(\sim q \vee q)$
$\Rightarrow \sim p \wedge t \equiv \sim p$
Comments
Srigowthami
Aug. 27, 2020, 8:12 p.m.
Thank you so much..these helped me alot ....
I have confusion in this chapter..after doing these bits ..I got clarity......Once again tq
