When a charged particle moves along a magnetic field line into a region where the field becomes stronger, the particle experiences a force that reduces the component of velocity parallel to the field. This force slows the motion along the field line and here reverses it, forming a Magnetic Mirror. The motion of a charged particle in a magnetic field is characterized by the change in the direction of motion. It is expected also as the magnetic field is capable of only changing the direction of motion. In order to keep the context of the study simplified, we assume the magnetic field to be uniform. This assumption greatly simplifies the description and lets us easily visualize the motion of a charged particle in a magnetic field.
Motion of a Charged Particle in a Magnetic Field
The motion of a charged particle when it is moving collinear with the field, the magnetic field is not affected by the field (i.e. if motion is just along or opposite to a magnetic field) ( $ \quad F=0$ ) Only the following two cases are possible:
The case I: When the charged particle is moving perpendicular to the field The angle between $\overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}}$ and $\overrightarrow{\mathrm{v}}$ is $\theta=90^{\circ}$
So the force will be maximum ( $=$ qvB ) and always perpendicular to motion (and also field);
Hence the charged particle will move along a circular path (with its plane perpendicular to the field).
Centripetal force is provided by the force qvB,
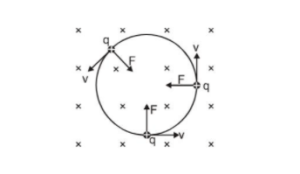
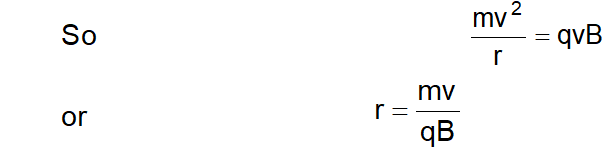
In case of the circular motion of a charged particle in a steady magnetic field :
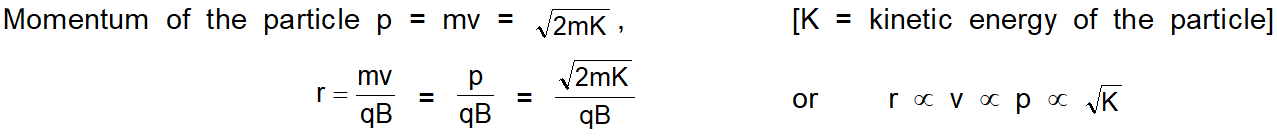
i.e., with the increase in speed or kinetic energy, the radius of the orbit increases. For uniform circular motion $v=\omega r$
Angular frequency of circular motion called cyclotron or gyro-frequency. $\omega=\frac{\mathrm{v}}{\mathrm{r}}=\frac{\mathrm{qB}}{\mathrm{m}}$
and the time period, $\quad \mathrm{T}=\frac{2 \pi}{\omega}=2 \pi \frac{\mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{qB}}$
i.e., time period (or frequency) is independent of speed of particle and radius of the orbit.
Time period depends only on the field B and the nature of the particle,
i.e., specific charge (q/m) of the particle.
This principle has been used in a large number of devices such as cyclotron (a particle accelerator), bubble-chamber (a particle detector) or mass-spectrometer etc.
the motion of a charged particle in an electric and magnetic field
case II : The charged particle is moving at an angle $\theta$ to the field :
$\left(\theta \neq 0^{\circ}, 90^{\circ} \text { or } 180^{\circ}\right)$
Resolving the velocity of the particle along and perpendicular to the field.
The particle moves with constant velocity v cos $\theta$ along the field ($\because$ no force acts on a charged particle when it moves parallel to the field).
And at the same time, it is also moving with velocity $v$ sin $\theta$ perpendicular to the field due to which it will describe a circle (in a plane perpendicular to the field)
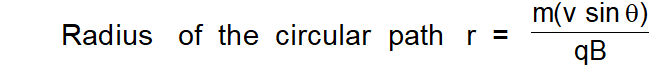
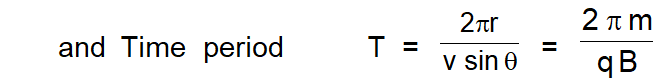
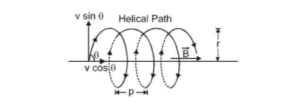
So the resultant path will be a helix with its axis parallel to the field $\overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}}$ as shown in fig. The pitch p of the helix $=$ linear distance travelled in one rotation
$p=T(v \cos \theta)=\frac{2 \pi m}{q B}(v \cos \theta)$
Also Read:
Biot Savart's Law
Click here for the Video tutorials of Magnetic Effect of Current Class 12
Motion of a Charged Particle in a Magnetic Field
The motion of a charged particle when it is moving collinear with the field, the magnetic field is not affected by the field (i.e. if motion is just along or opposite to a magnetic field) ( $ \quad F=0$ ) Only the following two cases are possible:
The case I: When the charged particle is moving perpendicular to the field The angle between $\overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}}$ and $\overrightarrow{\mathrm{v}}$ is $\theta=90^{\circ}$
So the force will be maximum ( $=$ qvB ) and always perpendicular to motion (and also field);
Hence the charged particle will move along a circular path (with its plane perpendicular to the field).
Centripetal force is provided by the force qvB,

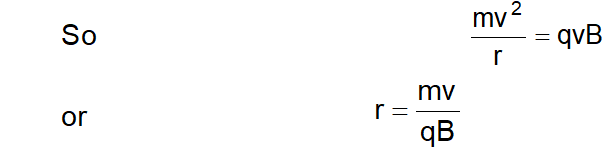
In case of the circular motion of a charged particle in a steady magnetic field :
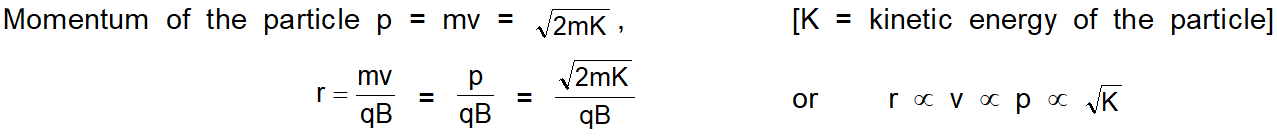
i.e., with the increase in speed or kinetic energy, the radius of the orbit increases. For uniform circular motion $v=\omega r$
Angular frequency of circular motion called cyclotron or gyro-frequency. $\omega=\frac{\mathrm{v}}{\mathrm{r}}=\frac{\mathrm{qB}}{\mathrm{m}}$
and the time period, $\quad \mathrm{T}=\frac{2 \pi}{\omega}=2 \pi \frac{\mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{qB}}$
i.e., time period (or frequency) is independent of speed of particle and radius of the orbit.
Time period depends only on the field B and the nature of the particle,
i.e., specific charge (q/m) of the particle.
This principle has been used in a large number of devices such as cyclotron (a particle accelerator), bubble-chamber (a particle detector) or mass-spectrometer etc.
the motion of a charged particle in an electric and magnetic field
case II : The charged particle is moving at an angle $\theta$ to the field :
$\left(\theta \neq 0^{\circ}, 90^{\circ} \text { or } 180^{\circ}\right)$
Resolving the velocity of the particle along and perpendicular to the field.
The particle moves with constant velocity v cos $\theta$ along the field ($\because$ no force acts on a charged particle when it moves parallel to the field).
And at the same time, it is also moving with velocity $v$ sin $\theta$ perpendicular to the field due to which it will describe a circle (in a plane perpendicular to the field)
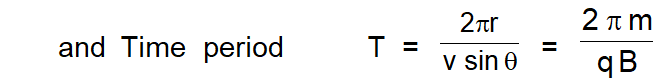

So the resultant path will be a helix with its axis parallel to the field $\overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}}$ as shown in fig. The pitch p of the helix $=$ linear distance travelled in one rotation
$p=T(v \cos \theta)=\frac{2 \pi m}{q B}(v \cos \theta)$
Also Read:
Biot Savart's Law
Click here for the Video tutorials of Magnetic Effect of Current Class 12
About eSaral At eSaral we are offering a complete platform for IIT-JEE & NEET preparation. The main mission behind eSaral is to provide education to each and every student in India by eliminating the Geographic and Economic factors, as a nation’s progress and development depends on the availability of quality education to each and every one. With the blend of education & technology, eSaral team made the learning personalized & adaptive for everyone.For free video lectures and complete study material, Download eSaral APP.
Comments
Click here to get exam-ready with eSaral
For making your preparation journey smoother of JEE, NEET and Class 8 to 10, grab our app now.
