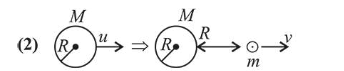
A satellite of mass m is launched vertically upwards with an initial speed u from the surface of the earth.
A satellite of mass $m$ is launched vertically upwards with an initial speed $u$ from the surface of the earth. After it reaches height $R$ ( $R=$ radius of the earth $)$, it
ejects a rocket of mass $\frac{m}{10}$ so that subsequently the
satellite moves in a circular orbit. The kinetic energy
of the rocket is ( $G$ is the gravitational constant; $M$ is the mass of the earth):
Correct Option: , 2
$\frac{1}{2} m u^{2}+\frac{-G M m}{R}=\frac{1}{2} m v^{2}+\frac{-G M m}{2 R}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{1}{2} m\left(v^{2}-u^{2}\right)=\frac{-G M m}{2 R}$
$\Rightarrow V=\sqrt{V=u^{2}-\frac{G M}{R}}$ ...(1)
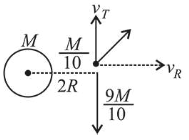
$v_{0}=\sqrt{\frac{G M}{2 R}}$ $\therefore v_{\text {rad }}=\frac{m \times v}{\left(\frac{m}{10}\right)}=10 v$
Ejecting a rocket of mass $\frac{m}{10}$
$\therefore \frac{9 m}{10} \times \sqrt{\frac{G M}{2 R}}=\frac{m}{10} \times v_{\tau} \Rightarrow V_{\tau}^{2}=81 \frac{G M}{2 R}$
Kinetic energy of rocket,
$\mathrm{KE}_{\text {rocket }}=\frac{1}{2} \frac{M}{10}\left(V_{T}^{2}+V_{r}^{2}\right)=\frac{1}{2} \times \frac{m}{10} \times\left(\left(u^{2}-\frac{G M}{R}\right) 100+81 \frac{G M}{R}\right)$
$=\frac{m}{20} \times 100\left(u^{2}-\frac{G M}{R}+\frac{81}{200} \frac{G M}{R}\right)$
$=5 m\left(u^{2}-\frac{119}{200} \frac{G M}{R}\right)$