Question:
A uniformly charged disc of radius $R$ having surface charge density $\sigma$ is placed in the xy plane with its center at the origin. Find the electric field intensity along the $\mathrm{Z}$-axis at a distance $\mathrm{Z}$ from origin :-
Correct Option: 1
Solution:
Consider a small ring of radius $\mathrm{r}$ and thickness $\mathrm{dr}$ on $\operatorname{disc} .$
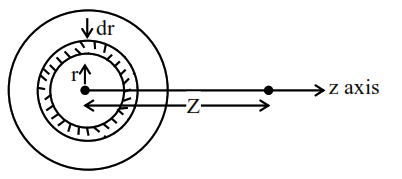
area of elemental ring on disc
$\mathrm{dA}=2 \pi \mathrm{rdr}$
charge on this ring $\mathrm{dq}=\sigma \mathrm{dA}$
$\mathrm{dEz}=\frac{\mathrm{kdqz}}{\left(\mathrm{z}^{2}+\mathrm{r}^{2}\right)^{3 / 2}}$
$\mathrm{E}=\int_{0}^{\mathrm{R}} \mathrm{dE}_{\mathrm{z}}=\frac{\sigma}{2 \in_{0}}\left[1-\frac{\mathrm{z}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{R}^{2}+\mathrm{z}^{2}}}\right]$
