Question:
An ideal battery of $4 \mathrm{~V}$ and resistance $\mathrm{R}$ are connected in series in the primary circuit of a potentionmeter of length $1 \mathrm{~m}$ and resistance $5 \Omega$. The value of $\mathrm{R}$, to give a potential difference of $5 \mathrm{mV}$ across $10 \mathrm{~cm}$ of potentiometer wire is:
Correct Option: , 3
Solution:
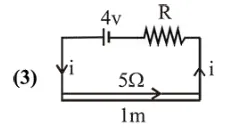
Current flowing through the circuit (I) is given by
$I=\left(\frac{4}{R+5}\right) A$
Resistance of length $10 \mathrm{~cm}$ of wire
$=5 \times \frac{10}{100}=0.5 \Omega$
According to question,
$5 \times 10^{-3}=\left(\frac{4}{R+5}\right) \cdot(0.5)$
$\therefore \frac{4}{\mathrm{R}+5}=10^{-2}$ or $\mathrm{R}+5=400 \Omega$
$\therefore \mathrm{R}=395 \Omega$
