Find the values of k for which the roots are real and equal in each of the following equations:
(i) $k x^{2}+4 x+1=0$
(ii) $k x^{2}-2 \sqrt{5} x+4=0$
(iii) $3 x^{2}-5 x+2 k=0$
(iv) $4 x^{2}+k x+9=0$
(v) $2 k x^{2}-40 x+25=0$
(vi) $9 x^{2}-24 x+k=0$
(vii) $4 x^{2}-3 k x+1=0$
(viii) $x^{2}-2(5+2 k) x+3(7+10 k)=0$
(ix) $(3 k+1) x^{2}+2(k+1) x+k=0$
(x) $k x^{2}+k x+1=-4 x^{2}-x$
(xi) $(k+1) x^{2}+2(k+3) x+(k+8)=0$
(xii) $x^{2}-2 k x+7 k-12=0$
(xiii) $(k+1) x^{2}-2(3 k+1) x+8 k+1=0$
(xiv) $(2 k+1) x^{2}+2(k+3) x+(k+5)=0$
(Xvii) $4 x^{2}-2(k+1) x+(k+4)=0$
(XViii) $x^{2}-2(k+1) x+k^{2}=0$
(xix) $k^{2} x^{2}-2(2 k-1) x+4=0$
(xx) $(k+1) x^{2}-2(k-1) x+1=0$
(xxi) $2 x^{2}+k x+3=0$
(xiii) $k x(x-2)+6=0$
(XXiv) $k x(x-2 \sqrt{5})+10=0$
(XXV) $p x(x-3)+9=0$
(xxvi) $4 x^{2}+p x+3=0$
(i) The given quadric equation is $k x^{2}+4 x+1=0$, and roots are real and equal
Then find the value of $k$.
Here, $a=k, b=4$ and, $c=1$
As we know that $D=b^{2}-4 a c$
Putting the value of $a=k, b=4$ and, $c=1$
$=(4)^{2}-4 \times k \times 1$
$=16-4 k$
The given equation will have real and equal roots, if $D=0$
Thus,
$16-4 k=0$
$4 k=16$
$k=4$
Therefore, the value of $k=4$
(ii) The given quadric equation is $k x^{2}-2 \sqrt{5} x+4=0$, and roots are real and equal
Then find the value of k.
Here, $a=k, b=-2 \sqrt{5}$ and, $c=4$
As we know that $D=b^{2}-4 a c$
Putting the value of $a=k, b=-2 \sqrt{5}$ and, $c=4$
$=(2 \sqrt{5})^{2}-4 \times k \times 4$
$=20-16 k$
The given equation will have real and equal roots, if D = 0
Thus,
Therefore, the value of $k=\frac{5}{4}$
(iii) The given quadric equation is $3 x^{2}-5 x+2 k=0$, and roots are real and equal
Then find the value of k.
Here, $a=3, b=-5$ and, $c=2 k$
As we know that $D=b^{2}-4 a c$
Putting the value of $a=3, b=-5$ and, $c=2 k$
$=(-5)^{2}-4 \times 3 \times k$
$=25-12 \mathrm{k}$
The given equation will have real and equal roots, if D = 0
Thus,
Therefore, the value of $k=\frac{25}{24}$
(iv) The given quadric equation is $4 x^{2}+k x+9=0$, and roots are real and equal Then find the value of $k$.
Here, $a=4, b=k$ and, $c=9$
As we know that $D=b^{2}-4 a c$
Putting the value of $a=4, b=k$ and, $c=9$
$=(k)^{2}-4 \times 4 \times 9$
$=k^{2}-144$
The given equation will have real and equal roots, if D = 0
Thus,
Therefore, the value of $k=\pm 12$
(v) The given quadric equation is $2 k x^{2}-40 x+25=0$, and roots are real and equal
Then find the value of k.
Here, $a=2 k, b=-40$ and, $c=25$
As we know that $D=b^{2}-4 a c$
Putting the value of $a=2 k, b=-40$ and,$c=25$
$=(-40)^{2}-4 \times 2 k \times 25$
$=1600-200 k$
The given equation will have real and equal roots, if D = 0
Thus,
$1600-200 k=0$
$200 k=1600$
$k=\frac{1600}{200}$
$=8$
Therefore, the value of $k=8$
(vi) The given quadric equation is $9 x^{2}-24 x+k=0$, and roots are real and equal
Then find the value of k.
Here, $a=9, b=-24$ and,$c=k$
As we know that $D=b^{2}-4 a c$
Putting the value of $a=9, b=-24$ and, $c=k$
$=(-24)^{2}-4 \times 9 \times k$
$=576-36 k$
The given equation will have real and equal roots, if D = 0
Thus,
Therefore, the value of $k=16$
(vii) The given quadric equation is $4 x^{2}-3 k x+1=0$, and roots are real and equal
Then find the value of $k$.
Here, $a=4, b=-3 k$ and,$c=1$
As we know that $D=b^{2}-4 a c$
Putting the value of $a=4, b=-3 k$ and, $c=1$
$=(-3 k)^{2}-4 \times 4 \times 1$
$=9 k^{2}-16$
The given equation will have real and equal roots, if D = 0
Thus,
$9 k^{2}-16=0$
$9 k^{2}=16$
$k=\sqrt{\frac{16}{9}}$
$=\pm \frac{4}{3}$
Therefore, the value of $k=\pm \frac{4}{3}$
(viii) The given quadric equation is $x^{2}-2(5+2 k) x+3(7+10 k)=0$, and roots are real and equal
Then find the value of k.
Here, $a=1, b=-2(5+2 k)$ and, $c=3(7+10 k)$
As we know that $D=b^{2}-4 a c$
Putting the value of $a=1, b=-2(5+2 k)$ and, $c=3(7+10 k)$
$=(-2(5+2 k))^{2}-4 \times 1 \times 3(7+10 k)$
$=4\left(25+20 k+4 k^{2}\right)-12(7+10 k)$
$=100+80 k+16 k^{2}-84-120 k$
$=16-40 k+16 k^{2}$
The given equation will have real and equal roots, if D = 0
Thus,
$16-40 k+16 k^{2}=0$
$8\left(2 k^{2}-5 k+2\right)=0$
$\left(2 k^{2}-5 k+2\right)=0$
Now factorizing of the above equation
$\left(2 k^{2}-5 k+2\right)=0$
$2 k^{2}-4 k-k+2=0$
$2 k(k-2)-1(k-2)=0$
$(k-2)(2 k-1)=0$
So, either
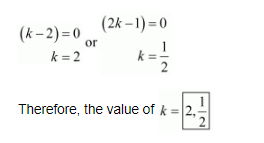
(ix) The given quadric equation is $(3 k+1) x^{2}+2(k+1) x+k=0$, and roots are real and equal
Then find the value of k.
Here, $a=(3 k+1), b=2(k+1)$ and,$c=k$
As we know that $D=b^{2}-4 a c$
Putting the value of $a=(3 k+1), b=2(k+1)$ and, $c=k$
$=(2(k+1))^{2}-4 \times(3 k+1) \times k$
$=4\left(k^{2}+2 k+1\right)-4 k(3 k+1)$
$=4 k^{2}+8 k+4-12 k^{2}-4 k$
$=-8 k^{2}+4 k+4$
The given equation will have real and equal roots, if D = 0
Thus,
$-8 k^{2}+4 k+4=0$
$-4\left(2 k^{2}-k-1\right)=0$
$\left(2 k^{2}-k-1\right)=0$
Now factorizing of the above equation
$\left(2 k^{2}-k-1\right)=0$
$2 k^{2}-2 k+k-1=0$
$2 k(k-1)+1(k-1)=0$
$(k-1)(2 k+1)=0$
So, either
$(k-1)=0$
$k=1$
or
$(2 k+1)=0$
$k=\frac{-1}{2}$
Therefore, the value of $k=1, \frac{-1}{2} \mid$
(x) The given quadric equation is $k x^{2}+k x+1=-4 x^{2}-x$, and roots are real and equal
Then find the value of $k$.
Here,
$k x^{2}+k x+1=-4 x^{2}-x$
$4 x^{2}+k x^{2}+k x+x+1=0$
$(4+k) x^{2}+(k+1) x+1=0$
So,
$a=(4+k), b=(k+1)$ and, $c=1$
As we know that $D=b^{2}-4 a c$
Putting the value of $a=(4+k), b=(k-1)$ and, $c=1$
$=(k+1)^{2}-4 \times(4+k) \times 1$
$=\left(k^{2}+2 k+1\right)-16-4 k$
$=k^{2}-2 k-15$
The given equation will have real and equal roots, if D = 0
Thus,
$k^{2}-2 k-15=0$
Now factorizing of the above equation
$k^{2}-2 k-15=0$
$k^{2}-5 k+3 k-15=0$
$k(k-5)+3(k-5)=0$
$(k-5)(k+3)=0$
So, either
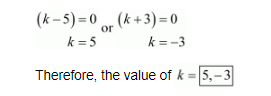
(xi) The given quadric equation is $(k+1) x^{2}+2(k+3) x+(k+8)=0$, and roots are real and equal
Then find the value of $k$.
Here,
$a=(k+1), b=2(k+3)$ and,$c=k+8$
As we know that $D=b^{2}-4 a c$
Putting the value of $a=(k+1), b=2(k+3)$ and, $c=k+8$
$=(2(k+3))^{2}-4 \times(k+1) \times(k+8)$
$=\left(4 k^{2}+24 k+36\right)-4\left(k^{2}+9 k+8\right)$
$=4 k^{2}+24 k+36-4 k^{2}-36 k-32$
$=-12 k+4$
The given equation will have real and equal roots, if D = 0
$-12 k+4=0$
$k=\frac{4}{12}$
$=\frac{1}{3}$
Therefore, the value of $k=\frac{1}{3}$
(xii) The given quadric equation is $x^{2}-2 k x+7 k-12=0$, and roots are real and equal
Then find the value of k.
Here,
$a=1, b=-2 k$ and,$c=7 k-12$
As we know that $D=b^{2}-4 a c$
Putting the value of $a=1, b=-2 k$ and, $c=7 k-12$
$=(-2 k)^{2}-4 \times 1 \times(7 k-12)$
$=4 k^{2}-28 k+48$
The given equation will have real and equal roots, if D = 0
$4 k^{2}-28 k+48=0$
$k^{2}-7 k+12=0$
Now factorizing of the above equation
$k^{2}-4 k-3 k+12=0$
$k(k-4)-3(k-4)=0$
$(k-4)(k-3)=0$
So, either
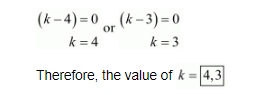
(xiii) The given quadric equation is $(k+1) x^{2}-2(3 k+1) x+8 k+1=0$, and roots are real and equal
Then find the value of $k$.
Here,
$a=k+1, b=-2(3 k+1)$ and, $c=8 k+1$
As we know that $D=b^{2}-4 a c$
Putting the value of $a=k+1, b=-2(3 k+1)$ and, $c=8 k+1$
$=(-2(3 k+1))^{2}-4 \times(k+1) \times(8 k+1)$
$=4\left(9 k^{2}+6 k+1\right)-4\left(8 k^{2}+9 k+1\right)$
$=36 k^{2}+24 k+4-32 k^{2}-36 k-4$
$=4 k^{2}-12 k$
The given equation will have real and equal roots, if D = 0
$4 k^{2}-12 k=0$
$k^{2}-3 k=0$
Now factorizing of the above equation
$k(k-3)=0$
So, either
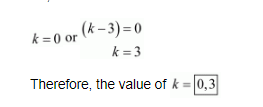
(xiv) The given quadric equation is $5 x^{2}-4 x+2+k\left(4 x^{2}-2 x-1\right)=0$, and roots are real and equal
Then find the value of $k$.
Here,
$5 x^{2}-4 x+2+k\left(4 x^{2}-2 x-1\right)=0$
$5 x^{2}-4 x+2+4 k x^{2}-2 k x-k=0$
$(5+4 k) x^{2}-(4+2 k) x+(2-k)=0$
So,
$a=(5+4 k), b=-(4+2 k)$ and, $c=(2-k)$
As we know that $D=b^{2}-4 a c$
Putting the value of $a=(5+4 k), b=-(4+2 k)$ and,$c=(2-k)$
$=\{-(4+2 k)\}^{2}-4 \times(5+4 k) \times(2-k)$
$=\left(16+16 k+4 k^{2}\right)-4\left(10+3 k-4 k^{2}\right)$
$=16+16 k+4 k^{2}-40-12 k+16 k^{2}$
$=20 k^{2}+4 k-24$
The given equation will have real and equal roots, if D = 0
Thus,
$20 k^{2}+4 k-24=0$
$4\left(5 k^{2}+k-6\right)=0$
$\left(5 k^{2}+k-6\right)=0$
Now factorizing of the above equation
$\left(5 k^{2}+k-6\right)=0$
$5 k^{2}+6 k-5 k-6=0$
$k(5 k+6)-1(5 k+6)=0$
$(5 k+6)(k-1)=0$
So, either
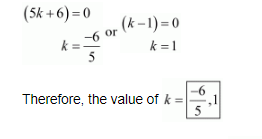
(xv) The given quadric equation is $(4-k) x^{2}+(2 k+4) x+8 k+1=0$, and roots are real and equal
Then find the value of $k$.
Here,
$a=4-k, b=(2 k+4)$ and,$c=8 k+1$
As we know that $D=b^{2}-4 a c$
Putting the value of $a=4-k, b=(2 k+4)$ and, $c=8 k+1$
$=(2 k+4)^{2}-4 \times(4-k) \times(8 k+1)$
$=\left(4 k^{2}+16 k+16\right)-4\left(-8 k^{2}+31 k+4\right)$
$=4 k^{2}+16 k+16+32 k^{2}-124 k-16$
$=36 k^{2}-108 k+0$
The given equation will have real and equal roots, if D = 0
$36 k^{2}-108 k+0=0$
$36\left(k^{2}-3 k\right)=0$
$\left(k^{2}-3 k\right)=0$
Now factorizing of the above equation
$k(k-3)=0$
So, either
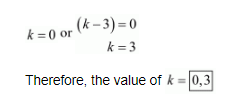
(xvi) The given quadric equation is $(2 k+1) x^{2}+2(k+3) x+k+5=0$, and roots are real and equal
Then find the value of $k$.
Here,
$a=(2 k+1), b=2(k+3)$ and,$c=k+5$
As we know that $D=b^{2}-4 a c$
Putting the value of $a=(2 k+1), b=2(k+3)$ and, $c=k+5$
$=\{2(k+3)\}^{2}-4 \times(2 k+1) \times(k+5)$
$=\left\{4\left(k^{2}+6 k+9\right)\right\}-4\left(2 k^{2}+11 k+5\right)$
$=4 k^{2}+24 k+36-8 k^{2}-44 k-20$
$=-4 k^{2}-20 k+16$
The given equation will have real and equal roots, if D = 0
$-4 k^{2}-20 k+16=0$
$-4\left(k^{2}+5 k-4\right)=0$
$\left(k^{2}+5 k-4\right)=0$
Now factorizing the above equation
$\left(k^{2}+5 k-4\right)=0$
$k=\frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^{2}-4 a c}}{2 a}$
$k=\frac{-5 \pm \sqrt{25+16}}{2}$
$k=\frac{-5 \pm \sqrt{41}}{2}$
So, either
Therefore, the value of $k=\frac{-5 \pm \sqrt{41}}{2}$
(xvii) The given quadric equation is $4 x^{2}-2(k+1) x+k+4=0$, and roots are real and equal
Then find the value of $k$.
Here,
$a=4, b=-2(k+1)$ and,$c=k+4$
As we know that $D=b^{2}-4 a c$
Putting the value of $a=4, b=-2(k+1)$ and, $c=k+4$
$=\{-2(k+1)\}^{2}-4 \times 4 \times(k+4)$
$=\left\{4\left(k^{2}+2 k+1\right)\right\}-16(k+4)$
$=4 k^{2}+8 k+4-16 k-64$
$=4 k^{2}-8 k-60$
The given equation will have real and equal roots, if D = 0
$4 k^{2}-8 k-60=0$
$4\left(k^{2}-2 k-15\right)=0$
$\left(k^{2}-2 k-15\right)=0$
Now factorizing of the above equation
$\left(k^{2}-2 k-15\right)=0$
$k^{2}+3 k-5 k-15=0$
$k(k+3)-5(k+3)=0$
$(k+3)(k-5)=0$
So, either
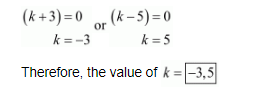
(xviii) The given quadric equation is $x^{2}-2(k+1) x+k^{2}=0$, and roots are real and equal
Then find the value of $k$.
Here,
$a=1, b=-2(k+1)$ and, $c=k^{2}$
As we know that $D=b^{2}-4 a c$
Putting the value of $a=1, b=-2(k+1)$ and, $c=k^{2}$
$=\{-2(k+1)\}^{2}-4 \times 1 \times k^{2}$
$=\left\{4\left(k^{2}+2 k+1\right)\right\}-4 k^{2}$
$=4 k^{2}+8 k+4-4 k^{2}$
$=8 k+4$
The given equation will have real and equal roots, if D = 0
$8 k+4=0$
$8 k=-4$
$k=\frac{-4}{8}$
$=\frac{-1}{2}$
Therefore, the value of $k=\frac{-1}{2}$
(xix) The given quadric equation is $k^{2} x^{2}-2(2 k-1) x+4=0$, and roots are real and equal
Then find the value of $k$.
Here,
$a=k^{2}, b=-2(2 k-1)$ and,$c=4$
As we know that $D=b^{2}-4 a c$
Putting the value of $a=k^{2}, b=-2(2 k-1)$ and, $c=4$
$=\{-2(2 k-1)\}^{2}-4 \times k^{2} \times 4$
$=\left\{4\left(4 k^{2}-4 k+1\right)\right\}-16 k^{2}$
$=16 k^{2}-16 k+4-16 k^{2}$
$=-16 k+4$
The given equation will have real and equal roots, if D = 0
$-16 k+4=0$
$16 k=4$
$k=\frac{4}{16}$
$=\frac{1}{4}$
Therefore, the value of $k=\frac{1}{4}$
$(\mathrm{xx})$ The given quadric equation is $(k+1) x^{2}-2(k-1) x+1=0$, and roots are real and equal Then find the value of $k$.
Here,
$a=k+1, b=-2(k-1)$ and,$c=1$
As we know that $D=b^{2}-4 a c$
Putting the value of $a=k+1, b=-2(k-1)$ and, $c=1$
$=\{-2(k-1)\}^{2}-4 \times(k+1) \times 1$
$=\left\{4\left(k^{2}-2 k+1\right)\right\}-4 k-4$
$=4 k^{2}-8 k+4-4 k-4$
$=4 k^{2}-12 k+0$
The given equation will have real and equal roots, if D = 0
$4 k^{2}-12 k+0=0$
$4 k^{2}-12 k=0$
Now factorizing of the above equation
$4 k(k-3)=0$
$k(k-3)=0$
So, either
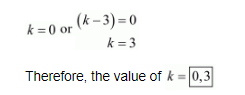
(xxi) The given quadric equation is $2 x^{2}+k x+3=0$, and roots are real and lequal
Then find the value of $k$.
Here,
$a=2, b=k$ and,$c=3$
As we know that $D=b^{2}-4 a c$
Putting the value of $a=2, b=k$ and, $c=3$
$=k^{2}-4 \times 2 \times 3$
$=k^{2}-24$
The given equation will have real and equal roots, if D = 0
$k^{2}-24=0$
$k^{2}=24$
$k=\sqrt{24}$
$=\sqrt{4 \times 6}$
$-+2 \sqrt{6}$
Therefore, the value of $k=\pm 2 \sqrt{6}$
(xxii) The given quadric equation is $k x(x-2)+6=0$, and roots are real and equal
Then find the value of $k$.
Here,
$k x(x-2)+6=0$
$k x^{2}-2 k x+6=0$
So,
$a=k, b=-2 k$ and,$c=6$
As we know that $D=b^{2}-4 a c$
Putting the value of $a=k, b=-2 k$ and, $c=6$
$=(-2 k)^{2}-4 \times k \times 6$
$=4 k^{2}-24 k$
The given equation will have real and equal roots, if D = 0
$4 k^{2}-24 k=0$
Now factorizing of the above equation
$4 k(k-6)=0$
$k(k-6)=0$
So, either
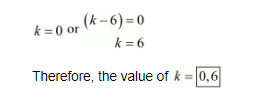
(xxiii) The given quadratic equation is $x^{2}-4 k x+k=0$, and roots are real and equal.
Then find the value of $k$.
Here,
$x^{2}-4 k x+k=0$
So,
$a=1, b=-4 k$ and $c=k$
As we know that $D=b^{2}-4 a c$
Putting the value of $a=1, b=-4 k$ and $c=k$.
$D=(-4 k)^{2}-4(1)(k)$
$=16 k^{2}-4 k$
The given equation will have real and equal roots, if D = 0.
So, $16 k^{2}-4 k=0$
Now factorizing the above equation,
$16 k^{2}-4 k=0$
$\Rightarrow 4 k(4 k-1)=0$
$\Rightarrow 4 k=0$ or $4 k-1=0$
$\Rightarrow k=0$ or $k=\frac{1}{4}$
Therefore, the value of $k=0, \frac{1}{4}$.
(xxiv) The given quadratic equation is $k x(x-2 \sqrt{5})+10=0$, and roots are real and equal.
Then find the value of $k$.
Here,
$k x(x-2 \sqrt{5})+10=0$
$\Rightarrow k x^{2}-2 \sqrt{5} k x+10=0$
So,
$a=k, b=-2 \sqrt{5} k$ and $c=10$
As we know that $D=b^{2}-4 a c$
Putting the value of $a=k, b=-2 \sqrt{5} k$ and $c=10$.
$D=(-2 \sqrt{5} k)^{2}-4(k)(10)$
$=20 k^{2}-40 k$
The given equation will have real and equal roots, if D = 0.
So, $20 k^{2}-40 k=0$
Now factorizing the above equation,
$20 k^{2}-40 k=0$
$\Rightarrow 20 k(k-2)=0$
$\Rightarrow 20 k=0$ or $k-2=0$
$\Rightarrow k=0$ or $k=2$
Therefore, the value of $k=0,2$.
(xxv) The given quadratic equation is $p x(x-3)+9=0$, and roots are real and equal.
Then find the value of $p$.
Here,
$p x(x-3)+9=0$
$\Rightarrow p x^{2}-3 p x+9=0$
So,
$a=p, b=-3 p$ and $c=9$
As we know that $D=b^{2}-4 a c$
Putting the value of $a=p, b=-3 p$ and $c=9$.
$D=(-3 p)^{2}-4(p)(9)$
$=9 p^{2}-36 p$
The given equation will have real and equal roots, if D = 0.
So, $9 p^{2}-36 p=0$
Now factorizing the above equation,
$9 p^{2}-36 p=0$
$\Rightarrow 9 p(p-4)=0$
$\Rightarrow 9 p=0$ or $p-4=0$
$\Rightarrow p=0$ or $p=4$
Therefore, the value of
( $\mathrm{xxvi)}$ The given quadratic equation is $4 x^{2}+p x+3=0$, and roots are real and equal.
Then find the value of $p$.
The given equation will have real and equal roots, if D = 0.
So, $p^{2}-48=0$
Now factorizing the above equation,
$p^{2}-48=0$
$\Rightarrow p^{2}-(4 \sqrt{3})^{2}=0$
$\Rightarrow(p-4 \sqrt{3})(p+4 \sqrt{3})=0$
$\Rightarrow p-4 \sqrt{3}=0$ or $p+4 \sqrt{3}=0$
$\Rightarrow p=4 \sqrt{3}$ or $p=-4 \sqrt{3}$
Therefore, the value of $p=\pm 4 \sqrt{3}$.
