If A(0, 0), b(2, 4) and C(6, 4) are the vertices of a ΔABC, find the equations of its sides.
Using two point form equation of lines AB, BC and AC can be find. Now A is origin so the lines passing through A (origin) are simply y = mx so we have to find slope of AB and AC.
For line AB,
$m=\frac{y_{2}-y_{1}}{x_{2}-x_{1}} \Rightarrow \frac{4-0}{2-0}=\frac{4}{2}$
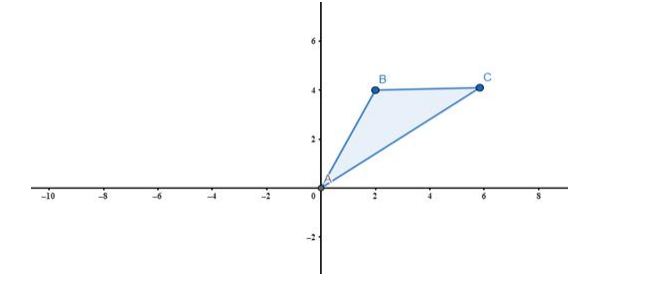
$m=2$
So, the equation of line $A B$ is $y=2 x$.
For line $A C$,
$\mathrm{m}=\frac{\mathrm{y}_{2}-\mathrm{y}_{1}}{\mathrm{x}_{2}-\mathrm{x}_{1}} \Rightarrow \frac{4-0}{6-0}=\frac{4}{6}$
$\mathrm{m}=\frac{2}{3}$
Now using y = mx
$y=\frac{2}{3} x \Rightarrow 2 x-3 y=0$
So, the equation of line AC is 2x - 3y = 0
Now for line BC, the y coordinate of both is same means horizontal line (parallel to the x - axis) then the equation of line BC is given as
y = 4
So, the required equations of lines for AB: y = 2x
AC: 2x - 3y = 0
BC: y = 4
