If $x^{2}+k(4 x+k-1)+2=0$ has equal roots, then $\mathrm{k}=$
(a) $-\frac{2}{3}, 1$
(b) $\frac{2}{3},-1$
(c) $\frac{3}{2}, \frac{1}{3}$
(d) $-\frac{3}{2},-\frac{1}{3}$
The given quadric equation is $x^{2}+k(4 x+k-1)+2=0$, and roots are equal
Then find the value of k.
$x^{2}+k(4 x+k-1)+2=0$
$x^{2}+4 k x+\left(k^{2}-k+2\right)=0$
Here, $a=1, b=4 k$ and, $c=k^{2}-k+2$
As we know that $D=b^{2}-4 a c$
Putting the value of $a=1, b=4 k$ and, $c=k^{2}-k+2$
$=(4 k)^{2}-4 \times 1 \times\left(k^{2}-k+2\right)$
$=16 k^{2}-4 k^{2}+4 k-8$
$=12 k^{2}+4 k-8$
$=4\left(3 k^{2}+k-2\right)$
The given equation will have real and distinct roots, if $D=0$
$4\left(3 k^{2}+k-2\right)=0$
$3 k^{2}+k-2=0$
$3 k^{2}+3 k-2 k-2=0$
$3 k(k+1)-2(k+1)=0$
$(k+1)(3 k-2)=0$
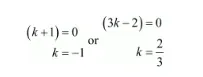
Therefore, the value of $k=\frac{2}{3} ;-1$
Thus, the correct answer is (b)
