In the given figure, O is a point in the interior of square ABCD such that ΔOAB is an equilateral triangle.
In the given figure, O is a point in the interior of square ABCD such that ΔOAB is an equilateral triangle. Show that ΔOCD is an isosceles triangle.
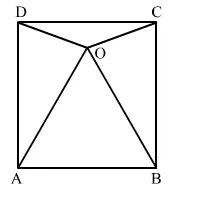
Given: In square ABCD, ΔOAB is an equilateral triangle.
To prove: ΔOCD is an isosceles triangle.
Proof:
$\because \angle D A B=\angle C B A=90^{\circ} \quad$ (Angles of square $A B C D$ )
And, $\angle O A B=O B A=60^{\circ}$ (Angles of equilateral $\triangle O A B$ )
$\therefore \angle D A B-\angle O A B=\angle C B A-\angle O B A=90^{\circ}-60^{\circ}$
$\Rightarrow \angle O A D=\angle O B C=30^{\circ} \quad \ldots \ldots$ (i)
Now, in ΔDAO and ΔCBO,
AD = BC (Sides of square ABCD)
AO = BO (Sides of equilateral ΔOAB)
ΔDAO
So, OD = OC (CPCT)
Hence, ΔOCD is an isosceles triangle.
