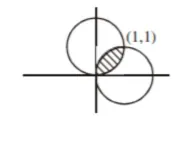
Let $C_{1}$ be the curve obtained by the solution of differential equation $2 x y \frac{d y}{d x}=y^{2}-x^{2}, x>0 \&$ Let the curve $C_{2}$ be the solution of $\frac{2 x y}{x^{2}-y^{2}}=\frac{d y}{d x}$
If both the curves pass through $(1,1)$, then the area enclosed by the curves $C_{1}$ and $\mathrm{C}_{2}$ is equal to :
Correct Option: , 2
$\frac{d y}{d x}=\frac{y^{2}-x^{2}}{2 x y}, \quad x \in(0, \infty)$
put $y=v x$
$\mathrm{x} \frac{\mathrm{dv}}{\mathrm{dx}}+\mathrm{v}=\frac{\mathrm{v}^{-}-1}{2 \mathrm{v}}$
$\frac{2 v}{v^{2}+1} d v=-\frac{d x}{x}$
Integrate,
$\ln \left(v^{2}+1\right)=-\ln x+C$
$\ln \left(\frac{y^{2}}{x^{2}}+1\right)=-\ln x+C$
put $x=1, y=1, C=\ln 2$
$\ln \left(\frac{y^{2}}{x^{2}}+1\right)=-\ln x+\ln 2$
$\Rightarrow x^{2}+y^{2}-2 x=0 \quad\left(\right.$ Curve $\left.C_{1}\right)$
Similarly,
$\frac{d y}{d x}=\frac{2 x y}{x^{2}-y^{2}}$
Put $y=v x$
$x^{2}+y^{2}-2 y=0$