P (a, b) is the mid-point of a line segment between axes. Show that equation of the line is $\frac{x}{a}+\frac{y}{b}=2$
Let AB be the line segment between the axes and let P (a, b) be its mid-point.
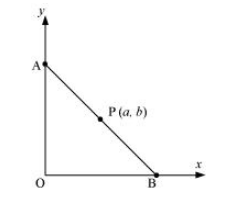
Let the coordinates of A and B be (0, y) and (x, 0) respectively.
Since P (a, b) is the mid-point of AB,
$\left(\frac{0+x}{2}, \frac{y+0}{2}\right)=(a, b)$
$\Rightarrow\left(\frac{x}{2}, \frac{y}{2}\right)=(a, b)$
$\Rightarrow \frac{x}{2}=a$ and $\frac{y}{2}=b$
$\therefore x=2 a$ and $y=2 b$
Thus, the respective coordinates of A and B are (0, 2b) and (2a, 0).
The equation of the line passing through points (0, 2b) and (2a, 0) is
$(y-2 b)=\frac{(0-2 b)}{(2 a-0)}(x-0)$
$y-2 b=\frac{-2 b}{2 a}(x)$
$a(y-2 b)=-b x$
i.e., $b x+a y=2 a b$
On dividing both sides by ab, we obtain
$\frac{b x}{a b}+\frac{a y}{a b}=\frac{2 a b}{a b}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{x}{a}+\frac{y}{b}=2$
Thus, the equation of the line is $\frac{x}{a}+\frac{y}{b}=2$.
Click here to get exam-ready with eSaral
For making your preparation journey smoother of JEE, NEET and Class 8 to 10, grab our app now.
