Prove that:
$\cos ^{-1} \frac{4}{5}+\sin ^{-1} \frac{3}{5}=\sin ^{-1} \frac{27}{11}$
To Prove: $\cos ^{-1} \frac{4}{5}+\sin ^{-1} \frac{3}{5}=\sin ^{-1} \frac{27}{11}$
Formula Used: $\sin ^{-1} x+\sin ^{-1} y=\sin ^{-1}\left(x \times \sqrt{1-y^{2}}+y \times \sqrt{1-x^{2}}\right)$
Proof:
$\mathrm{LHS}=\cos ^{-1} \frac{4}{5}+\sin ^{-1} \frac{3}{5} \ldots(1)$
Let $\cos \theta=\frac{4}{5}$
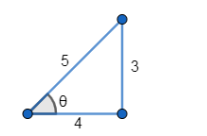
Therefore $\theta=\cos ^{-1} \frac{4}{5} \ldots$ (2)
From the figure, $\sin \theta=\frac{3}{5}$
$\Rightarrow \theta=\sin ^{-1} \frac{3}{5} \ldots$ (3)
From (2) and (3),
$\cos ^{-1} \frac{4}{5}=\sin ^{-1} \frac{3}{5}$
Substituting in (1), we get
$\mathrm{LHS}=\sin ^{-1} \frac{3}{5}+\sin ^{-1} \frac{3}{5}$
$=\sin ^{-1}\left(2 \times \frac{3}{5} \times \sqrt{1-\left(\frac{3}{5}\right)^{2}}\right)$
$=\sin ^{-1}\left(2 \times \frac{3}{5} \times \sqrt{1-\frac{9}{25}}\right)$
$=\sin ^{-1}\left(2 \times \frac{3}{5} \times \sqrt{\frac{16}{25}}\right)$
$=\sin ^{-1}\left(2 \times \frac{3}{5} \times \frac{4}{5}\right)$
$=\sin ^{-1} \frac{24}{25}$
