A block of mass Mis kept on a rough horizontal surface. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the surface is $p$. The block is to be pulled by applying a force to it. What minimum force is needed to slide the block? In which direction should this force act?
Let minimum force required be $\mathrm{P}$ at an angle $\theta$.
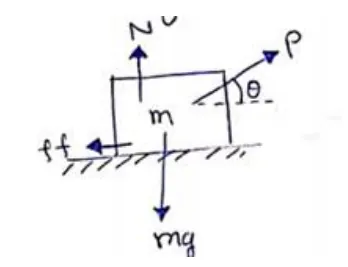
$N+P \sin \theta=m g$ (vertical equilibrium) -(i)
$P \cos \theta=\mu N$ (Body is about to move) -(ii)
From (i)
$P \cos \theta=\mu(m g-P \sin \theta)$
$P=\frac{\mu m g}{\cos \theta+\mu \sin \theta}$
To minimize $\mathrm{P}$, we have to maximize $y=\cos \theta+\mu \sin \theta$
$\frac{d y}{d \theta}=\frac{d}{d \theta}(\cos \theta+\mu \sin \theta)$
$\frac{d y}{d \theta}=-\sin \theta+\mu \cos \theta=0$
$\tan \theta=\mu$
$\theta=\tan ^{-1} \mu$
Maximum value of
$y=\frac{1}{\sqrt{\mu^{2}+1}}+\mu \cdot \frac{\mu}{\sqrt{\mu^{2}+1}}$
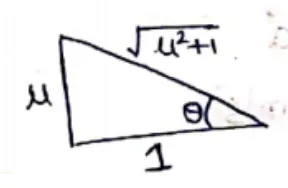
$y_{\max }=\sqrt{1+\mu^{2}}$
Put in (3)
$P_{\min }=\frac{\mu m g}{\sqrt{1+\mu^{2}}}$ at $\theta=\tan ^{-1} \mu$
