Figure shows a small block of mass $\mathrm{m}$ kept at the left end of a larger block of mass Mand length I. The system can slide on a horizontal road. The system is started towards right with an initial velocity v. The friction coefficient between the road and the bigger block is $\mu$ and that between the block is $\mu / 2$. Find the time elapsed before the smaller blocks separates from the bigger block.
Initial velocity of both blocks is same. So, $U_{r e l}=0$
When $\mathrm{m}$ separates from M. $S_{r e l}=l$
Let $a_{m}$ and $a_{M}$ be the acceleration of the blocks $m$ and $M$ respectively with respect to ground.
Here, $a_{m}{ }^{a_{M}}$ as both blocks separates from each other.
So, $a_{r e l}=a_{m}-a_{M}$
$S_{r e l}=U_{r e l} t+\frac{1}{2} a_{r e l} t^{2}$
$l=0+\frac{1}{2}\left(a_{m}-a_{M}\right) t^{2}$
$t=\sqrt{\frac{2 l}{\left(a_{m}-a_{M}\right.}}-(\mathrm{i})$
Now, FBD of mass $m$
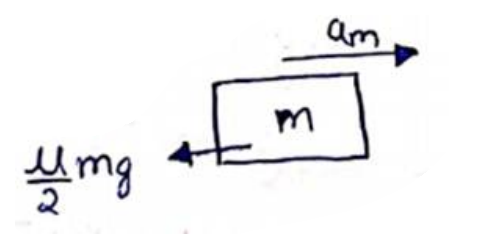
$F_{N}=$ mass $\times$ acceleration
$m a_{m}=0-\frac{\mu}{2} m g$
$a_{m}=\frac{-\mu g}{2}$
FBD of mass $M$
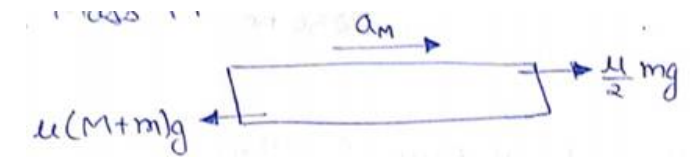
$M a_{M}=\frac{\mu}{2} m g-\mu(M+m) g$
$a_{M}=-\mu g-\frac{\mu m g}{2 M}$
Subtract (ii) and (iii)
$a_{m}-a_{M}=\frac{\mu g}{2}+\frac{\mu m g}{2 M}$
Put in e.q. (i)
$t=\sqrt{\frac{4 M l}{(M+m) \mu g}}$
