A body of mass $m$ makes an elastic collision with another identical body at rest. Show that if the collision is not head-on, the bodies go right angle to each other after the collision.
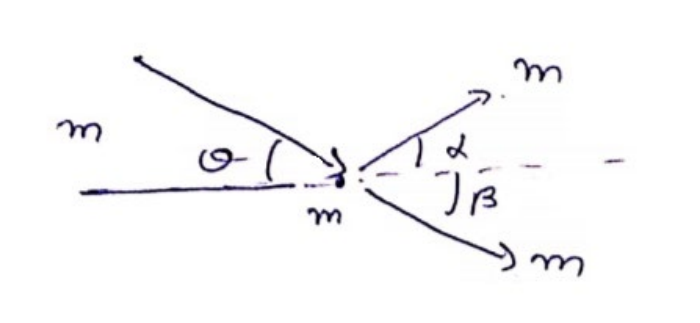
If $m$ is not colliding head-on, along $x$-axis, use C.O.L.M $m v \cos \theta=m\left(v_{1} \cos \alpha+v_{2} \cos \beta\right)-(1)$
Along y-axis, $-m v \sin \theta=m\left(v_{1} \sin \alpha-v_{2} \sin \beta\right)-(2)$
Use C.O.E.L
$\frac{1}{2} m v^{2}=\frac{1}{2} m\left(v_{1}^{2}+v_{2}^{2}\right)$
Squaring (1) and (2) and add them,
$v^{2}=v_{1}^{2}\left(\cos ^{2} \alpha+\sin ^{2} \alpha\right)+v_{2}^{2}\left(\cos ^{2} \beta+\sin ^{2} \beta\right)+2 v_{1} v_{2}(\cos \alpha \cos \beta-\sin \alpha \sin \beta)$
$v^{2}=v_{1}^{2}+v_{2}^{2}+2 v_{1} v_{2} \cos (\alpha+\beta)$
$\cos (\alpha+\beta)=0=\pi / 2$
$\therefore \alpha+\beta=\pi / 2$
