A block of mass $\mathrm{m}$ is placed on a triangular block of mass $M$, which in turn is placed on a horizontal surface as shown in figure. Assuming frictionless surfaces between the velocities of the triangular block when the smaller block reaches the bottom end.
Along x-direction ${ }^{a_{C O M}}=0$
$\Rightarrow \frac{m a_{x}-(M+m)\left(a_{2}\right)}{(M+m+m)}=0$
$\Rightarrow a_{2}=\frac{m a_{x}}{m+M}$
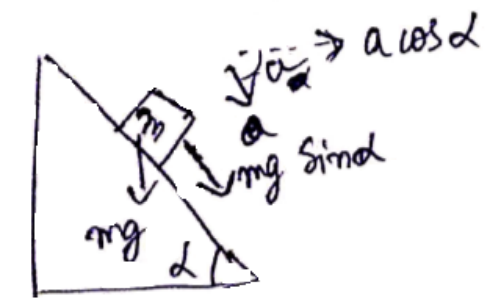
$m a=m g \sin \alpha$
$a_{x}=a \cos \alpha=g \sin \alpha \cos \alpha$
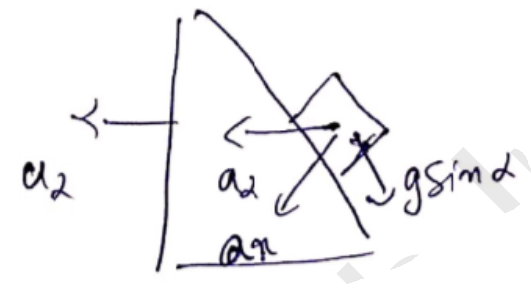
$a_{r}=$ resultant $=g \sin \alpha-a_{\alpha} \sin \alpha$
$=g \sin \alpha\left[\frac{M+m \sin ^{2} \alpha}{M+m}\right]$
Vertical distance travelled by $\frac{h}{\mathrm{~m}=\sin \alpha}=y$
Use law of kinematics,
$t=\sqrt{\frac{2 y}{a_{r}}}=\sqrt{\frac{2 h}{a_{r} \sin \alpha}}$
$\{$ velocity of $M$ block $\}$
$=\frac{m g \cos \alpha}{M+m} \sqrt{\frac{2 h \sin \alpha[M+m]}{g \sin \alpha \cdot\left[M+m \sin ^{2} \alpha\right]}}$
$=\sqrt{\frac{2 m^{2} g^{2} h \cos ^{2} \alpha}{(M+m)\left(M+m \sin ^{2} \alpha\right)}}$
