The friction coefficient between a road and the type of a vehicle is $4 / 3$. Find the maximum incline the road may have so that once hard brakes are applied and the wheel starts skidding, the vehicle going down at a speed of $36 \mathrm{~km} / \mathrm{hr}$ is stopped within $5 \mathrm{~m}$.
$u=36 \times \frac{5}{18}=10 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$
$v=0 ; s=5 \mathrm{~m}$
$v^{2}=u^{2}+2 a s$
$0^{2}=(10)^{2}+2(a)(5)$
$a=-10 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}^{2}$
Now, by translatory motion equation
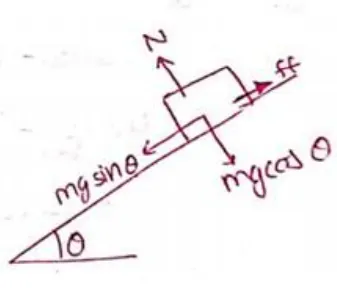
$m g \sin \theta-f f=m a$
$m g \sin \theta-\mu N=m a$
$m g \sin \theta-\mu m g \cos \theta=m a$
$10 \sin \theta-\frac{4}{3} \times 10 \times \cos \theta=(-10)$
$\sin \theta+1=\frac{4}{3} \sqrt{1-\sin ^{2} \theta}$
Squaring
$9(1+\sin \theta)^{2}=16\left(1-\sin ^{2} \theta\right)$
$9\left(1+\sin ^{2} \theta+2 \sin \theta\right)=16-16 \sin ^{2} \theta$
$25 \sin ^{2} \theta+18 \sin \theta-7=0$
On solving,
$\theta=16^{\circ}$
