A uniform rod of length $L$ lies on a smooth horizontal table. A particle moving on a table strikes the rod perpendicularly at an end and stops. Find the distance travelled by the centre of the rod by the time it turns through a right angle. Show that if the mass of the rod is four times that of the particle, the collision is elastic.
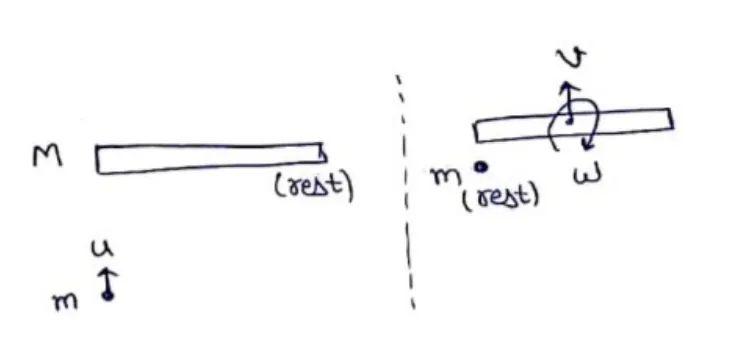
Momentum conservation
$P_{i}=P_{f}$
$m u+0=m(0)+M(v)$
$\mathrm{V}=\frac{\operatorname{mu}}{M}$
Angular Momentum conservation $L_{i}=L_{f}$
$0+m u\left(\frac{\Sigma}{2}\right)=\left(\frac{M L^{2}}{12}\right) \omega+0$
$\omega=\frac{6 m u}{M L}$
Time to rotate by $90^{\circ}$
$\omega=\frac{\theta}{t}$
$t=\frac{(\pi / 2)}{\left(\frac{6 m u}{M L}\right)}$
$\mathrm{t}=\frac{\pi M L}{12 \mathrm{mu}}$
distance travelled by rod
distance $=$ speed $x$ time
$=\left(\frac{m U}{M}\right) \times\left(\frac{\pi M L}{12 m u}\right)$
$\mathrm{S}=\frac{\pi L}{12}$
Now, if $\mathrm{M}=4 \mathrm{~m}$ then
$K E_{i}=\frac{1}{2} m u^{2}$
$K E_{f}=\frac{1}{2} M v^{2}+\frac{1}{2} I \omega^{2}$
$\frac{1}{2}(4 m)\left(\frac{m u}{4 m}\right)^{2}+\frac{1}{2}\left(\frac{M L^{2}}{12}\right)\left(\frac{6 m u}{M L}\right)^{2}$
$K E_{f}=\frac{1}{2} m u^{2}$
Hence proved.
