Four particles of equal masses $M$ move along a circle of radius $R$ under the action of their mutual gravitational attraction. Find the speed of each particle.
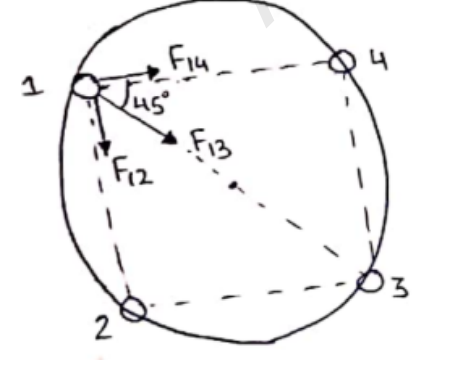
Here, $\mathrm{r}_{13}=2 \mathrm{R}$
$r_{14}=2 R \cos 45=\sqrt{2} R$
$r_{12}=2 R \sin 45=\sqrt{2} R$
Now, force on particle 1
Due to particle 4: $\mathrm{F}_{14}=\frac{\mathrm{GMM}}{(\sqrt{2} \mathrm{R})^{2}}=\frac{\mathrm{GM}^{2}}{2 \mathrm{R}^{2}}$
Due to particle 2: $\mathrm{F}_{12}=\frac{\mathrm{GMM}}{(\sqrt{2} \mathrm{R})^{\mathrm{2}}}=\frac{\mathrm{GM}^{2}}{2 \mathrm{R}^{2}}$
Due to particle 1: $F_{13}=\frac{\text { GMM }}{(2 R)^{2}}=\frac{G^{2}}{4 R^{2}}$
Resultant of $\mathrm{F}_{14} \& \mathrm{~F}_{12}=\sqrt{\mathrm{F}_{12}^{2}+\mathrm{F}_{14}^{2}+2\left(\mathrm{~F}_{12}\right)\left(\mathrm{F}_{14}\right) \cos 90^{\circ}}$
$=\sqrt{\left(\frac{\mathrm{GM}^{2}}{2 \mathrm{R}^{2}}\right)^{2}+\left(\frac{\mathrm{GM}^{2}}{2 \mathrm{R}^{2}}\right)^{2}}$
$\mathrm{F}_{\mathrm{R}}=\frac{\mathrm{GM}^{2}}{\sqrt{2} \mathrm{R}^{2}}$ (along $\mathrm{r}_{13}$ direction)
Net resultant force, $\mathrm{F}_{\mathrm{N}}=\mathrm{F}_{\mathrm{R}}+\mathrm{F}_{\mathrm{B}}$
Since particle is revolving in a circle. So, this is centripetal force.
$\mathrm{F}_{\mathrm{N}}=\frac{\mathrm{Mv}^{2}}{\mathrm{R}}$
$\frac{\mathrm{GM}^{2}}{4 \mathrm{R}^{2}}=\frac{\mathrm{Mv}^{2}}{\mathrm{R}}$
$\mathrm{v}=\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{GM}}{\mathrm{R}}\left(\frac{2 \sqrt{2}+1}{4}\right)}$
