Show that A(3, 2), B(0, 5), C(-3, 2) and D(0, -1) are the vertices of a square.
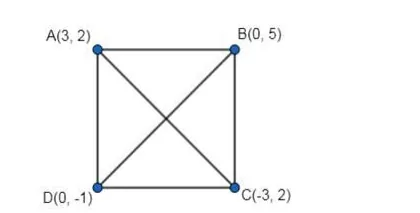
Given: The points are $A(3,2), B(0,5), C(-3,2)$ and $D(0,-1)$.
Note: For a quadrilateral to be a square, all the sides of the quadrilateral must be equal in length and the diagonals must be equal in length as well.
$A B=\sqrt{(0-3)^{2}+(5-2)^{2}}=\sqrt{9+9}$
$=3 \sqrt{2}$ units
$B C=\sqrt{(-3-0)^{2}+(2-5)^{2}}=\sqrt{9+9}$
$=3 \sqrt{2}$ units
$D A=\sqrt{(3-0)^{2}+(2+1)^{2}}=\sqrt{9+9}$
$=3 \sqrt{2}$ units
Therefore, AB = BC = CD = DA …..(1)
$A C=\sqrt{(-3-3)^{2}+(2-2)^{2}}$
$=6$ units
$B D=\sqrt{(0-0)^{2}+(-1-5)^{2}}$
$=6$ units
Therefore, $A C=B D \ldots .(2)$
From 1 and 2, we have all the sides of ABCD are equal and the diagonals are equal in length as well.
Therefore, $\mathrm{ABCD}$ is a square.
Hence, the points $A, B, C$ and $D$ are the vertices of a square.
