The hypotenuse of a right angled triangle has its ends at the points (1, 3) and (−4, 1). Find the equation of the legs (perpendicular sides) of the triangle.
Let A(1,3) and B(−4,1) be the coordinates of the end points of the hypotenuse.
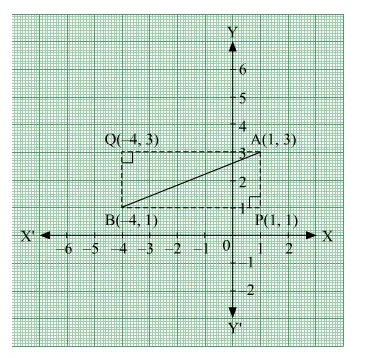
Now, plotting the line segment joining the points A(1,3) and B(−4,1) on the coordinate plane, we will get two right triangles with AB as the hypotenuse. Now from the diagram, it is clear that the point of intersection of the other two legs of the right triangle having AB as the hypotenuse can be either P or Q.
CASE 1: When ∆ APB is taken.
The perpendicular sides in ∆ APB are AP and PB.
Now, side PB is parallel to x-axis and at a distance of 1 units above x-axis.
So, equation of PB is, y=1 or y−1=0.
The side AP is parallel to y-axis and at a distance of 1 units on the right of y-axis.
So, equation of AP is x=1 or x−1=0.
CASE 2: When ∆ AQB is taken.
The perpendicular sides in ∆ AQB are AQ and QB.
Now, side AQ is parallel to x-axis and at a distance of 3 units above x-axis.
So, equation of AQ is, y=3 or y−3=0.
The side QB is parallel to y-axis and at a distance of 4 units on the left of y-axis.
So, equation of QB is x=−4 or x+4=0.
Hence, the equation of the legs are :
x=1, y=1 or x=−4, y=3
