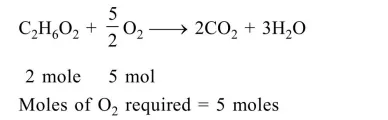Question:
The ratio of the mass percentages of ' $\mathrm{C} \& \mathrm{H}^{\prime}$ and ' $\mathrm{C} \& \mathrm{O}^{\prime}$ of a saturated acyclic
organic compound ' $\mathrm{X}$ ' are $4: 1$ and $3: 4$ respectively. Then, the moles of oxygen gas required for complete combustion of two moles of
organic compound ' $X$ ' is
Solution:
$\mathrm{C}: \mathrm{H}=4: 1$
$\mathrm{C}: \mathrm{O}=3: 4$
Mass ratio
$\mathrm{C}: \mathrm{H}: \mathrm{O}=12: 3: 16$
Mole ratio
$\mathrm{C}: \mathrm{H}: \mathrm{O}=1: 3: 1$
Empirical formula $=\mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{O}$
Molecular formula $=\mathrm{C}_{2} \mathrm{H}_{6} \mathrm{O}_{2}$
(saturated acyclic organic compound)