Two ions of masses 4 amu and 16 amu have charges $+2 \mathrm{e}$ and $+3 \mathrm{e}$ respectively. These ions pass through the region of constant perpendicular magnetic field. The kinetic energy of both ions is same. Then :
Correct Option: , 2
$\mathrm{r}=\frac{\mathrm{P}}{\mathrm{qB}}=\frac{\sqrt{2 \mathrm{mk}}}{\mathrm{qB}}$
Given they have same kinetic energy
$r \propto \frac{\sqrt{m}}{q}$
$\frac{r_{1}}{r_{2}}=\frac{\sqrt{4}}{2} \times \frac{3}{\sqrt{16}}=\frac{3}{4}$
$\mathrm{r}_{2}=\frac{4 \mathrm{r}_{1}}{3}$( $r_{2}$ is for hearier ion and $r_{1}$ is for lighter ion)
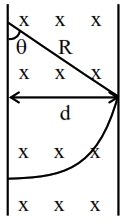
$\sin \theta=\frac{d}{R}$
$\theta \rightarrow$ Deflection
$\theta \propto \frac{1}{\mathrm{R}}$
$(\mathrm{R} \rightarrow$ Radius of path $)$
$\because \mathrm{R}_{2}>\mathrm{R}_{1} \Rightarrow \theta_{2}<\theta_{1}$
Click here to get exam-ready with eSaral
For making your preparation journey smoother of JEE, NEET and Class 8 to 10, grab our app now.
