Two narrow bores of diameter $5.0 \mathrm{~mm}$ and $8.0 \mathrm{~mm}$ are joined together to form a U-shaped tube open at both ends. If this U-tube contains water, what is the difference in the level of two limbs of the tube. [Take surface tension of water $\mathrm{T}=7.3 \times 10^{-2} \mathrm{Nm}^{-1}$, angle of contact $=0, \mathrm{~g}=10 \mathrm{~ms}^{-2}$ and density of water $=1.0 \times 10^{3} \mathrm{~kg} \mathrm{~m}^{-3}$ ]
Correct Option: , 2
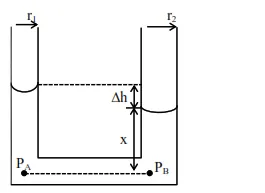
We have $\mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{A}}=\mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{B}}$. [Points $\mathrm{A} \& \mathrm{~B}$ at same horizontal level]
$\therefore \mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{atmm}}-\frac{2 \mathrm{~T}}{\mathrm{r}_{1}}+\rho g(\mathrm{x}+\Delta \mathrm{h})=\mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{atm}}-\frac{2 \mathrm{~T}}{\mathrm{r}_{2}}+\rho g \mathrm{x}$
$\therefore \rho \mathrm{g} \Delta \mathrm{h}=2 \mathrm{~T}\left[\frac{1}{\mathrm{r}_{1}}-\frac{1}{\mathrm{r}_{2}}\right]$
$=2 \times 7.3 \times 10^{-2}\left[\frac{1}{2.5 \times 10^{-3}}-\frac{1}{4 \times 10^{-3}}\right]$
$\therefore \Delta \mathrm{h}=\frac{2 \times 7.3 \times 10^{-2} \times 10^{3}}{10^{3} \times 10}\left[\frac{1}{2.5}-\frac{1}{4}\right]$
$=2.19 \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{~m}=2.19 \mathrm{~mm}$
Hence option (2)
