What are the major transport mechanisms for $\mathrm{CO}_{2}$ ? Explain.
Plasma and red blood cells transport carbon dioxide. This is because they are readily soluble in water.
(1) Through plasma:
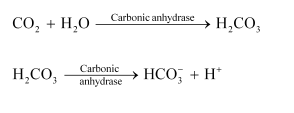
About $7 \%$ of $\mathrm{CO}_{2}$ is carried in a dissolved state through plasma. Carbon dioxide combines with water and forms carbonic acid.
$$
\mathrm{CO}_{2}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \longrightarrow \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{CO}_{3}
$$
(Carbonic acid)
Since the process of forming carbonic acid is slow, only a small amount of carbon dioxide is carried this way.
(2) Through RBCs:
About $20-25 \%$ of $\mathrm{CO}_{2}$ is transported by the red blood cells as carbaminohaemoglobin. Carbon dioxide binds to the amino groups on the polypeptide chains of haemoglobin and forms a compound known as carbaminohaemoglobin.
(3) Through sodium bicarbonate:
About $70 \%$ of carbon dioxide is transported as sodium bicarbonate. $\mathrm{As} \mathrm{CO}_{2}$ diffuses into the blood plasma, a large part of it combines with water to form carbonic acid in the presence of the enzyme carbonic anhydrase. Carbonic anhydrase is a zinc enzyme that speeds up the formation of carbonic acid. This carbonic acid dissociates into bicarbonate $\left(\mathrm{HCO}_{3}{ }^{-}\right)$and hydrogen ions $\left(\mathrm{H}^{+}\right)$.
Click here to get exam-ready with eSaral
For making your preparation journey smoother of JEE, NEET and Class 8 to 10, grab our app now.
