Which of the following are the roots of $3 x^{2}+2 x-1=0 ?$
(i) $-1$
(ii) $\frac{1}{3}$
(iii) $-\frac{1}{2}$
The given equation is $\left(3 \mathrm{x}^{2}+2 \mathrm{x}-1=0\right)$.
(i) $\mathrm{x}=(-1)$
L.H .S. $=\mathrm{x}^{2}+2 \mathrm{x}-1$
$=3 \times(-1)^{2}+2 \times(-1)-1$
$=3-2-1$
$=0$
$=$ R.H.S.
Thus, $(-1)$ is a root of $\left(3 x^{2}+2 x-1=0\right)$.
(ii) On substituting $\mathrm{x}=\frac{1}{3}$ in the given equation, we get:
L.H.S. $=3 \mathrm{x}^{2}+2 \mathrm{x}-1$
$=3 \times\left(\frac{1}{3}\right)^{2}+2 \times \frac{1}{3}-1$
$=\not{3}^{1} \times \frac{1}{-9_{3}}+\frac{2}{3}-1$
$=\frac{1+2-3}{3}$
$=\frac{0}{3}$
$=0$
$=$ R.H.S.
Thus, $\left(\frac{1}{3}\right)$ is a root of $\left(3 \mathrm{x}^{2}+2 \mathrm{x}-1=0\right)$.
(iii) On substituting $\mathrm{x}=\left(-\frac{1}{2}\right)$ in the given equation, we get:
L.H.S. $=3 x^{2}+2 x-1$
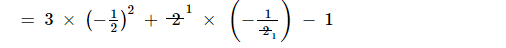
$=3 \times \frac{1}{4}-1-1$
$=\frac{3}{4}-2$
$=\frac{3-8}{4}$
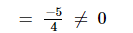
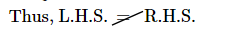
Hence, $\left(-\frac{1}{2}\right)$ is a not solution of $\left(3 \mathrm{x}^{2}+2 \mathrm{x}-1=0\right)$
