Hey, do you want to learn about the sign convention for lens? If yes. Then keep reading.
Sign Convention
- Whenever and where possible, rays of light are taken to travel from left to right.
- The transverse distance measured from the optical center and is taken to be positive while those below it negative.
- Longitudinal distances are measured from the optical center and are taken to be positive if in the direction of light propagation and negative if opposite to it e.g., according to our convention case of a
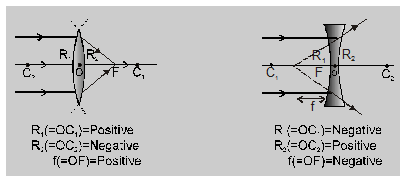
While using the sign convention, it must be kept in mind that -
(a) To calculate an unknown quantity the known quantities are substituted with a sign in a given formula.
(b) In the result sign must be interpreted as there are number of sign conventions and the same sign has a different meaning in different conventions.
Rules for image formation
In order to locate the image formed by a lens graphically following rules are adopted -
- A ray passing through the optical center proceeds undeviated through the lens. (by definition of optical center).
- A ray passing through the first focus or directed towards it, after refraction from the lens becomes parallel to the principal axis. (by definition of $F_{1}$)
- A ray passing parallel to the principal axis after refraction through the lens passes or appears to pass through $\mathrm{F}_{2}$ (by definition of $\mathrm{F}_{2}$).
- Only two rays from the same point of an object are needed for image formation and the point where the rays after refraction through the lens intersect or appear to intersect is the image of the object. If they actually intersect each other the image is real and if they appear to intersect the image is said to be virtual.
So, that's all from this article. I hope you get the idea about the Sign convention for the lens. If you found this article informative then please share it with your friends. If you have any confusion related to this topic, then you can ask in the comments section down below.
For a better understanding of this chapter, please check the detailed notes of Ray Optics. To watch Free Learning Videos on physics by Saransh Gupta sir Install the eSaral App.
