Introduction
According to colloidal solution definition, it is defined as a solution in which a material is evenly suspended in a liquid. Some of the Examples of Colloidal Solution are gelatin; muddy water, Butter, blood, Colored Glass. Know the various types of colloidal solution and difference between true solution and colloidal solution.
Here You will Study about
Colloidal Solution & its Examples
Comparison of Suspension, Colloidal Solution & True Solution
Types of Colloidal Solution
The foundation of colloid chemistry was Laid by an English scientist, Thomas Graham in 1861.
Definition of Colloidal Solution:
A colloidal solution, generally identified as a colloidal suspension, is a mixture in which the substances are regularly suspended in a fluid. While colloidal systems can occur in any one of the three main states of matter, solid, liquid, or gas, a colloidal solution unambiguously refers to a liquid mixture.
Examples of Colloidal Solution
Whipped cream, mayonnaise, milk, butter, gelatin, jelly, muddy water, plaster, colored glass etc. Examples of Colloids discuss different types of colloidal solution.
Comparison of suspensions, colloids and true solution

Types of Colloidal solutions
A colloidal system comprises of two phases. The substance distributed as the colloidal particles is called Dispersed phase the internal phase or the discontinuous phase. Dispersion medium is defined as the second continuous phase in which the colloidal particles are dispersed. For example, for a colloidal solution of copper in water, copper particles constitute the dispersed phase and water the dispersion medium. Depending on the physical states of dispersed phase or dispersion medium, colloidal solutions are eight types
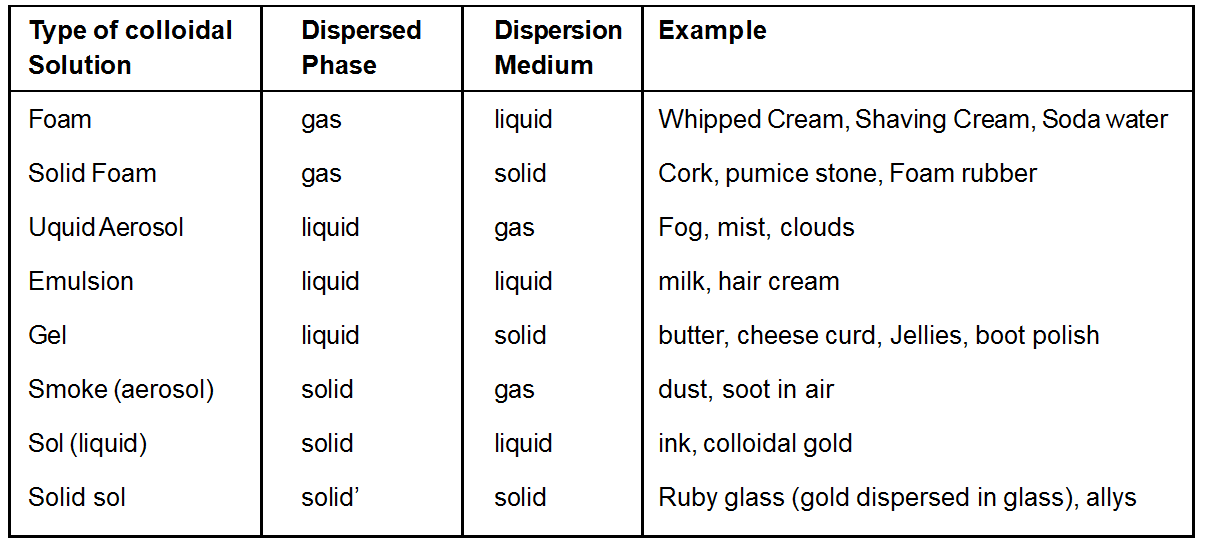 A colloidal dispersion of one gas in another is not possible since the two gases would give a homogeneous molecular structure.
We restrict our study mainly to colloidal systems which consist of a solid substance dispersed in a liquid. These are frequently referred to as sols or colloidal solutions, the colloidal solutions in water as the dispersion medium are termed hydrosols or Aqua sols. When the dispersion medium is alcohol or benzene, the sols are referred to as Alcohols and Benzenols respectively.
A colloidal dispersion of one gas in another is not possible since the two gases would give a homogeneous molecular structure.
We restrict our study mainly to colloidal systems which consist of a solid substance dispersed in a liquid. These are frequently referred to as sols or colloidal solutions, the colloidal solutions in water as the dispersion medium are termed hydrosols or Aqua sols. When the dispersion medium is alcohol or benzene, the sols are referred to as Alcohols and Benzenols respectively.
click here to continue . . .
Download eSaral App and ask your doubts for free at Discussion Forum.

 A colloidal dispersion of one gas in another is not possible since the two gases would give a homogeneous molecular structure.
We restrict our study mainly to colloidal systems which consist of a solid substance dispersed in a liquid. These are frequently referred to as sols or colloidal solutions, the colloidal solutions in water as the dispersion medium are termed hydrosols or Aqua sols. When the dispersion medium is alcohol or benzene, the sols are referred to as Alcohols and Benzenols respectively.
A colloidal dispersion of one gas in another is not possible since the two gases would give a homogeneous molecular structure.
We restrict our study mainly to colloidal systems which consist of a solid substance dispersed in a liquid. These are frequently referred to as sols or colloidal solutions, the colloidal solutions in water as the dispersion medium are termed hydrosols or Aqua sols. When the dispersion medium is alcohol or benzene, the sols are referred to as Alcohols and Benzenols respectively.
