Helmholtz coil is named after the German physicist Hermann von Helmholtz. It is comprised of two identical magnetic coils positioned in parallel to each other, and their centers are aligned in the same x-
Helmholtz Coils
The two coaxial coils of equal radii placed at a distance equal to the radius of either of the coils and in which the same current in the same direction is flowing are known as Helmholtz coils.For these coils $x=\frac{a}{2}, I_{1}=I_{2}=I, a_{1}=a_{2}=a$
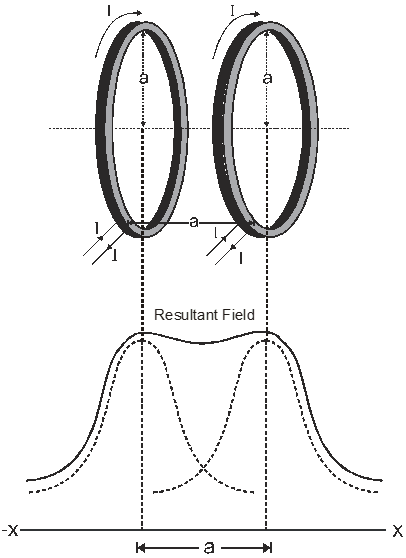
The two coils are placed mutually parallel to each other these coils are used to produce a uniform magnetic field. In between two coils along the axis at the middle point rate of change of magnetic field is constant, so if distance increases from a coil magnetic field decrease, but the distance from another coil decreases, so magnetic field due to second coil increases and hence the resultant magnetic field produced in the region between two coils remains uniform.
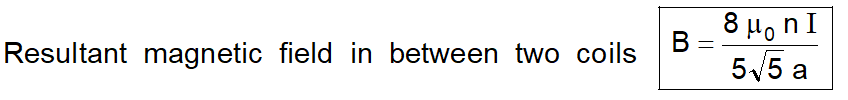
or $\mathrm{B}=0.76 \frac{\mu_{0} n \mathrm{I}}{a} \quad$ or $\mathrm{B}=1.423 \mathrm{B}_{\mathrm{C}}$
(Bc is a magnetic field at the center of a single coil.)\
Also Read: Biot Savart's Law
Click here for the Video tutorials of Magnetic Effect of Current Class 12
About eSaral
At eSaral we are offering a complete platform for IIT-JEE & NEET preparation. The main mission behind eSaral is to provide education to each and every student in India by eliminating the Geographic and Economic factors, as a nation’s progress and development depends on the availability of quality education to each and every one. With the blend of education & technology, eSaral team made the learning personalized & adaptive for everyone.
For free video lectures and complete study material, Download eSaral APP.
