Hey, do you want to learn about Newton's Laws of Motion? if so. Then you are at the right place.
 Fig. (a) shows a fish suspended from a spring scale. In the figure (b), force vectors are used to represent the forces exerted on the fish. The fish's weight Fe is the gravitational force exerted on it by the earth (directed downward) and Fs is the force exerted by the scale (directed upward).
Fig. (a) shows a fish suspended from a spring scale. In the figure (b), force vectors are used to represent the forces exerted on the fish. The fish's weight Fe is the gravitational force exerted on it by the earth (directed downward) and Fs is the force exerted by the scale (directed upward).
$\vec{F}=\frac{d \vec{p}}{d t}$ .........(A)
i.e., $\vec{F}=\frac{d}{d t}(m \vec{v}) \quad$ [as $\left.\vec{p}=m \vec{v}\right]$
i.e., $\vec{F}=m \frac{d \vec{v}}{d t}+\vec{v} \frac{d m}{d t}$ ..........(B)
Now for a body as m = constant, $\left(\frac{\mathrm{dm}}{\mathrm{dt}}\right)=0$
SO $\vec{F}=m\left(\frac{d \vec{v}}{d t}\right)$
or $\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}=\mathrm{ma}$ [as $\left.\vec{a}=\frac{d \vec{v}}{d t}\right]$ .........(C)
In physics we also have situations (such as rocket motion) in which mass of the body changes but velocity of mass is constant. In such situations as
$\overrightarrow{\mathrm{V}}$ = constant so $\frac{\overrightarrow{\mathrm{dv}}}{\mathrm{dt}}=0$
and eqn. (B) reduces to
$$\mathop F\limits^ \to = \mathop v\limits^ \to {{dm} \over {dt}}$$ .........(D)
Let force on 1st due to 2nd is $\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}_{12}=\frac{\overrightarrow{\mathrm{d} \mathrm{p}}_{1}}{\mathrm{dt}}$ ......(1)
and force on 2nd due to 1st is $\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}_{21}=\frac{\overrightarrow{\mathrm{d} \mathrm{p}}_{2}}{\mathrm{dt}}$ ......(2)
Adding the two equations, we have $\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}_{12}+\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}_{21}=\frac{\overrightarrow{\mathrm{dp}}_{1}}{\mathrm{dt}}+\frac{\overrightarrow{\mathrm{d} \mathrm{p}}_{2}}{\mathrm{dt}}=\frac{\mathrm{d}}{\mathrm{dt}}\left(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{p}}_{1}+\overrightarrow{\mathrm{p}}_{2}\right)$
Since no external force acts on the system, the total of momentum of the system must be constant i.e. time rate of change of momentum of the system should be zero. Therefore, the above equation becomes
$\vec{F}_{12}+\vec{F}_{21}=0 \quad$ or $\quad \vec{F}_{21}=-\vec{F}_{12}$
For a better understanding of this chapter, please check the detailed notes of the Law of Motion. If you want more Free Learning Videos and Study Material Then don't forget to download the eSaral App.
Newton's first law of motion
- Every body continues its state of rest or of uniform motion until an external force is applied over it.
- Newton's I law gives the qualitative definition of force, according to which "force is that external cause which tends to change or actually change the state of motion of the body".
- Newton's I law is called "Law of Inertia" by Galelio.
- Inertia is that property of body owing to which the body opposes any change in its state of motion.
- Inertia µ mass.
Types of inertia :
Inertia of rest.
Inertia of rest is the inability of body to change its state of rest by itself.Examples of inertia of rest :
- A person standing in a bus falls backward when the bus suddenly starts moving.
- The leaves or fruits from a tree fall just at the instant when we shake the tree.
- The dust particles inside a woollen blanket fall off when it is beaten by a stick.
- When a stone hits a window pane, the glass is broken into a number of pieces whereas if the high speed bullet strikes the pane, it leaves a clean hole.
Inertia of motion.
Inertia of motion is the inability of the body to change its state of motion by itself.Examples of inertia of motion :
- A man getting down of a moving bus or train falls forward.
- Before taking a long jump an athlete runs for some distance.
- A ball thrown upwards in a running train continues to move along with the train.
Inertia of direction
It is the inability of the body to change its direction of motion by itself.Examples of inertia of direction :
- When a car suddenly takes a bend, the passengers are thrown in the outward direction.
- A body released from a balloon rising up continues to move in the direction of balloon.
 Fig. (a) shows a fish suspended from a spring scale. In the figure (b), force vectors are used to represent the forces exerted on the fish. The fish's weight Fe is the gravitational force exerted on it by the earth (directed downward) and Fs is the force exerted by the scale (directed upward).
Fig. (a) shows a fish suspended from a spring scale. In the figure (b), force vectors are used to represent the forces exerted on the fish. The fish's weight Fe is the gravitational force exerted on it by the earth (directed downward) and Fs is the force exerted by the scale (directed upward).
Newton's second law of motion
According to this law, the rate of change of momentum is directly proportional to the applied force. The change in momentum takes place in the direction of applied force. Newton's II law gives the quantitative definition of force. i.e. $\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}=\frac{\Delta \overrightarrow{\mathrm{p}}}{\Delta \mathrm{t}}$ If Dt is vanishingly small then $\vec{F}=\frac{\overrightarrow{d p}}{d t}$ Out of Newton's three laws of motion, the most fundamental one is second law, because I and III laws can be derived from it. If external force is zero, then $\vec{F}=\frac{d \vec{p}}{d t}$ = 0 or $\overrightarrow{\mathrm{p}}$ = constant Or = constant, this constant may be zero i.e. condn. of rest. Which is first lawApplication of Newton's Second Law
When force changes the state of rest or motion of a body, by Newton's Second Law$\vec{F}=\frac{d \vec{p}}{d t}$ .........(A)
i.e., $\vec{F}=\frac{d}{d t}(m \vec{v}) \quad$ [as $\left.\vec{p}=m \vec{v}\right]$
i.e., $\vec{F}=m \frac{d \vec{v}}{d t}+\vec{v} \frac{d m}{d t}$ ..........(B)
Now for a body as m = constant, $\left(\frac{\mathrm{dm}}{\mathrm{dt}}\right)=0$
SO $\vec{F}=m\left(\frac{d \vec{v}}{d t}\right)$
or $\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}=\mathrm{ma}$ [as $\left.\vec{a}=\frac{d \vec{v}}{d t}\right]$ .........(C)
In physics we also have situations (such as rocket motion) in which mass of the body changes but velocity of mass is constant. In such situations as
$\overrightarrow{\mathrm{V}}$ = constant so $\frac{\overrightarrow{\mathrm{dv}}}{\mathrm{dt}}=0$
and eqn. (B) reduces to
$$\mathop F\limits^ \to = \mathop v\limits^ \to {{dm} \over {dt}}$$ .........(D)
Newton's third law of motion
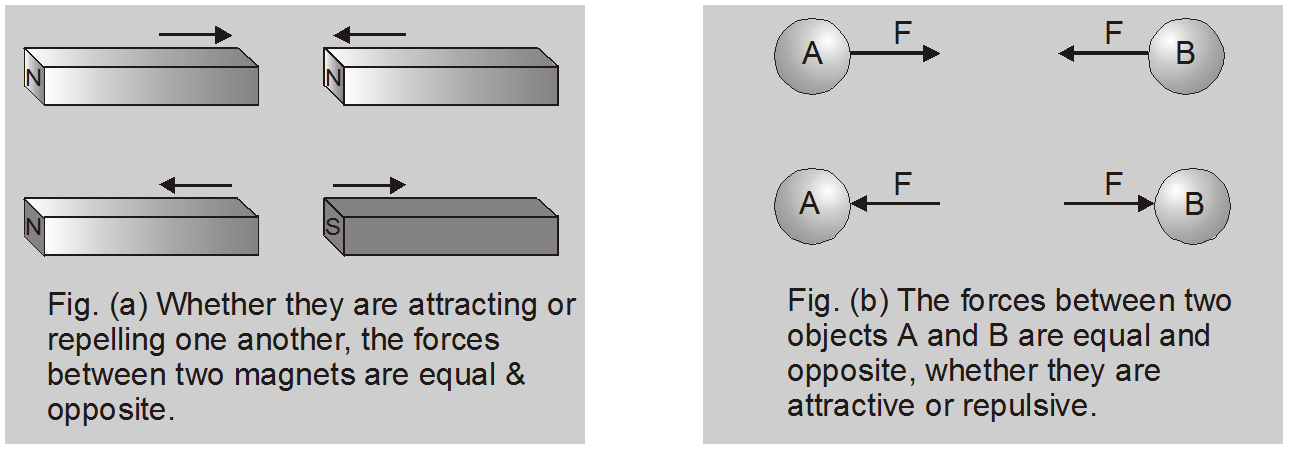
To every action, there is always equal and opposite reaction or the mutual actions of two bodies upon each other are always directed to contrary parts. The first and second laws are statements about a single object, whereas the third law is a statement about two objects.- [A] According to this law, every action has equal and opposite reaction. Action and reaction act on different bodies and they are simultaneous. There can be no reaction without action.

- If an object A exerts a force F on an object B, then B exerts an equal and opposite force (–F) on A.
- Newton's III law contradicts theory of relativity, because it states that force signals can travel with infinite speed while theory of relativity states that nothing can travel with a velocity greater than velocity of light.
- Action and reaction never cancel each other.
- Newton's III law can be derived from II law.
Let force on 1st due to 2nd is $\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}_{12}=\frac{\overrightarrow{\mathrm{d} \mathrm{p}}_{1}}{\mathrm{dt}}$ ......(1)
and force on 2nd due to 1st is $\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}_{21}=\frac{\overrightarrow{\mathrm{d} \mathrm{p}}_{2}}{\mathrm{dt}}$ ......(2)
Adding the two equations, we have $\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}_{12}+\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}_{21}=\frac{\overrightarrow{\mathrm{dp}}_{1}}{\mathrm{dt}}+\frac{\overrightarrow{\mathrm{d} \mathrm{p}}_{2}}{\mathrm{dt}}=\frac{\mathrm{d}}{\mathrm{dt}}\left(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{p}}_{1}+\overrightarrow{\mathrm{p}}_{2}\right)$
Since no external force acts on the system, the total of momentum of the system must be constant i.e. time rate of change of momentum of the system should be zero. Therefore, the above equation becomes
$\vec{F}_{12}+\vec{F}_{21}=0 \quad$ or $\quad \vec{F}_{21}=-\vec{F}_{12}$
For a better understanding of this chapter, please check the detailed notes of the Law of Motion. If you want more Free Learning Videos and Study Material Then don't forget to download the eSaral App.
