Abdul travelled 300 km by train and 200 km by taxi, it took him 5 hours 30 minutes. But if he travels 260 km by train and 240 km by taxi he takes 6 minutes longer. Find the speed of the train and that of the taxi.
Let the speed of the train be x km/hour that of the taxi be y km/hr, we have the following cases
Case I: When Abdul travels 300 Km by train and the 200 Km by taxi
Time taken by Abdul to travel $300 \mathrm{Km}$ by train $=\frac{300}{x} h r s$
Time taken by Abdul to travel $200 \mathrm{Km}$ by taxi $=\frac{200}{y} h r s$
Total time taken by Abdul to cover $500 \mathrm{Km}=\frac{300}{x}+\frac{200}{y}$
It is given that total time taken in 5 hours 30 minutes
$\frac{300}{x}+\frac{200}{y}=5$ hours $30 \mathrm{~min}$ utes
$100\left(\frac{3}{x}+\frac{2}{y}\right)=5 \frac{30}{60}$
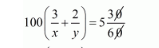
$100\left(\frac{3}{x}+\frac{2}{y}\right)=5 \frac{1}{2}$
$100\left(\frac{3}{x}+\frac{2}{y}\right)=\frac{11}{2}$
$\left(\frac{3}{x}+\frac{2}{y}\right)=\frac{11}{2} \times \frac{1}{100}$
$\frac{3}{x}+\frac{2}{y}=\frac{11}{200} \cdots(i)$
Case II: When Abdul travels 260 Km by train and the 240 km by taxi
Time taken by Abdul to travel $260 \mathrm{Km}$ by train $=\frac{260}{x} h r s$
Time taken by Abdul to travel $240 \mathrm{Km}$ by taxi $=\frac{240}{y} h r s$
In this case total time of the journey is 5 hours 36 minutes
$\frac{260}{x}+\frac{240}{y}=5$ hrs $36 \mathrm{~min}$ utes
$\frac{260}{x}+\frac{240}{y}=5 \frac{36}{60}$
$\frac{260}{x}+\frac{240}{y}=5 \frac{6}{10}$
$\frac{260}{x}+\frac{240}{y}=5 \frac{3}{5}$
$20\left(\frac{13}{x}+\frac{12}{y}\right)=\frac{28}{5}$
$\left(\frac{13}{x}+\frac{12}{y}\right)=\frac{28}{5} \times \frac{1}{20}$
$\frac{13}{x}+\frac{12}{y}=\frac{7}{25}$...$(i i)$
Putting $\frac{1}{x}=v|$ and, $\frac{1}{y}=u$, the equations ( $i$ ) and (ii) reduces to
$3 u+2 v=\frac{11}{200} \cdots(i i i)$
$13 u+12 v=\frac{7}{25} \cdots(i v)$
Multiplying equation (i i i) by 6 the above system of equation becomes
$18 u+12 v=\frac{33}{100} \cdots(v)$
Subtracting equation $(i v)$ from $(v)$ we get
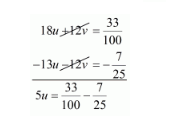
$5 u=\frac{33}{100}-\frac{7 \times 4}{25 \times 4}$
$5 u=\frac{33}{100}-\frac{28}{100}$
$5 u=\frac{33-28}{100}$
$5 u=\frac{5}{100}$
$u=\frac{5}{100} \times \frac{1}{5}$
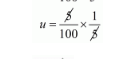
$u=\frac{1}{100}$
Putting $u=\frac{1}{100}$ in equation $(i i i)$, we get
$3 u+2 v=\frac{11}{200}$
$3 \times \frac{1}{100}+2 v=\frac{11}{200}$
$\frac{3}{100}+2 v=\frac{11}{200}$
$2 v=\frac{11}{200}-\frac{3}{100}$
$2 v=\frac{11}{200}-\frac{3 \times 2}{100 \times 2}$
$2 v=\frac{11-6}{200}$
$2 v=\frac{5}{200}$
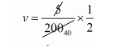
$v=\frac{1}{80}$
Now
$u=\frac{1}{100}$
$\frac{1}{x}=\frac{1}{100}$
$x=100$
and
$\mathrm{s}=\frac{1}{80}$
$\frac{1}{y}=\frac{1}{80}$
$y=80$
Hence, the speed of the train is $100 \mathrm{~km} / \mathrm{lm}$,
The speed of the taxi is 80km/h
