An analysis of monthly wages paid to workers in two firms A and B, belonging to the same industry, gives the following results:
An analysis of monthly wages paid to workers in two firms A and B, belonging to the same industry, gives the following results:
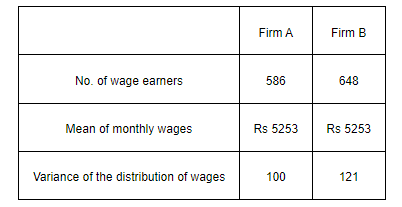
(i) Which firm A or B pays larger amount as monthly wages?
(ii) Which firm, A or B, shows greater variability in individual wages?
(i) Monthly wages of firm A = Rs 5253
Number of wage earners in firm A = 586
$\therefore$ Total amount paid $=$ Rs $5253 \times 586$
Monthly wages of firm B = Rs 5253
Number of wage earners in firm B = 648
$\therefore$ Total amount paid $=$ Rs $5253 \times 648$
Thus, firm B pays the larger amount as monthly wages as the number of wage earners in firm B are more than the number of wage earners in firm A.
(ii) Variance of the distribution of wages in firm $\mathrm{A}\left(\sigma_{1}^{2}\right)=100$
$\therefore$ Standard deviation of the distribution of wages in firm
$\mathrm{A}\left(\left(\sigma_{1}\right)=\sqrt{100}=10\right.$
Variance of the distribution of wages in firm $\mathrm{B}\left(\sigma_{2}^{2}\right)=121$
$\therefore$ Standard deviation of the distribution of wages in firm $\mathrm{B}\left(\sigma_{2}^{2}\right)=\sqrt{121}=11$
The mean of monthly wages of both the firms is same i.e., 5253. Therefore, the firm with greater standard deviation will have more variability.
Thus, firm B has greater variability in the individual wages.
