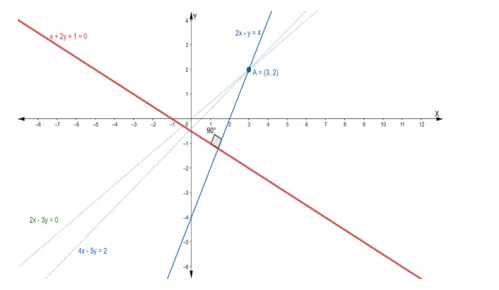
Find the equation of the line through the intersection of the lines 2x – 3y = 0 and $4 x-5 y=2$ and which is perpendicular to the line $x+2 y+1=0$
Suppose the given two lines intersect at a point $P\left(x_{1}, y_{1}\right) .$ Then, $\left(x_{1}, y_{1}\right)$ satisfies each of the given equations.
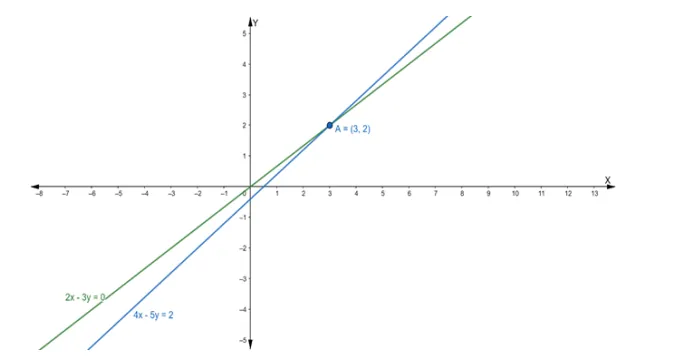
$2 x-3 y=0 \ldots$ (i)
$4 x-5 y=2 \ldots$ (ii)
Now, we find the point of intersection of eq. (i) and (ii)
Multiply the eq. (i) by 2, we get
$4 x-6 y=0 \ldots$ (iii)
On subtracting eq. (iii) from (ii), we get
$4 x-5 y-4 x+6 y=2-0$
$\Rightarrow y=2$
Putting the value of y in eq. (i), we get
$2 x-3(2)=0$
$\Rightarrow 2 x-6=0$
$\Rightarrow 2 x=6$
$\Rightarrow x=3$
Hence, the point of intersection $P\left(x_{1}, y_{1}\right)$ is $(3,2)$
Now, we know that, when two lines are perpendicular, then the product of their slope is equal to $-1$
$m_{1} \times m_{2}=-1$
$\Rightarrow$ Slope of the given line $\times$ Slope of the perpendicular line $=-1$
$\therefore\left(-\frac{1}{2}\right) \times$ Slope of the perpendicular line $=-1$
$\Rightarrow$ The slope of the perpendicular line $=2$
So, the slope of a line which is perpendicular to the given line is 2
Then the equation of the line passing through the point $(3,2)$ having slope 2 is:
$y-y_{1}=m\left(x-x_{1}\right)$
$\Rightarrow y-2=2(x-3)$
$\Rightarrow y-2=2 x-6$
$\Rightarrow 2 x-y-6+2=0$
$\Rightarrow 2 x-y-4=0$