Find the probability distribution of the number of successes in two tosses of a die, where a success is defined as
Find the probability distribution of the number of successes in two tosses of a die, where a success is defined as
(i) number greater than 4
(ii) six appears on at least one die
When a die is tossed two times, we obtain (6 × 6) = 36 number of observations.
Let X be the random variable, which represents the number of successes.
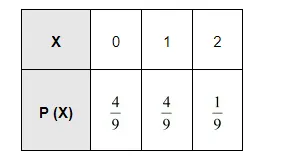
i. Here, success refers to the number greater than 4 .
$P(X=0)=P$ (number less than or equal to 4 on both the tosses) $=\frac{4}{6} \times \frac{4}{6}=\frac{4}{9}$
$P(X=1)=P$ (number less than or equal to 4 on first toss and greater than 4 on second toss) $+P$ (number greater than 4 on first toss and less than or equal to 4 on second toss)
$=\frac{4}{6} \times \frac{2}{6}+\frac{4}{6} \times \frac{2}{6}=\frac{4}{9}$
Thus, the probability distribution is as follows.
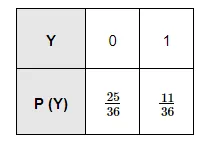
(ii) Here, success means six appears on at least one die.
$P(Y=0)=P($ six appears on none of the dice $)=\frac{5}{6} \times \frac{5}{6}=\frac{25}{36}$
$P(Y=1)=P$ (six appears on at least one of the dice) $=\frac{1}{6} \times \frac{5}{6}+\frac{5}{6} \times \frac{1}{6}+\frac{1}{6} \times \frac{1}{6}=\frac{11}{36}$
Thus, the required probability distribution is as follows.