Without torque, there would be no twists and turns, no spins! Wouldn’t life be boring that way? Torque gives a rotational motion to an object that would otherwise not be possible. So here we will study about Torque and Torque on a Current loop in a Magnetic Field in detailed derivation.
 The magnitude of the torque $\vec{\tau}$ is given by
The magnitude of the torque $\vec{\tau}$ is given by
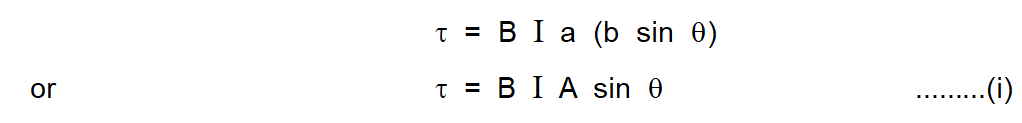 where $A$ is the area of the coil.
But $\mathrm{IA}=\mathrm{M}$ (magnitude of magnetic dipole moment)
where $A$ is the area of the coil.
But $\mathrm{IA}=\mathrm{M}$ (magnitude of magnetic dipole moment)
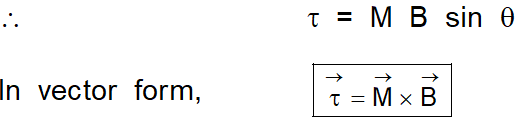 The direction of the torque is vertically downwards along the axis of suspension [dotted line in fig (b)]
It will rotate the loop clockwise about its axis.
Note 1. If the rectangular loop has N turns, then the torque increases N times and becomes $\mathrm{N} \mathrm{B}$ I $\mathrm{A} \sin \theta$
Note 2
$\mathrm{eq}^{\mathrm{n}}$ (i) could also be written as $\vec{\tau}=\mathrm{I}(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{A}} \times \overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}})$ OR $\vec{\tau}=\mathrm{I} \mathrm{A} \hat{\mathrm{n}} \times \overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}}$
where $\hat{\mathrm{n}}$ is a unit vector normal to the plane of the loop.
Also Read:
Biot Savart's Law
Click here for the Video tutorials of Magnetic Effect of Current Class 12
About eSaral
At eSaral we are offering a complete platform for IIT-JEE & NEET preparation. The main mission behind eSaral is to provide education to each and every student in India by eliminating the Geographic and Economic factors, as a nation’s progress and development depends on the availability of quality education to each and every one. With the blend of education & technology, eSaral team made the learning personalized & adaptive for everyone.
For free video lectures and complete study material, Download eSaral APP.
The direction of the torque is vertically downwards along the axis of suspension [dotted line in fig (b)]
It will rotate the loop clockwise about its axis.
Note 1. If the rectangular loop has N turns, then the torque increases N times and becomes $\mathrm{N} \mathrm{B}$ I $\mathrm{A} \sin \theta$
Note 2
$\mathrm{eq}^{\mathrm{n}}$ (i) could also be written as $\vec{\tau}=\mathrm{I}(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{A}} \times \overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}})$ OR $\vec{\tau}=\mathrm{I} \mathrm{A} \hat{\mathrm{n}} \times \overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}}$
where $\hat{\mathrm{n}}$ is a unit vector normal to the plane of the loop.
Also Read:
Biot Savart's Law
Click here for the Video tutorials of Magnetic Effect of Current Class 12
About eSaral
At eSaral we are offering a complete platform for IIT-JEE & NEET preparation. The main mission behind eSaral is to provide education to each and every student in India by eliminating the Geographic and Economic factors, as a nation’s progress and development depends on the availability of quality education to each and every one. With the blend of education & technology, eSaral team made the learning personalized & adaptive for everyone.
For free video lectures and complete study material, Download eSaral APP.
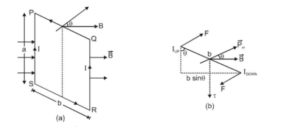
Torque Experienced by a Current Loop in a Uniform Magnetic Field
Let us consider a rectangular current loop PQRS of sides a and b suspended vertically in a uniform magnetic field. $\overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}}$. Let $\theta$ be the angle between the direction of $\overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}}$ and the vector perpendicular to the plane of the loop. Let us first consider the two straight parts PQ and RS. The forces acting on these parts are clearly equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. These forces are collinear, so, the net force or net torque due to this pair of forces is zero. The forces on the straight current segments SP and QR are (i) equal in magnitude (ii) opposite in direction (iii) not collinear. These forces are shown in figure (b). This pair of forces produce a torque whose lever arm is b sin\theta. Magnitude of each force $=\mathrm{B} \mathrm{I}$ a The magnitude of the torque $\vec{\tau}$ is given by
The magnitude of the torque $\vec{\tau}$ is given by
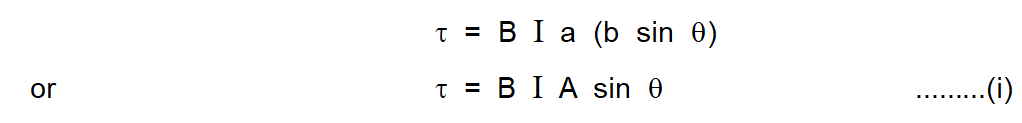 where $A$ is the area of the coil.
But $\mathrm{IA}=\mathrm{M}$ (magnitude of magnetic dipole moment)
where $A$ is the area of the coil.
But $\mathrm{IA}=\mathrm{M}$ (magnitude of magnetic dipole moment)
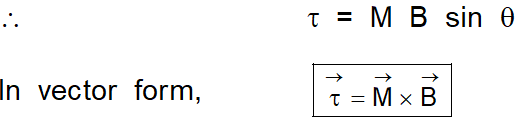 The direction of the torque is vertically downwards along the axis of suspension [dotted line in fig (b)]
It will rotate the loop clockwise about its axis.
Note 1. If the rectangular loop has N turns, then the torque increases N times and becomes $\mathrm{N} \mathrm{B}$ I $\mathrm{A} \sin \theta$
Note 2
$\mathrm{eq}^{\mathrm{n}}$ (i) could also be written as $\vec{\tau}=\mathrm{I}(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{A}} \times \overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}})$ OR $\vec{\tau}=\mathrm{I} \mathrm{A} \hat{\mathrm{n}} \times \overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}}$
where $\hat{\mathrm{n}}$ is a unit vector normal to the plane of the loop.
Also Read:
Biot Savart's Law
Click here for the Video tutorials of Magnetic Effect of Current Class 12
About eSaral
At eSaral we are offering a complete platform for IIT-JEE & NEET preparation. The main mission behind eSaral is to provide education to each and every student in India by eliminating the Geographic and Economic factors, as a nation’s progress and development depends on the availability of quality education to each and every one. With the blend of education & technology, eSaral team made the learning personalized & adaptive for everyone.
For free video lectures and complete study material, Download eSaral APP.
The direction of the torque is vertically downwards along the axis of suspension [dotted line in fig (b)]
It will rotate the loop clockwise about its axis.
Note 1. If the rectangular loop has N turns, then the torque increases N times and becomes $\mathrm{N} \mathrm{B}$ I $\mathrm{A} \sin \theta$
Note 2
$\mathrm{eq}^{\mathrm{n}}$ (i) could also be written as $\vec{\tau}=\mathrm{I}(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{A}} \times \overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}})$ OR $\vec{\tau}=\mathrm{I} \mathrm{A} \hat{\mathrm{n}} \times \overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}}$
where $\hat{\mathrm{n}}$ is a unit vector normal to the plane of the loop.
Also Read:
Biot Savart's Law
Click here for the Video tutorials of Magnetic Effect of Current Class 12
About eSaral
At eSaral we are offering a complete platform for IIT-JEE & NEET preparation. The main mission behind eSaral is to provide education to each and every student in India by eliminating the Geographic and Economic factors, as a nation’s progress and development depends on the availability of quality education to each and every one. With the blend of education & technology, eSaral team made the learning personalized & adaptive for everyone.
For free video lectures and complete study material, Download eSaral APP.