Hey, do you want to know What are the properties of semiconductors? If yes. Then keep reading
Semiconductor
There are a large number of materials that have resistivities lying between those of an insulator and a conductor (See table). Such materials are known as ‘semiconductors’.
At absolute zero, pure and perfect crystals of the semiconductors are nonconducting, their resistivity approaching to the resistivity of an insulator. They can be made conducting by adding impurities, thermal agitation, and lattice defects etc.
Resistivity of a semiconductor depends upon the temperature, and it decreases with the rise in temperature; consequently, a semiconductor crystal becomes conducting even at room temperature.
At room temperature, their resistivity lies in the range of $10^{2}$ to $10^{9}$ ohm-cm. and is thus intermediate between the resistivity of a good conductor ($10^{-8}$ ohm-cm) and insulator ($10^{14}$ to $10^{22}$ ohm.cm.).
Electrical resistivity of various materials at 20°C in ohm-meter.
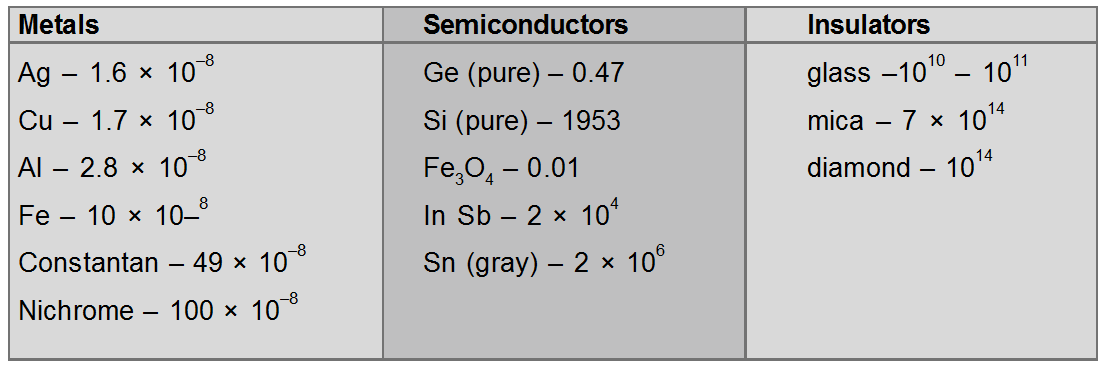
At $20^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$ resistivity of semiconductors lying between metals and insulators. But at low temperatures, semiconductor behaves as an insulator, because the resistivity of a semiconductor depends strongly on temperature.
Properties:
- They have a negative temperature coefficient of resistance means the resistance of semiconductors decreases with an increase in temperature and vice-versa.
- Their electrical conductivity is very much affected by even a very minute amount of impurity added to it.
- Covalent Bond
- Crystalline Structure Silicon $\left({ }_{14} \mathrm{Si}^{28}\right)$, germanium $\left({ }_{32} \mathrm{Ge}^{73}\right)$ and tin $\left({ }_{50} \mathrm{Sn}^{119}\right)$ in crystalline form have the same crystal structure and similar electrical properties.
Silicon and germanium are the most popular semiconductors, because of the importance of Ge and Si in present-day electronics.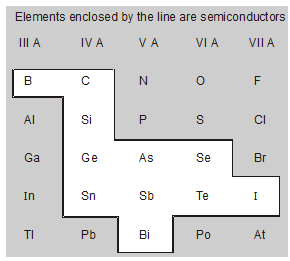
There are also a number of compound semiconductors, such as metallic oxides and sulphides which are also of great particle importance.
So, that's all from this article. I hope you get the idea about What are the properties of semiconductors. If you found this article informative then please share it with your friends. If you have any confusion related to this topic, then you can ask in the comments section down below.
For a better understanding of this chapter, please check the detailed notes of Electronics. To watch Free Learning Videos on physics by Saransh Gupta sir Install the eSaral App.
