Lets study about Moment of Inertia of a Rigid Body and Physical Significance of Moment of Inertia here.
MOMENT OF INERTIA OF RIGID BODY
It is the property of a body due to which it opposes any change in its state of rest or uniform rotation. Analytically for a particle of mass m rotating in a circle of radius R, moment of inertia of a particle of mass m about the axis of rotation is given by:
$\mathrm{I}=\mathrm{mR}^{2}$ . . . . .(1)
So for a body made up of number of particles (discrete distribution) of masses $m_{1}, m_{2}, \ldots \ldots \ldots$. etc. at
distance $r_{1}, r_{2}, \ldots$ etc. respectively from the axis of rotation, then moment of inertia of all these particles are
$m_{1} r_{1}^{2}, m_{2} r_{2}^{2}, \ldots$ and moment of intertia of body ( $I$ ) is the algebric sum of moment of inertia of all these
particles-
i.e. $\quad \mathrm{I}=\mathrm{m}_{1} \mathrm{r}_{1}^{2}+\mathrm{m}_{2} \mathrm{r}_{2}^{2}+\ldots \ldots+\mathrm{m}_{\mathrm{r}_{1} \mathrm{i}}^{2}+\mathrm{m}_{\mathrm{n}} \mathrm{r}_{\mathrm{n}}^{2}=\sum_{i=1}^{\mathrm{n}} \mathrm{m}_{\mathrm{r}_{1}} \mathrm{r}_{1}^{2} \ldots \ldots(2)$
$\quad \quad \mathrm{m}_{\mathrm{i}}=\mathrm{mass}$ of ith particle
$r_{i}=$ distance of ith particle from axis of rotation
While for a continuous distribution of mass, treating the element of mass dm as particle at position r from
axis of Rotation.
$$
\begin{array}{ll}{\text { dI }=\mathrm{dm} \mathrm{r}^{2},} & {\text { i.e., } \quad \mathrm{I}=\int \mathrm{r}^{2} \mathrm{d} \mathrm{m}}\end{array}
$$ . . . . (3)
It is a scalar quantity
Unit : M.K.S.: $\mathrm{kg}-\mathrm{m}^{2},$ C. G.S. : $\mathrm{gm}-\mathrm{cm}^{2}$
Dimension : $\mathrm{M}^{1} \mathrm{L}^{2} \mathrm{T}^{0}$
Moment of inertia depends on the following factors.
i) Mass of body
ii) Mass distribution of body or shape, size and density of body.
iii) On the position of the axis of rotation.
The more is the distribution of mass with respect to axis of rotation the more will be moment of
inertia.
Moment of Inertia does not depend on the following factors.
(i) Angular velocity
(ii) Angular Acceleration
(iii) Torque
(iv) Angular Momentum
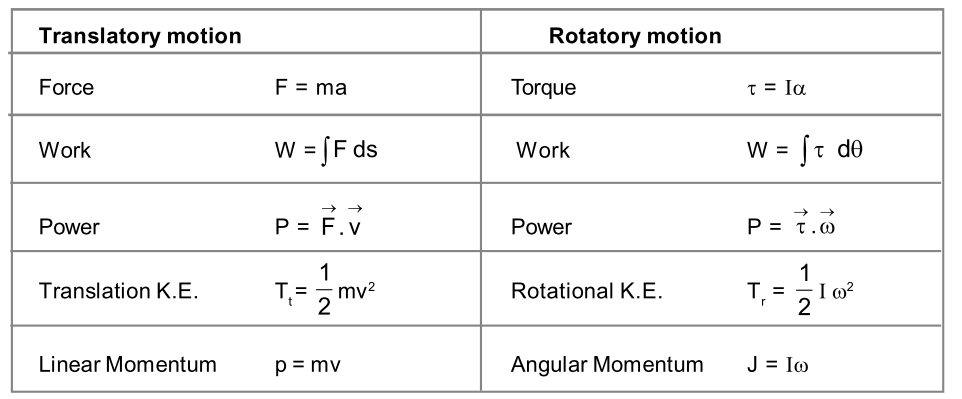
PHYSICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF MOMENT OF INERTIA:Comparison of the expression for rotational motion with corresponding relations for translatory motion as
given in table I, we get moment of inertia plays same role in rotatory motion as mass in translatory
motion, i.e., if a body has large moment of inertia, it is difficult to start rotation or to stop it if rotating. Large
moment of inertia also helps in keeping the motion uniform. Due to this reason stationary engines are
provided with fly-wheels having large moment of inertia.
Inertia for rotational motion is moment of inertia.
 Introduction to Rotational Dynamics
Moment of Inertia
Moment of Inertia: Perpendicular and Parallel axis theorem
Radius of Gyration
Law of Conservation of Angular Momentum
Conservation of Angular Momentum Examples
Kinetic Energy of a Rotating Body
Work done in rotatory Motion
Rotational Power
Combine Translational and Rotational Motion
Rolling without slipping
Rolling on a plane surface
Rolling on a Inclined Plane
For Latest updates, Subscribe our Youtube Channel
Introduction to Rotational Dynamics
Moment of Inertia
Moment of Inertia: Perpendicular and Parallel axis theorem
Radius of Gyration
Law of Conservation of Angular Momentum
Conservation of Angular Momentum Examples
Kinetic Energy of a Rotating Body
Work done in rotatory Motion
Rotational Power
Combine Translational and Rotational Motion
Rolling without slipping
Rolling on a plane surface
Rolling on a Inclined Plane
For Latest updates, Subscribe our Youtube Channel
 Introduction to Rotational Dynamics
Moment of Inertia
Moment of Inertia: Perpendicular and Parallel axis theorem
Radius of Gyration
Law of Conservation of Angular Momentum
Conservation of Angular Momentum Examples
Kinetic Energy of a Rotating Body
Work done in rotatory Motion
Rotational Power
Combine Translational and Rotational Motion
Rolling without slipping
Rolling on a plane surface
Rolling on a Inclined Plane
For Latest updates, Subscribe our Youtube Channel
Introduction to Rotational Dynamics
Moment of Inertia
Moment of Inertia: Perpendicular and Parallel axis theorem
Radius of Gyration
Law of Conservation of Angular Momentum
Conservation of Angular Momentum Examples
Kinetic Energy of a Rotating Body
Work done in rotatory Motion
Rotational Power
Combine Translational and Rotational Motion
Rolling without slipping
Rolling on a plane surface
Rolling on a Inclined Plane
For Latest updates, Subscribe our Youtube Channel 