Hey, are you a class 9 Student and Looking for Ways to Download NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths chapter 3 Exercise 3.1? If Yes then you are at the right place.
Here we have listed Class 9 maths chapter 3 exercise 3.1 solutions in PDF that is prepared by Kota’s top IITian’s Faculties by keeping Simplicity in mind.
If you want to score high in your class 9 Maths Exam then it is very important for you to have a good knowledge of all the important topics, so to learn and practice those topics you can use eSaral NCERT Solutions.
In this article, we have listed NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 that you can download to start your preparations anytime.

So, that’s all from this article. I hope you enjoyed this post. If you found this article helpful then please share it with other students.
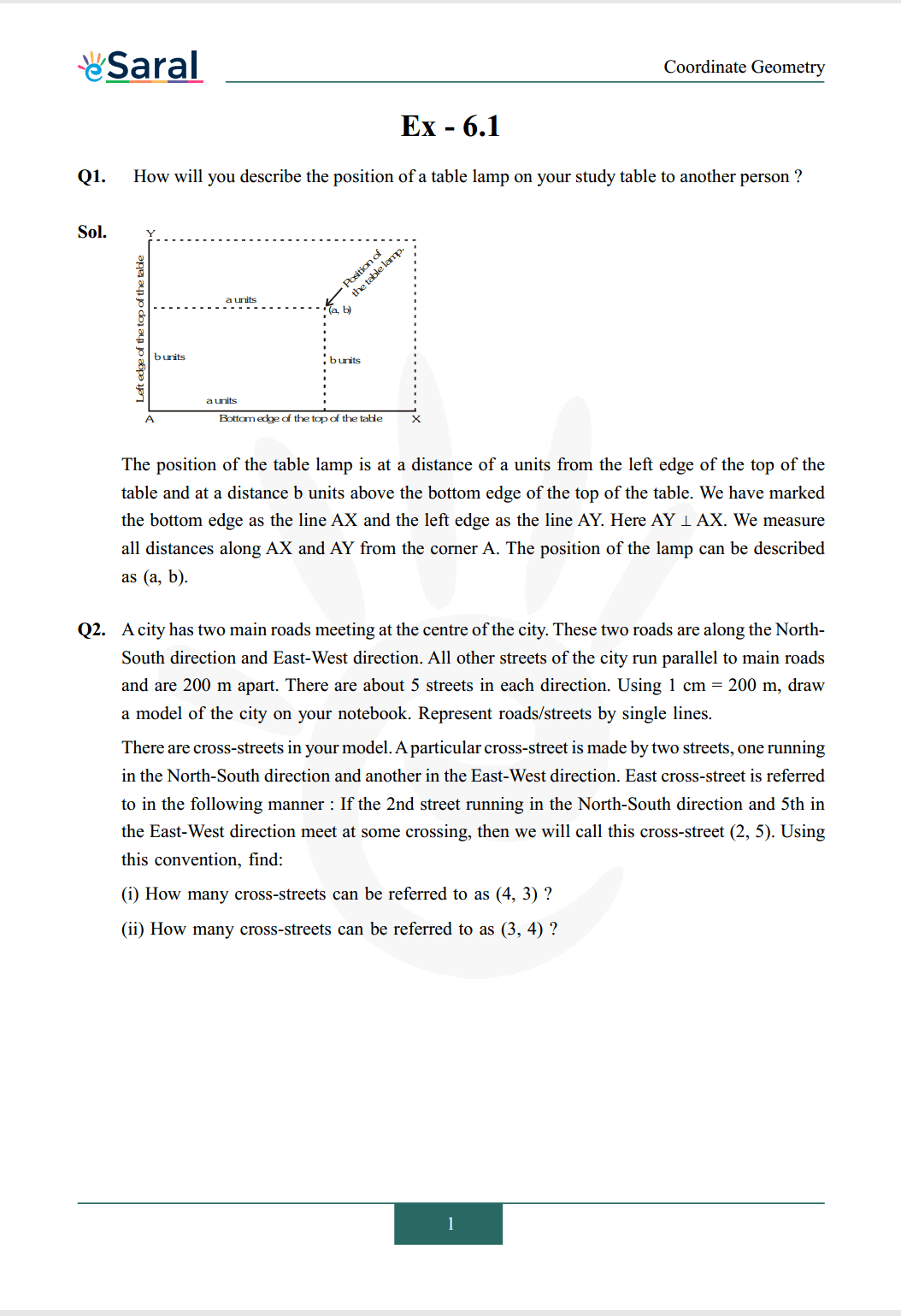
Q1. How will you describe the position of a table lamp on your study table to another person?
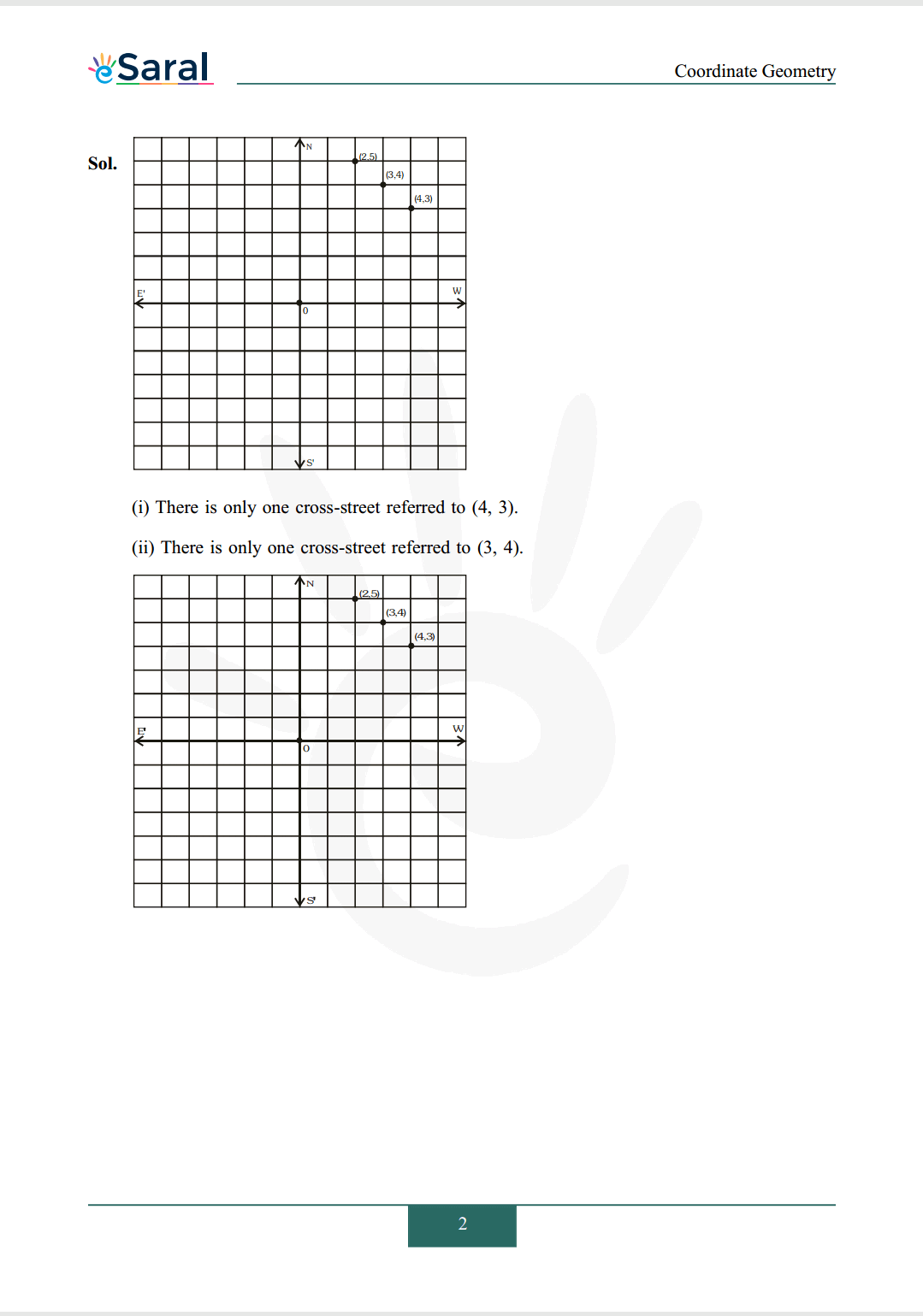
Q2. A city has two main roads meeting at the centre of the city. These two roads are along the NorthSouth direction and East-West direction. All other streets of the city run parallel to main roads and are $200 \mathrm{~m}$ apart. There are about 5 streets in each direction. Using $1 \mathrm{~cm}=200 \mathrm{~m}$, draw a model of the city on your notebook. Represent roads/streets by single lines. There are cross-streets in your model. A particular cross-street is made by two streets, one running in the North-South direction and another in the East-West direction. East cross-street is referred to in the following manner: If the 2 nd street running in the North-South direction and 5 th in the East-West direction meet at some crossing, then we will call this cross-street $(2,5)$. Using this convention, find:
(i) How many cross-streets can be referred to as $(4,3) ?$
(ii) How many cross-streets can be referred to as $(3,4)$ ?
Also Read,
Class 9 NCERT Maths Book Free PDF
Class 9 NCERT Maths Exemplar Free PDF
Download Complete Solutions for Class 9 chapter 3 PDF
Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2.1 Solutions Free
Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2.2 Solutions Free
Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2.3 Solutions Free
Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2.4 Solutions Free
Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2.5 Solutions Free
If you have any Confusion related to NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 then feel free to ask in the comments section down below.
To watch Free Learning Videos on Class 9 by Kota’s top Faculties Install the eSaral App
Here we have listed Class 9 maths chapter 3 exercise 3.1 solutions in PDF that is prepared by Kota’s top IITian’s Faculties by keeping Simplicity in mind.
If you want to score high in your class 9 Maths Exam then it is very important for you to have a good knowledge of all the important topics, so to learn and practice those topics you can use eSaral NCERT Solutions.
In this article, we have listed NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 that you can download to start your preparations anytime.
So, without wasting more time Let’s start.
Download The PDF of NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 "Coordinate Geometry"

So, that’s all from this article. I hope you enjoyed this post. If you found this article helpful then please share it with other students.
All Questions of Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1
Once you complete the chapter 3 then you can revise Ex. 3.1 by solving following questions
Q1. How will you describe the position of a table lamp on your study table to another person?
Q2. A city has two main roads meeting at the centre of the city. These two roads are along the NorthSouth direction and East-West direction. All other streets of the city run parallel to main roads and are $200 \mathrm{~m}$ apart. There are about 5 streets in each direction. Using $1 \mathrm{~cm}=200 \mathrm{~m}$, draw a model of the city on your notebook. Represent roads/streets by single lines. There are cross-streets in your model. A particular cross-street is made by two streets, one running in the North-South direction and another in the East-West direction. East cross-street is referred to in the following manner: If the 2 nd street running in the North-South direction and 5 th in the East-West direction meet at some crossing, then we will call this cross-street $(2,5)$. Using this convention, find:
(i) How many cross-streets can be referred to as $(4,3) ?$
(ii) How many cross-streets can be referred to as $(3,4)$ ?
Also Read,
Class 9 NCERT Maths Book Free PDF
Class 9 NCERT Maths Exemplar Free PDF
Download Complete Solutions for Class 9 chapter 3 PDF
Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2.1 Solutions Free
Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2.2 Solutions Free
Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2.3 Solutions Free
Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2.4 Solutions Free
Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2.5 Solutions Free
If you have any Confusion related to NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 then feel free to ask in the comments section down below.
To watch Free Learning Videos on Class 9 by Kota’s top Faculties Install the eSaral App