We have learn now what a resistance it. Now let's see how the combination of resistances can be used in a circuit to control the flow of current and voltage division. Majorly the combination of these resistances are of 2 types: Series and Parallel. Here we will be taken both in detail below.
Contents:
 Series Combination[/caption]
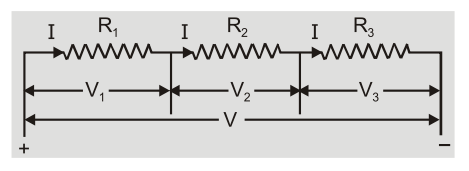
Potential difference across each resistance is different and is directly proportional to its resistance ${\rm{V}} \propto {\rm{R}}.$
So $\quad {{\rm{V}}_1} = {\rm{I}}{{\rm{R}}_1};\quad {{\rm{V}}_2} = {\rm{I}}{R_2}\quad $ and $\quad {{\rm{V}}_3} = {\rm{I}}{{\rm{R}}_3}$
Series Combination[/caption]
Potential difference across each resistance is different and is directly proportional to its resistance ${\rm{V}} \propto {\rm{R}}.$
So $\quad {{\rm{V}}_1} = {\rm{I}}{{\rm{R}}_1};\quad {{\rm{V}}_2} = {\rm{I}}{R_2}\quad $ and $\quad {{\rm{V}}_3} = {\rm{I}}{{\rm{R}}_3}$
 Parallel Combination[/caption]
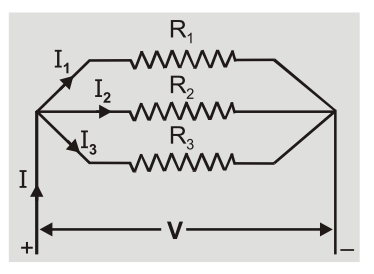
Current through each resistance is different and is inversely proportional to resistance of resistor.
$l \propto 1/R.$ So $\quad {I_1} = {V \over {{R_1}}},{I_2} = {V \over {{R_2}}}\quad $ and $\quad {I_3} = {V \over {{R_3}}}$
Also Read:
Parallel Combination[/caption]
Current through each resistance is different and is inversely proportional to resistance of resistor.
$l \propto 1/R.$ So $\quad {I_1} = {V \over {{R_1}}},{I_2} = {V \over {{R_2}}}\quad $ and $\quad {I_3} = {V \over {{R_3}}}$
Also Read:
Combination of Resistances
A series circuit comprises a path along which the whole current flows through each component. A parallel circuit comprises branches so that the current divides and only part of it flows through any branch. The voltage, or potential difference, across each branch of a parallel circuit is the same, but the currents may vary. In a home electrical circuit, for instance, the same voltage is applied across each light or appliance, but each of these loads draws a different amount of current, according to its power requirements. A number of similar batteries connected in parallel provides greater current than a single battery, but the voltage is the same as for a single battery. [source] Let's start with Combination of resistances with series combination at first then parallel combination.Series Combination
Resistances are said to be connected in series between two points if they provide only a single path between two points. Resistances are connected in series if same current flows through each resistance when some potential difference is applied across the combination. [caption id="attachment_4662" align="aligncenter" width="359"] Series Combination[/caption]
Potential difference across each resistance is different and is directly proportional to its resistance ${\rm{V}} \propto {\rm{R}}.$
So $\quad {{\rm{V}}_1} = {\rm{I}}{{\rm{R}}_1};\quad {{\rm{V}}_2} = {\rm{I}}{R_2}\quad $ and $\quad {{\rm{V}}_3} = {\rm{I}}{{\rm{R}}_3}$
Series Combination[/caption]
Potential difference across each resistance is different and is directly proportional to its resistance ${\rm{V}} \propto {\rm{R}}.$
So $\quad {{\rm{V}}_1} = {\rm{I}}{{\rm{R}}_1};\quad {{\rm{V}}_2} = {\rm{I}}{R_2}\quad $ and $\quad {{\rm{V}}_3} = {\rm{I}}{{\rm{R}}_3}$
- The series combination obeys law of conservation of energy So $V = {V_1} + {V_2} + {V_3} = I\left( {{R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3}} \right)$ Equivalent resistance ${{\rm{R}}_{\rm{s}}} = {{\rm{V}} \over {\rm{I}}} = {{\rm{R}}_1} + {{\rm{R}}_2} + {{\rm{R}}_3}$
- The equivalent resistance is equal to sum of individual resistances.
- The equivalent resistance is greater than largest of individual resistance.
- The resistances are connected in series
- to increase the resistance and
- to divide large potential difference across many resistances.
- In ‘n’ identical resistances R are connected in series then the equivalent resistance Rs = nR
- This combination is used in resistance boxes and sometimes in decorative bulbs.
- In resistances connected in series if one resistance get open the current in whole circuit will become zero.
Parallel Combination
Resistances are said to be connected in parallel between two points if it is possible to proceed from one point to another along different paths. Resistances are said to be in parallel if potential across each resistance is same and equal to applied potential. [caption id="attachment_4663" align="aligncenter" width="220"] Parallel Combination[/caption]
Current through each resistance is different and is inversely proportional to resistance of resistor.
$l \propto 1/R.$ So $\quad {I_1} = {V \over {{R_1}}},{I_2} = {V \over {{R_2}}}\quad $ and $\quad {I_3} = {V \over {{R_3}}}$
Parallel Combination[/caption]
Current through each resistance is different and is inversely proportional to resistance of resistor.
$l \propto 1/R.$ So $\quad {I_1} = {V \over {{R_1}}},{I_2} = {V \over {{R_2}}}\quad $ and $\quad {I_3} = {V \over {{R_3}}}$
- The parallel combination obeys the conservation of charge. So $\quad {\rm{I}} = {{\rm{I}}_1} + {{\rm{I}}_2} + {{\rm{I}}_3} = {\rm{V}}\left( {{1 \over {{{\rm{R}}_1}}} + {1 \over {{{\rm{R}}_2}}} + {1 \over {{{\rm{R}}_3}}}} \right)$ Reciprocal of equivalent resistance ${1 \over {{{\rm{R}}_{\rm{p}}}}} = {{\rm{I}} \over {\rm{V}}} = {1 \over {{{\rm{R}}_1}}} + {1 \over {{{\rm{R}}_2}}} + {1 \over {{{\rm{R}}_3}}}$
- The reciprocal of equivalent resistance is equal to sum of reciprocal of individual resistances.
- The equivalent resistance is smaller than smallest of individual resistance.
- The resistances are connected in parallel to decrease resistance.
- If ‘n’ identical resistances $R$ are connected in parallel then equivalent resistance ${R_p} = R/n$
- This combination is used in household electrical appliances.
- In resistances connected in parallel if one resistance becomes open then also all others will work as usual.
- In case of two resistances in parallel ${{{{\rm{I}}_1}} \over {{{\rm{I}}_2}}} = {{{{\rm{R}}_2}} \over {{{\rm{R}}_1}}}\quad $ and $\quad {{\rm{I}}_1} + {{\rm{I}}_2} = {\rm{I}}$ So $\quad {{\rm{I}}_1} = {{{{\rm{R}}_2}{\rm{I}}} \over {{{\rm{R}}_1} + {{\rm{R}}_2}}}\quad $ and $\quad {{\rm{I}}_2} = {{{{\rm{R}}_1}{\rm{I}}} \over {{{\rm{R}}_1} + {{\rm{R}}_2}}}$
Solved Examples on Combination of Resistances
Q.Find equivalent resistance between the points $A$ and $B$ ?
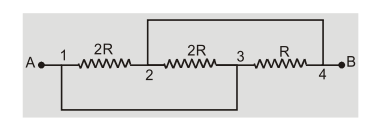

Ans.Point 1 and 3 are at same potential. Similarly point 2 and 4 are at same potential. Joining resistance between 1 and 2,2 and 3,3 and 4 we find that they all are in parallel.
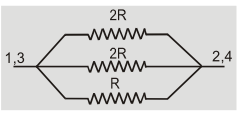 So equivalent resistance ${1 \over {{R_p}}} = {1 \over {2R}} + {1 \over {2R}} + {1 \over R} = {2 \over R}\quad $ or $\quad {R_p} = R/2$
So equivalent resistance ${1 \over {{R_p}}} = {1 \over {2R}} + {1 \over {2R}} + {1 \over R} = {2 \over R}\quad $ or $\quad {R_p} = R/2$
 So equivalent resistance ${1 \over {{R_p}}} = {1 \over {2R}} + {1 \over {2R}} + {1 \over R} = {2 \over R}\quad $ or $\quad {R_p} = R/2$
So equivalent resistance ${1 \over {{R_p}}} = {1 \over {2R}} + {1 \over {2R}} + {1 \over R} = {2 \over R}\quad $ or $\quad {R_p} = R/2$
Q.Five resistors are connected as shown. Find equivalent resistance between the points ${\rm{B}}$ and ${\rm{C}}$ .
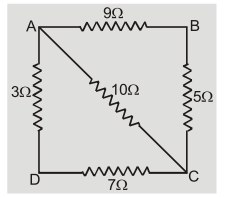

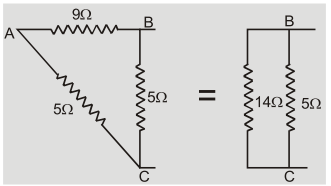
Ans.Resistance of arm ${\rm{ADC}} = 3 + 7 = 10\Omega $ .
This is in parallel to 10$\Omega $ of arm AC. Their parallel combination gives equivalent resistance of 5$\Omega$
So effective resistance between ${\rm{B}}$ and ${\rm{C}}$
${{\rm{R}}_{{\rm{eq}}}} = {{14 \times 5} \over {14 + 5}} = {{70} \over {19}} = 3.684\Omega $

Q.When two resistances are joined in series their resistance is 40$\Omega $ and when they are joined in parallel the resistance is 7.5$\Omega $ . Find the individual resistances?
Ans.Let the two resistances be ${R_1}$ and ${R_2}$
When connected in series ${R_1} + {R_2} = 40$
When connected in parallel ${{{R_1}{R_2}} \over {{R_1} + {R_2}}} = 7.5\quad $ so $\quad {R_1}{R_2} = 7.5 \times 40 = 300$
${\left( {{R_1} - {R_2}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{R_1} + {R_2}} \right)^2} - 4{R_1}{R_2} = {40^2} - 4 \times 300 = 400$
So $\quad {R_1} - {R_2} = 20\Omega $
Solving 1 and 2 we have ${R_1} = 30\Omega $ and ${R_2} = 10\Omega $
Q.Twelve equal resistances $R$ are used to generate shape of a cube. Calculate equivalent resistance across the side of cube?
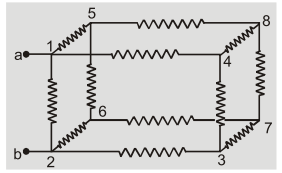

Ans.By symmetry potential at point 4 and 5 is same. Similarly potential at point 3 and 6 is same. The equivalent circuits can be drawn
as :
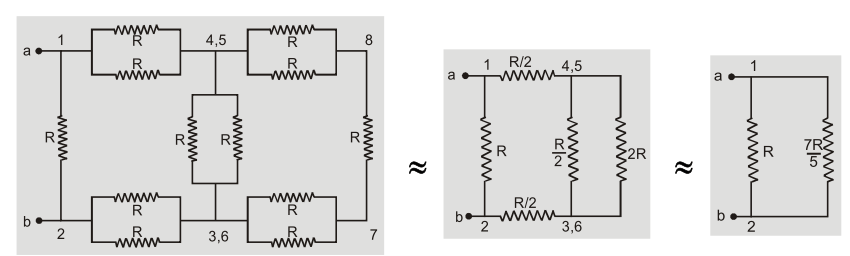 The equivalent resistance between a and b is ${{\rm{R}}_{{\rm{eq}}}} = {{{\rm{R}} \times {7 \over 5}{\rm{R}}} \over {{\rm{R}} + {7 \over 5}{\rm{R}}}} = {7 \over {12}}{\rm{R}}$
The equivalent resistance between a and b is ${{\rm{R}}_{{\rm{eq}}}} = {{{\rm{R}} \times {7 \over 5}{\rm{R}}} \over {{\rm{R}} + {7 \over 5}{\rm{R}}}} = {7 \over {12}}{\rm{R}}$
 The equivalent resistance between a and b is ${{\rm{R}}_{{\rm{eq}}}} = {{{\rm{R}} \times {7 \over 5}{\rm{R}}} \over {{\rm{R}} + {7 \over 5}{\rm{R}}}} = {7 \over {12}}{\rm{R}}$
The equivalent resistance between a and b is ${{\rm{R}}_{{\rm{eq}}}} = {{{\rm{R}} \times {7 \over 5}{\rm{R}}} \over {{\rm{R}} + {7 \over 5}{\rm{R}}}} = {7 \over {12}}{\rm{R}}$
Q.Calculate the current shown by ammeter A in the circuit shown in fig.
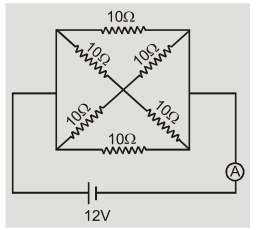

Ans.The equivalent circuits can be drawn as
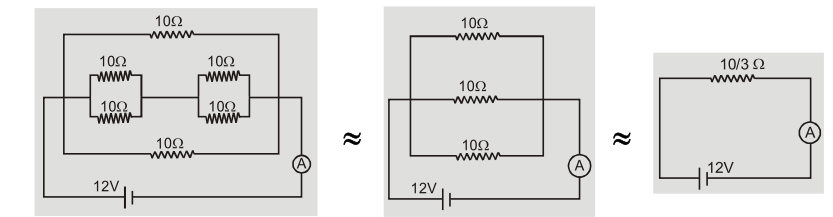 The equivalent resistance of circuit is ${{\rm{R}}_{{\rm{eq}}}} = {{10} \over 3}\Omega $
The current ${\rm{I}} = {{\rm{E}} \over {{{\rm{R}}_{{\rm{eq}}}}}} = {{12} \over {10/3}} = 3.6{\rm{A}}$
The equivalent resistance of circuit is ${{\rm{R}}_{{\rm{eq}}}} = {{10} \over 3}\Omega $
The current ${\rm{I}} = {{\rm{E}} \over {{{\rm{R}}_{{\rm{eq}}}}}} = {{12} \over {10/3}} = 3.6{\rm{A}}$
 The equivalent resistance of circuit is ${{\rm{R}}_{{\rm{eq}}}} = {{10} \over 3}\Omega $
The current ${\rm{I}} = {{\rm{E}} \over {{{\rm{R}}_{{\rm{eq}}}}}} = {{12} \over {10/3}} = 3.6{\rm{A}}$
The equivalent resistance of circuit is ${{\rm{R}}_{{\rm{eq}}}} = {{10} \over 3}\Omega $
The current ${\rm{I}} = {{\rm{E}} \over {{{\rm{R}}_{{\rm{eq}}}}}} = {{12} \over {10/3}} = 3.6{\rm{A}}$
Q.The resistance between the points A and B in the following diagram Fig. will be-
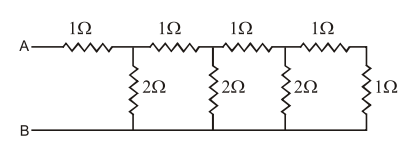 $(1)\,4\Omega $
$(2)\,8\Omega $
$(3)\,6\Omega $
$(4)\,2\Omega $
$(1)\,4\Omega $
$(2)\,8\Omega $
$(3)\,6\Omega $
$(4)\,2\Omega $
 $(1)\,4\Omega $
$(2)\,8\Omega $
$(3)\,6\Omega $
$(4)\,2\Omega $
$(1)\,4\Omega $
$(2)\,8\Omega $
$(3)\,6\Omega $
$(4)\,2\Omega $
Ans. $\quad {\rm{R}} = {{\left( {{{\rm{R}}_1} + {{\rm{R}}_2}} \right)} \over 2} + {1 \over 2}{\left[ {{{\left( {{{\rm{R}}_1} + {{\rm{R}}_2}} \right)}^2} + 4{{\rm{R}}_3}\left( {{{\rm{R}}_1} + {{\rm{R}}_2}} \right)} \right]^{{1 \over 2}}} \ldots \ldots \ldots $ (1)
${\rm{R}}1 = 1\Omega ,{{\rm{R}}_2} = 0.{{\rm{R}}_3} = 2\Omega $
From eqs. $(1)$ and $(2)$
${\rm{R}} = {1 \over 2} + {1 \over 2}\left[ {1 + 4 \times 2 \times 4{1 \over 2}[1 + 3] = 2\Omega } \right.$
Q.Calculate equivalent resistance between A and B
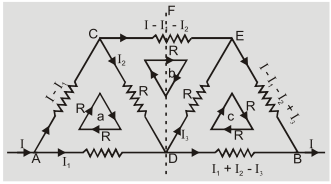

Ans.After distribution of current using loop rule for
$\quad $ Loop a $ - \left( {{\rm{I}} - {{\rm{I}}_1}} \right){\rm{R}} - {{\rm{I}}_2}{\rm{R}} + {{\rm{I}}_1}{\rm{R}} = 0\quad $ or $\quad 2{{\rm{I}}_1} - {{\rm{I}}_2} = {\rm{I}}$
Loop b $ - \left( {1 - {{\rm{I}}_1} - {{\rm{I}}_2}} \right){\rm{R}} + {{\rm{I}}_3}{\rm{R}} + {{\rm{I}}_2}{\rm{R}} = 0\quad $ or $\quad {{\rm{I}}_1} + 2{{\rm{I}}_2} + {{\rm{I}}_3} = {\rm{I}}$
Loop ${\rm{c}} - {{\rm{I}}_3}{\rm{R}} - \left( {{\rm{I}} - {{\rm{I}}_1} - {{\rm{I}}_2} + {{\rm{I}}_3}} \right){\rm{R}} + \left( {{{\rm{I}}_1} + {{\rm{I}}_2} - {{\rm{I}}_3}} \right){\rm{R}} = 0\quad $ or $\quad 2{{\rm{I}}_1} + 2{{\rm{I}}_2} - 3{{\rm{I}}_3} = {\rm{I}}$
Solving for ${{\rm{I}}_1},{{\rm{I}}_2}$ and ${{\rm{I}}_3}$ we get,
${{\rm{I}}_1} = {4 \over 7}{\rm{I}},{{\rm{I}}_2} = {{\rm{I}} \over 7},{{\rm{I}}_3} = {{\rm{I}} \over 7}$
Here ${{\rm{I}}_2} = {{\rm{I}}_3}$ so, no distribution of current takes place at D so it is a pseudo junction.
The equivalent circuit becomes.
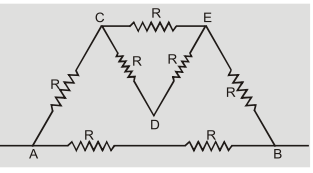 Resistance of triangle DCE is R parallel to $({\rm{R}} + {\rm{R}}) = {2 \over 3}{\rm{R}}$
Resistance of network other than ${\rm{AB}} = {\rm{R}} + {2 \over 3}{\rm{R}} + {\rm{R}} = {8 \over 3}{\rm{R}}$
Equivalent resistance between ${\rm{AB}}$
${{\rm{R}}_{{\rm{eq}}}} = {{2{\rm{R}} \times {{8{\rm{R}}} \over 3}} \over {2{\rm{R}} + {{8{\rm{R}}} \over 3}}} = {8 \over 7}{\rm{R}}$
Resistance of triangle DCE is R parallel to $({\rm{R}} + {\rm{R}}) = {2 \over 3}{\rm{R}}$
Resistance of network other than ${\rm{AB}} = {\rm{R}} + {2 \over 3}{\rm{R}} + {\rm{R}} = {8 \over 3}{\rm{R}}$
Equivalent resistance between ${\rm{AB}}$
${{\rm{R}}_{{\rm{eq}}}} = {{2{\rm{R}} \times {{8{\rm{R}}} \over 3}} \over {2{\rm{R}} + {{8{\rm{R}}} \over 3}}} = {8 \over 7}{\rm{R}}$
 Resistance of triangle DCE is R parallel to $({\rm{R}} + {\rm{R}}) = {2 \over 3}{\rm{R}}$
Resistance of network other than ${\rm{AB}} = {\rm{R}} + {2 \over 3}{\rm{R}} + {\rm{R}} = {8 \over 3}{\rm{R}}$
Equivalent resistance between ${\rm{AB}}$
${{\rm{R}}_{{\rm{eq}}}} = {{2{\rm{R}} \times {{8{\rm{R}}} \over 3}} \over {2{\rm{R}} + {{8{\rm{R}}} \over 3}}} = {8 \over 7}{\rm{R}}$
Resistance of triangle DCE is R parallel to $({\rm{R}} + {\rm{R}}) = {2 \over 3}{\rm{R}}$
Resistance of network other than ${\rm{AB}} = {\rm{R}} + {2 \over 3}{\rm{R}} + {\rm{R}} = {8 \over 3}{\rm{R}}$
Equivalent resistance between ${\rm{AB}}$
${{\rm{R}}_{{\rm{eq}}}} = {{2{\rm{R}} \times {{8{\rm{R}}} \over 3}} \over {2{\rm{R}} + {{8{\rm{R}}} \over 3}}} = {8 \over 7}{\rm{R}}$
Q.Calculate the effective resistance between A and B in following network.
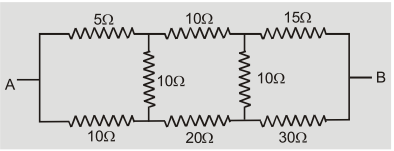

Ans.Ratio of upper resistances 5 : 10 : 15=1 : 2 : 3
Ratio of lower resistances 10 : 20 : 30=1 : 2 : 3
The ratio is same so resistance in middle are not useful.
Equivalent resistance =(5+10+15)| |(10+20+30)
So ${R_{{\rm{ eq }}}} = {{30 \times 60} \over {30 + 60}} = 20\Omega $
Q.Calculate potential difference between points d and b in the circuit.
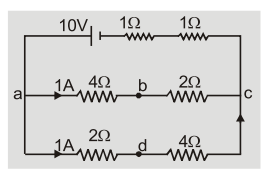

Ans.Using voltage rule from ${\rm{b}}$ to ${\rm{d}}$ via c we get
${{\rm{V}}_{\rm{b}}} - 1 \times 2 + 4 \times 1 = {{\rm{V}}_{\rm{d}}}\quad $ or $\quad {{\rm{V}}_{\rm{d}}} - {{\rm{V}}_{\rm{b}}} = 2$ volt.
- Types and Effects of Electric Current
- Ohm’s Law and Resistance
- Combination of Resistances
- EMF and Internal Resistances of a Cell
- Cells Connected in Series, parallel and Mixed
- Kirchhoff’s Circuit Law
- Electric Currents in Conductors
- Wheatstone Bridge
- Post office Box
- Wheatstone Meter Bridge
- Moving Coil galvanometer
- Ammeter and Voltmeter
- Potentiometer Working Principle
Comments
Lorena Martinez
Nov. 19, 2022, 5:30 p.m.
Excelente información. Reciban un cordial saludo desde nuestra nueva web de Euromillones. La mayor lotería de Europa con millones de seguidores en ese continente que participan en sus sorteos cada martes y viernes. <a href="https://jugareuromillones.com" rel="nofollow ugc">Resultados Euromillones</a>
